Insurance sandboxes provide a controlled regulatory environment allowing insurers and startups to test innovative products under real market conditions with reduced risk. Proof of concept (PoC) focuses on validating the feasibility and technical viability of an insurance solution before full-scale development and market launch. Explore the distinct advantages of insurance sandboxes and PoCs to enhance innovation strategies in the insurance sector.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between an insurance sandbox and a proof of concept is crucial for accurate risk assessment and regulatory compliance. Insurance sandboxes allow companies to test innovative products in a controlled environment under regulatory supervision, enabling real-world data collection and consumer protection. Proof of concept demonstrates the feasibility of new insurance technologies or processes before full-scale development, minimizing resource waste and validating ideas. Distinguishing these stages ensures efficient innovation management and strategic decision-making in the insurance industry.
Comparison Table
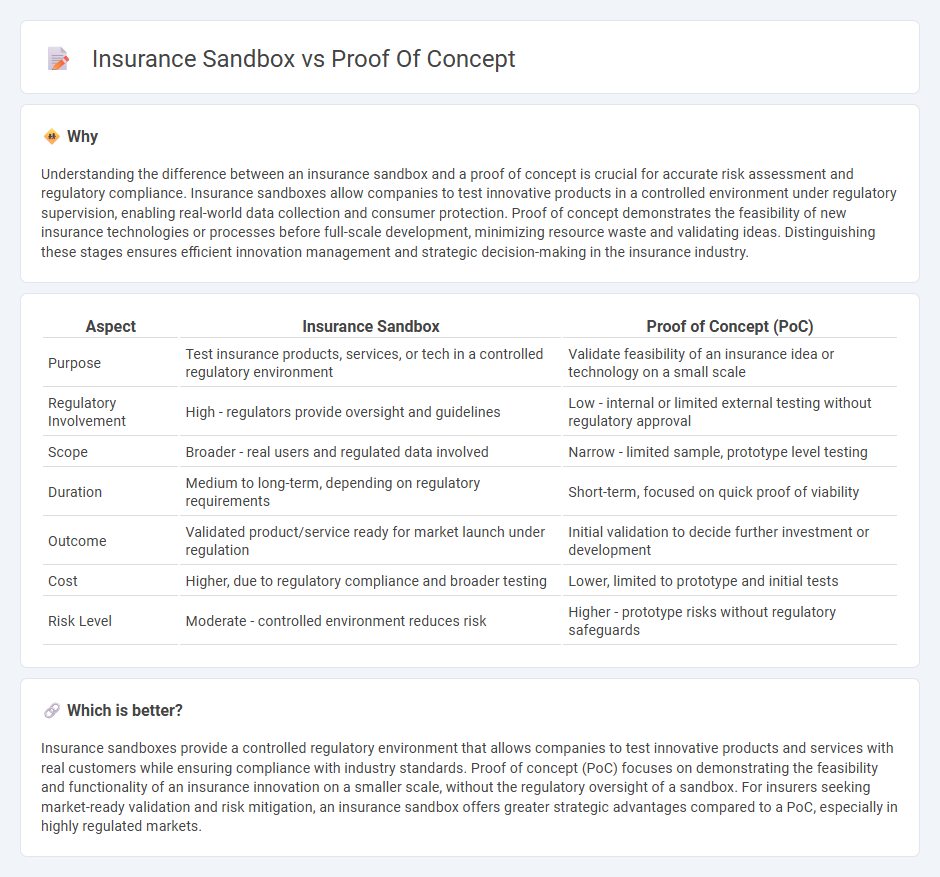
| Aspect | Insurance Sandbox | Proof of Concept (PoC) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Test insurance products, services, or tech in a controlled regulatory environment | Validate feasibility of an insurance idea or technology on a small scale |
| Regulatory Involvement | High - regulators provide oversight and guidelines | Low - internal or limited external testing without regulatory approval |
| Scope | Broader - real users and regulated data involved | Narrow - limited sample, prototype level testing |
| Duration | Medium to long-term, depending on regulatory requirements | Short-term, focused on quick proof of viability |
| Outcome | Validated product/service ready for market launch under regulation | Initial validation to decide further investment or development |
| Cost | Higher, due to regulatory compliance and broader testing | Lower, limited to prototype and initial tests |
| Risk Level | Moderate - controlled environment reduces risk | Higher - prototype risks without regulatory safeguards |
Which is better?
Insurance sandboxes provide a controlled regulatory environment that allows companies to test innovative products and services with real customers while ensuring compliance with industry standards. Proof of concept (PoC) focuses on demonstrating the feasibility and functionality of an insurance innovation on a smaller scale, without the regulatory oversight of a sandbox. For insurers seeking market-ready validation and risk mitigation, an insurance sandbox offers greater strategic advantages compared to a PoC, especially in highly regulated markets.
Connection
Insurance sandboxes provide a controlled regulatory environment where innovators can test new insurance products and technologies without full regulatory compliance. Proof of concept (PoC) initiatives within these sandboxes validate the feasibility and effectiveness of innovative insurance solutions before broader market deployment. This connection accelerates innovation by reducing risks and regulatory barriers while ensuring consumer protection.
Key Terms
Regulatory Compliance
Proof of concept (PoC) in insurance centers on validating innovative solutions' technical feasibility and initial market fit, with limited regulatory oversight during early-stage development. Insurance sandboxes provide a controlled regulatory environment allowing insurers to test new products and services under relaxed compliance rules, facilitating alignment with regulatory requirements while minimizing risks. Explore the nuances and implications of these approaches to enhance compliance strategies in insurance innovation.
Risk Assessment
Proof of concept projects in risk assessment validate new methodologies by testing algorithms on controlled datasets to identify potential financial risks. Insurance sandboxes offer a regulatory framework for insurers to experiment with innovative risk models in a live environment while ensuring compliance and consumer protection. Explore how these approaches enhance risk assessment accuracy and regulatory confidence by learning more about their practical applications.
Piloting Mechanism
Proof of concept (PoC) and insurance sandbox both serve as piloting mechanisms to test innovative insurance solutions in controlled environments. PoCs validate technical feasibility and operational viability by developing prototypes or limited implementations, whereas insurance sandboxes allow insurers to experiment with regulatory flexibilities under the supervision of regulators to ensure consumer protection. Explore how these mechanisms accelerate insurance innovation through practical risk assessment and market readiness testing.
Source and External Links
Proof of Concept: Definition, Guide, and Examples - A proof of concept is a tool used to demonstrate the feasibility or viability of an idea by collecting evidence of its practical or business potential, typically at a small scale before committing to full development.
Proof of Concept (POC): Definition, Steps and Examples - A proof of concept is an early-stage feasibility study that verifies whether a new idea can solve real-world problems, be implemented with current technology, and avoid major roadblocks, conducted right after the ideation phase.
Proof of concept - A proof of concept is a preliminary demonstration of an idea or method to show its feasibility, without needing to develop a complete product, often small and focused on whether the underlying principle works.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com