Digital real estate offers investors the potential for high returns through virtual property ownership and development in metaverse platforms, leveraging blockchain technology for secure transactions. Bonds provide a more stable and predictable income stream by lending capital to governments or corporations with fixed interest payments and lower risk. Explore the advantages and risks of both to determine the best investment strategy for your portfolio.
Why it is important
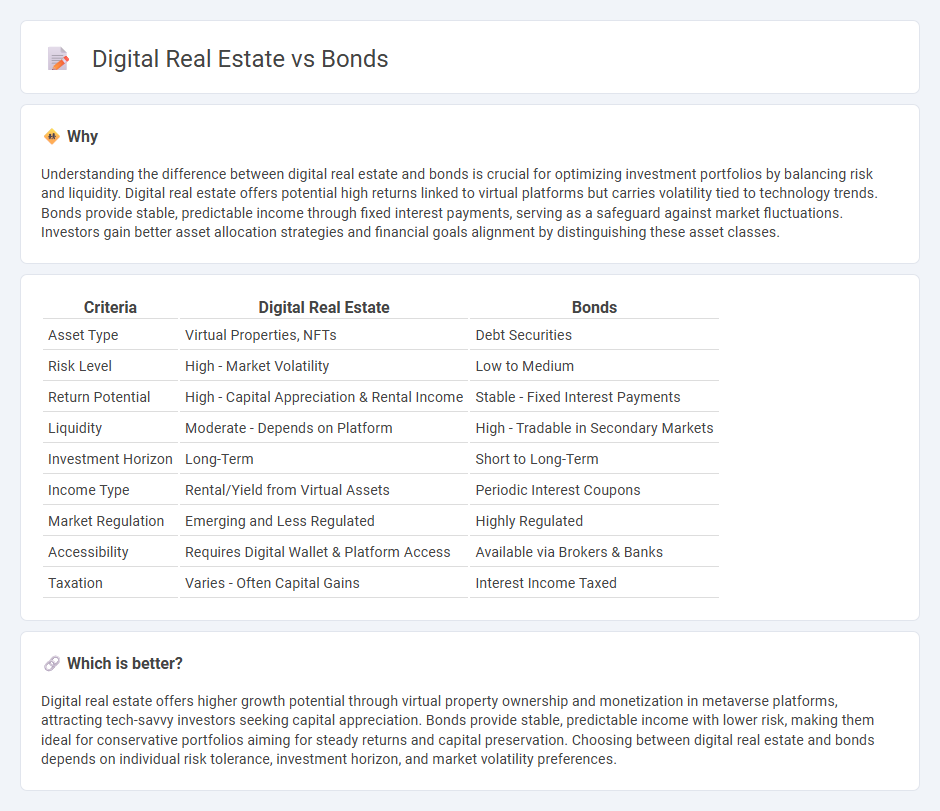
Understanding the difference between digital real estate and bonds is crucial for optimizing investment portfolios by balancing risk and liquidity. Digital real estate offers potential high returns linked to virtual platforms but carries volatility tied to technology trends. Bonds provide stable, predictable income through fixed interest payments, serving as a safeguard against market fluctuations. Investors gain better asset allocation strategies and financial goals alignment by distinguishing these asset classes.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Digital Real Estate | Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Virtual Properties, NFTs | Debt Securities |
| Risk Level | High - Market Volatility | Low to Medium |
| Return Potential | High - Capital Appreciation & Rental Income | Stable - Fixed Interest Payments |
| Liquidity | Moderate - Depends on Platform | High - Tradable in Secondary Markets |
| Investment Horizon | Long-Term | Short to Long-Term |
| Income Type | Rental/Yield from Virtual Assets | Periodic Interest Coupons |
| Market Regulation | Emerging and Less Regulated | Highly Regulated |
| Accessibility | Requires Digital Wallet & Platform Access | Available via Brokers & Banks |
| Taxation | Varies - Often Capital Gains | Interest Income Taxed |
Which is better?
Digital real estate offers higher growth potential through virtual property ownership and monetization in metaverse platforms, attracting tech-savvy investors seeking capital appreciation. Bonds provide stable, predictable income with lower risk, making them ideal for conservative portfolios aiming for steady returns and capital preservation. Choosing between digital real estate and bonds depends on individual risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market volatility preferences.
Connection
Digital real estate offers a new form of asset ownership through tokenized properties, which can be backed by bond issuance to provide stable returns and liquidity. Bonds issued against digital real estate projects attract investors seeking fixed income with the potential for capital appreciation tied to property value growth. This intersection enhances portfolio diversification, combining the stability of bonds with the innovative potential of digital real estate assets.
Key Terms
Yield
Bonds typically offer fixed, lower yields with lower risk and steady income, while digital real estate investments, such as virtual properties in metaverse platforms, can deliver higher yields but come with increased market volatility and speculative risks. Digital real estate yield is driven by factors like demand for virtual spaces, rental income, and digital asset appreciation, contrasting with bonds' predictable coupon payments. Explore the nuances of yield differences between bonds and digital real estate to optimize your investment strategy.
Liquidity
Bonds offer high liquidity, allowing investors to quickly buy or sell on major exchanges with minimal price impact, making them suitable for those seeking stable, accessible assets. Digital real estate, while growing in popularity, often involves less liquid markets with longer transaction times and fewer buyers, reflecting its emerging status in the investment landscape. Explore more about how liquidity differences impact portfolio strategy and risk management.
Asset Backing
Bonds are traditionally backed by the creditworthiness of the issuer, providing fixed income through interest payments and principal repayment. Digital real estate investment involves owning tokenized property assets on blockchain platforms, offering exposure to real-world property value and rental income streams. Explore deeper insights into how asset backing influences risk and returns in these two financial instruments.
Source and External Links
Bonds | Investor.gov - Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations where investors lend money in exchange for periodic interest and the return of principal at maturity, offering predictable income and capital preservation.
Bond (finance) - Wikipedia - Bonds function as loans to issuers and are primarily purchased by institutions for their lower volatility compared to stocks, offering fixed interest payments and legal protections in bankruptcy.
What is a Bond and How do they Work? - Vanguard - Bonds provide investors income through interest payments and help reduce portfolio volatility, with issuers agreeing to repay the principal on a set date, though bond market values fluctuate over time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com