Wine funds offer investors exposure to rare and collectible wines, leveraging the wine market's historical resistance to inflation and economic downturns. Commodities funds, on the other hand, provide diversified access to physical goods like metals, energy, and agriculture, often serving as a hedge against currency fluctuations and inflation. Explore the distinct benefits and risks of wine funds versus commodities funds to identify the best fit for your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between wine funds and commodities funds is crucial because wine funds invest in collectible wines with appreciation based on rarity and vintage, while commodities funds trade in raw materials like gold, oil, or agricultural products influenced by market demand and supply dynamics. Accurate knowledge enables investors to align their portfolios with desired risk levels, liquidity needs, and potential returns specific to each asset class. Wine funds often appeal to those seeking tangible, alternative assets with potential tax benefits, contrasting with commodities funds that typically offer high liquidity and volatility. Making informed decisions can optimize asset diversification and enhance overall investment strategy performance.
Comparison Table
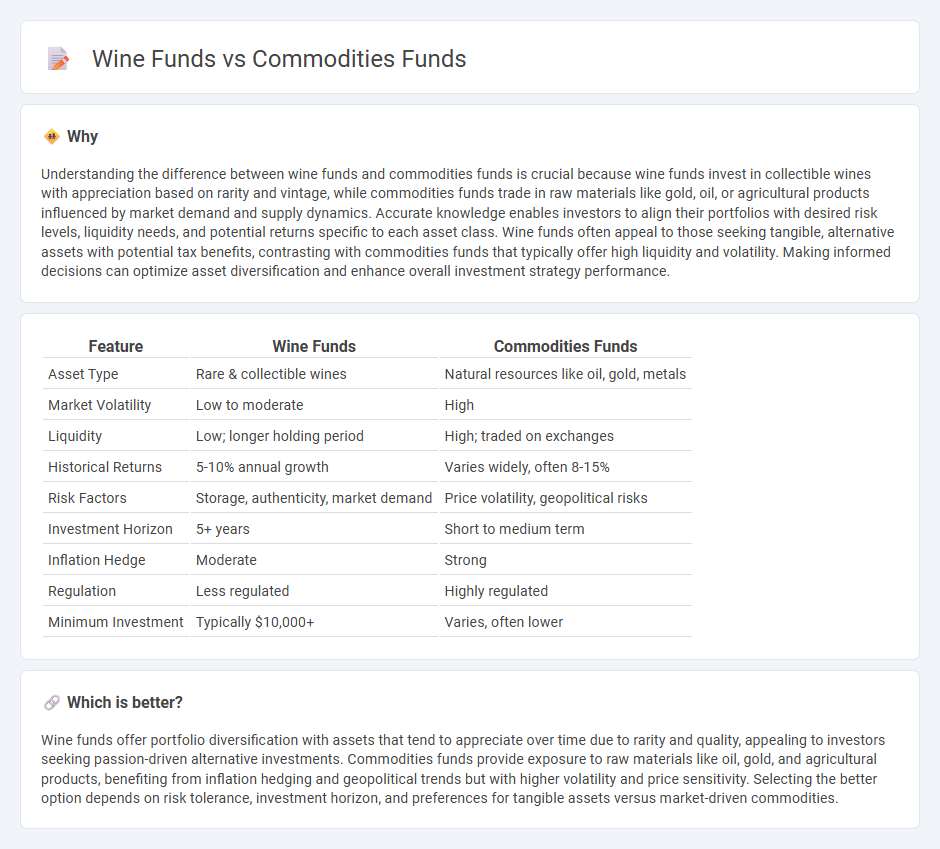
| Feature | Wine Funds | Commodities Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Rare & collectible wines | Natural resources like oil, gold, metals |
| Market Volatility | Low to moderate | High |
| Liquidity | Low; longer holding period | High; traded on exchanges |
| Historical Returns | 5-10% annual growth | Varies widely, often 8-15% |
| Risk Factors | Storage, authenticity, market demand | Price volatility, geopolitical risks |
| Investment Horizon | 5+ years | Short to medium term |
| Inflation Hedge | Moderate | Strong |
| Regulation | Less regulated | Highly regulated |
| Minimum Investment | Typically $10,000+ | Varies, often lower |
Which is better?
Wine funds offer portfolio diversification with assets that tend to appreciate over time due to rarity and quality, appealing to investors seeking passion-driven alternative investments. Commodities funds provide exposure to raw materials like oil, gold, and agricultural products, benefiting from inflation hedging and geopolitical trends but with higher volatility and price sensitivity. Selecting the better option depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and preferences for tangible assets versus market-driven commodities.
Connection
Wine funds and commodities funds are connected through their shared focus on tangible asset investment, offering diversification beyond traditional equities and bonds. Both funds capitalize on market demand and supply dynamics, with wine funds hinging on rare vintages and aging potential, while commodities funds trade physical goods like metals, energy, or agricultural products. Investors leverage these funds to hedge against inflation and market volatility while seeking alternative returns linked to global economic trends and consumer preferences.
Key Terms
**Commodities Funds:**
Commodities funds invest in physical goods such as oil, gold, and agricultural products, providing diversification and a hedge against inflation. These funds track commodity prices, making them sensitive to global supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and currency fluctuations. Explore the unique benefits and risks of commodities funds to enhance your investment portfolio knowledge.
Futures Contracts
Commodities funds primarily invest in futures contracts of raw materials like oil, gold, and agricultural products, offering liquidity and price exposure to global markets. Wine funds, by contrast, invest directly in physical wine assets or vineyards, focusing on the collectible and appreciation value rather than futures contracts. Explore how futures contracts shape investment dynamics in commodities funds versus the tangible asset approach of wine funds.
Diversification
Commodities funds offer diversification by investing in raw materials like oil, gold, and agricultural products, mitigating risks associated with inflation and market volatility. Wine funds provide exposure to alternative assets by acquiring fine wines, which tend to have low correlation with traditional financial markets and can appreciate over time due to rarity and demand. Explore more about how these funds complement investment portfolios and balance risk.
Source and External Links
Commodities ETFs - ETF Database - Categorizes and details exchange-traded funds that invest in specific or multiple commodities, including metals, livestock, oil, coffee, and sugar, with performance metrics for each fund.
Why and How to Invest in Commodities | U.S. Bank - Offers an overview of investing in commodities through funds, highlighting risks, diversification benefits, and considerations around ETFs, mutual funds, and alternative investments.
Commodities Strategy - A Class - Overview - Guggenheim Investments - Features a mutual fund designed to track the performance of the S&P GSCI Commodity Index, with expense ratios, distribution frequency, and key fund details included.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com