Carbon credit arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differences in carbon credits across various markets, enabling investors to profit from transaction inefficiencies and regional regulatory variations. In contrast, carbon offset projects focus on generating emissions reductions through activities like reforestation or renewable energy, providing measurable environmental impacts alongside potential financial returns. Explore how these strategies differ in risk, return, and sustainability impact to optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
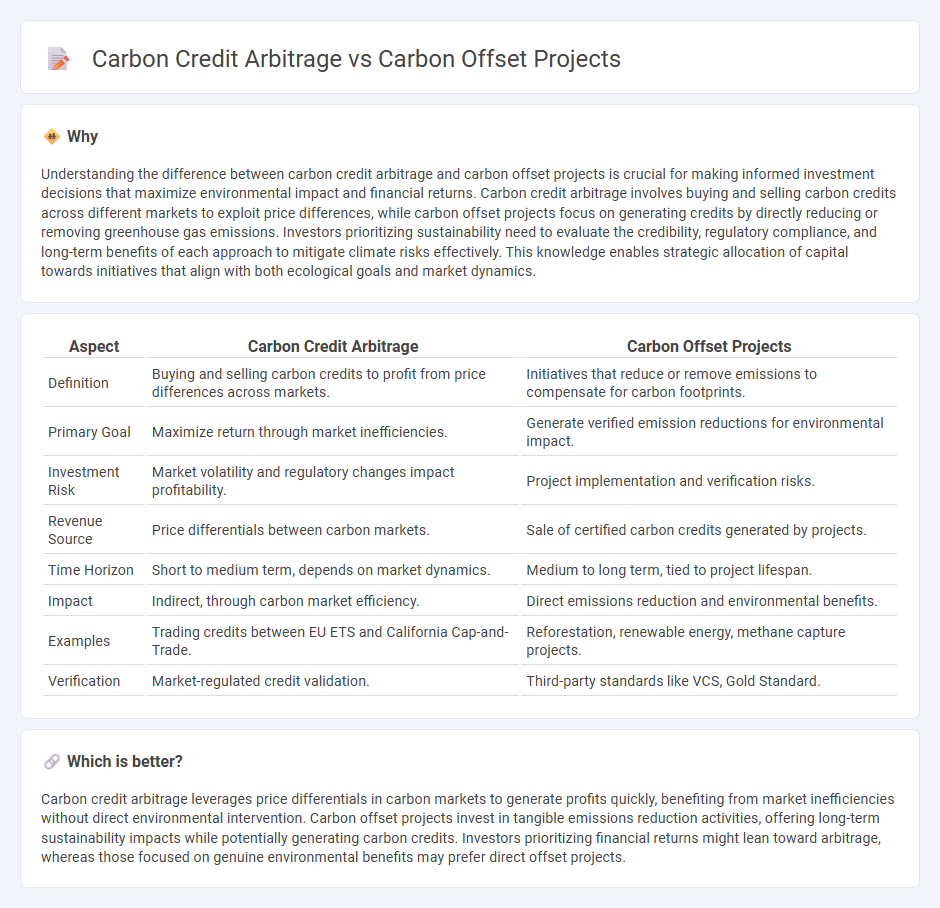
Understanding the difference between carbon credit arbitrage and carbon offset projects is crucial for making informed investment decisions that maximize environmental impact and financial returns. Carbon credit arbitrage involves buying and selling carbon credits across different markets to exploit price differences, while carbon offset projects focus on generating credits by directly reducing or removing greenhouse gas emissions. Investors prioritizing sustainability need to evaluate the credibility, regulatory compliance, and long-term benefits of each approach to mitigate climate risks effectively. This knowledge enables strategic allocation of capital towards initiatives that align with both ecological goals and market dynamics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credit Arbitrage | Carbon Offset Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling carbon credits to profit from price differences across markets. | Initiatives that reduce or remove emissions to compensate for carbon footprints. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize return through market inefficiencies. | Generate verified emission reductions for environmental impact. |
| Investment Risk | Market volatility and regulatory changes impact profitability. | Project implementation and verification risks. |
| Revenue Source | Price differentials between carbon markets. | Sale of certified carbon credits generated by projects. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, depends on market dynamics. | Medium to long term, tied to project lifespan. |
| Impact | Indirect, through carbon market efficiency. | Direct emissions reduction and environmental benefits. |
| Examples | Trading credits between EU ETS and California Cap-and-Trade. | Reforestation, renewable energy, methane capture projects. |
| Verification | Market-regulated credit validation. | Third-party standards like VCS, Gold Standard. |
Which is better?
Carbon credit arbitrage leverages price differentials in carbon markets to generate profits quickly, benefiting from market inefficiencies without direct environmental intervention. Carbon offset projects invest in tangible emissions reduction activities, offering long-term sustainability impacts while potentially generating carbon credits. Investors prioritizing financial returns might lean toward arbitrage, whereas those focused on genuine environmental benefits may prefer direct offset projects.
Connection
Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences between carbon markets to generate profits while driving capital towards carbon offset projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These offset projects, such as reforestation or renewable energy installations, create verified carbon credits that serve as tradable assets in global markets. Efficient arbitrage boosts liquidity and investment in offset initiatives, accelerating carbon reduction efforts and supporting environmental sustainability.
Key Terms
Additionality
Carbon offset projects emphasize additionality by ensuring emissions reductions occur uniquely due to the project, creating genuine environmental benefits beyond business-as-usual scenarios. Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences in carbon markets without necessarily guaranteeing additional emission reductions, often raising concerns about the true impact on climate goals. Explore further to understand how additionality shapes the effectiveness of climate finance strategies.
Verification
Verification plays a critical role in ensuring the credibility of carbon offset projects by confirming that emissions reductions are real, measurable, and permanent through rigorous third-party audits. Carbon credit arbitrage involves trading verified credits across different markets to capitalize on price disparities, relying heavily on standardized verification protocols to maintain market integrity. Explore detailed methodologies and standards behind verification processes to better understand their impact on carbon management strategies.
Price spread
Carbon offset projects generate verifiable emission reductions by investing in renewable energy, reforestation, and methane capture, creating carbon credits priced based on project type and location. Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price spreads between different carbon markets or credit types, capitalizing on regulatory differences and market inefficiencies to buy low and sell high. Explore how price spread dynamics influence carbon markets and investment strategies for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Types Of Carbon Offsetting Projects That Can Lead Businesses To ... - Carbon offset projects fall into two main categories: Avoidance projects, which prevent emissions such as forest conservation and renewable energy, and Removal projects, which actively remove CO2 from the atmosphere like reforestation and direct air capture.
Scientifically Verified Carbon Projects and Pricing - Cool Effect - Verified carbon projects include methane capture, biochar soil enhancement, renewable energy, and reforestation efforts, ensuring transparency and science-backed impact for individuals and businesses offsetting emissions.
Carbon Offset Programs Guide and Examples for 2025 - Persefoni - Programs like Verra's Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) certify a wide range of projects in agriculture, forestry, energy, and waste management ensuring rigorous validation and monitoring of carbon offset initiatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com