Microinsurance provides affordable risk protection tailored for low-income individuals and small businesses, covering specific needs like health, agriculture, and property. Reinsurance involves transferring risk from insurers to larger entities to ensure financial stability and manage large-scale claims effectively. Discover the key differences and benefits of microinsurance and reinsurance to understand their roles in the insurance ecosystem.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microinsurance and reinsurance is crucial because microinsurance provides affordable coverage to low-income individuals, enhancing financial inclusion, while reinsurance involves risk transfer between insurance companies to maintain global market stability. Knowing these distinctions helps stakeholders design appropriate products and manage risks effectively. Microinsurance typically covers specific local risks with low premiums and benefits, whereas reinsurance supports insurers' solvency by spreading large-scale risks. Clear awareness aids consumers, insurers, and regulators in optimizing protection strategies and ensuring market resilience.
Comparison Table
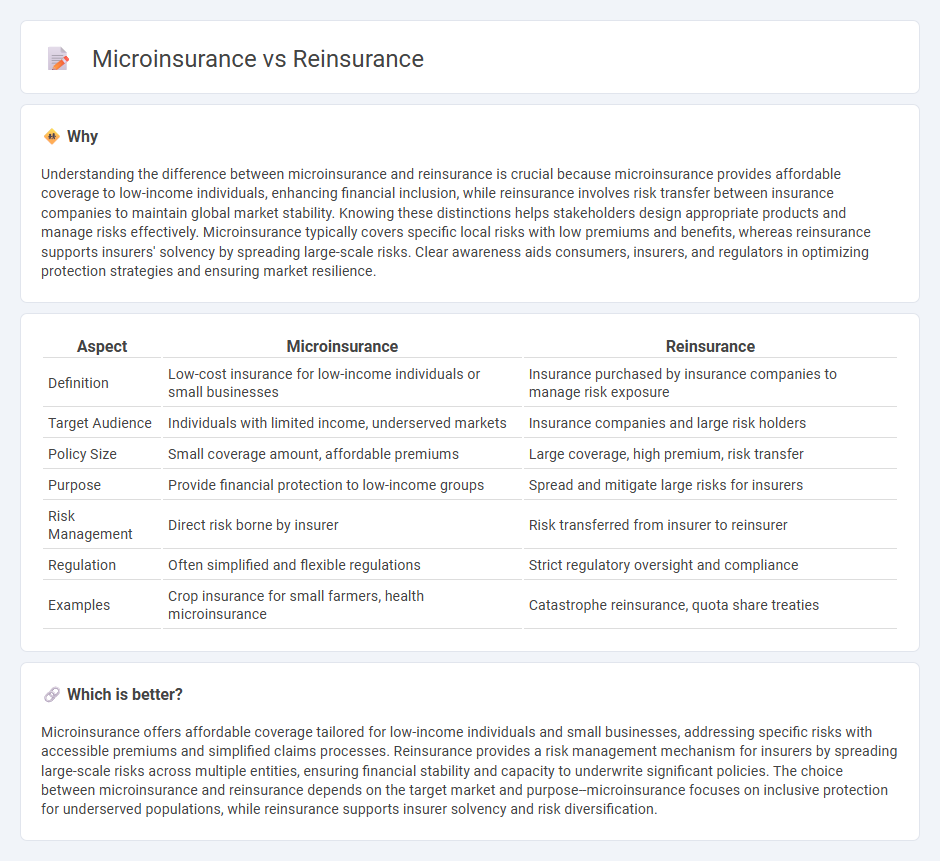
| Aspect | Microinsurance | Reinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Low-cost insurance for low-income individuals or small businesses | Insurance purchased by insurance companies to manage risk exposure |
| Target Audience | Individuals with limited income, underserved markets | Insurance companies and large risk holders |
| Policy Size | Small coverage amount, affordable premiums | Large coverage, high premium, risk transfer |
| Purpose | Provide financial protection to low-income groups | Spread and mitigate large risks for insurers |
| Risk Management | Direct risk borne by insurer | Risk transferred from insurer to reinsurer |
| Regulation | Often simplified and flexible regulations | Strict regulatory oversight and compliance |
| Examples | Crop insurance for small farmers, health microinsurance | Catastrophe reinsurance, quota share treaties |
Which is better?
Microinsurance offers affordable coverage tailored for low-income individuals and small businesses, addressing specific risks with accessible premiums and simplified claims processes. Reinsurance provides a risk management mechanism for insurers by spreading large-scale risks across multiple entities, ensuring financial stability and capacity to underwrite significant policies. The choice between microinsurance and reinsurance depends on the target market and purpose--microinsurance focuses on inclusive protection for underserved populations, while reinsurance supports insurer solvency and risk diversification.
Connection
Microinsurance provides affordable coverage to low-income populations by pooling risks, which necessitates reinsurance to help primary insurers manage potential large-scale losses and improve financial stability. Reinsurance enables microinsurance providers to expand their reach without bearing excessive risk, facilitating greater access to insurance services in underserved markets. This risk transfer mechanism is crucial for maintaining the viability of microinsurance schemes and enhancing their capacity to withstand catastrophic events.
Key Terms
Risk Transfer
Reinsurance provides large-scale risk transfer by allowing insurance companies to offload portions of their risk portfolios to other insurers, thereby stabilizing financial outcomes and protecting against catastrophic losses. Microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable, tailored coverage that mitigates specific risks like health emergencies, crop failures, or natural disasters through risk pooling and community-based models. Explore how these distinct risk transfer mechanisms impact insurance markets and vulnerable populations in greater detail.
Coverage Scope
Reinsurance primarily provides insurance companies with financial protection against substantial losses by covering large-scale risks and catastrophic events, whereas microinsurance targets low-income individuals with affordable policies tailored for smaller, everyday risks such as health, crop failure, or property damage. While reinsurance enhances the stability of insurers by spreading risk across the industry, microinsurance expands accessibility to vulnerable populations who are typically underserved by traditional insurance markets. Explore how both solutions complement each other in creating resilient financial ecosystems for diverse risk exposures.
Premium Size
Reinsurance typically involves large premium sizes to cover substantial insurance risks transferred from primary insurers, often amounting to millions or billions of dollars. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with much smaller premium sizes, usually ranging from a few cents to a few dollars, designed to make coverage affordable and accessible. Explore detailed comparisons on premium structures and risk management to better understand the benefits of reinsurance versus microinsurance.
Source and External Links
REINSURANCE - The American Council of Life Insurers - Reinsurance is a risk management tool that allows insurers to transfer risk and manage capital by passing some or all of an insurance risk to another insurer.
What is reinsurance? - Reinsurance is a method insurance companies use to transfer some of the risk from their policies to protect against large losses.
What is Reinsurance? - Reinsurance acts as insurance for insurance companies, helping them manage unforeseen losses and stabilize their business operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com