Flood risk mapping identifies and quantifies areas prone to flooding by analyzing precipitation patterns, river flows, and topography to inform insurance underwriting and risk management. Landslide vulnerability analysis assesses slope stability, soil composition, and rainfall intensity to determine susceptibility zones critical for property insurance and disaster mitigation. Explore how integrating both approaches can enhance comprehensive risk assessment and optimize insurance coverage strategies.
Why it is important
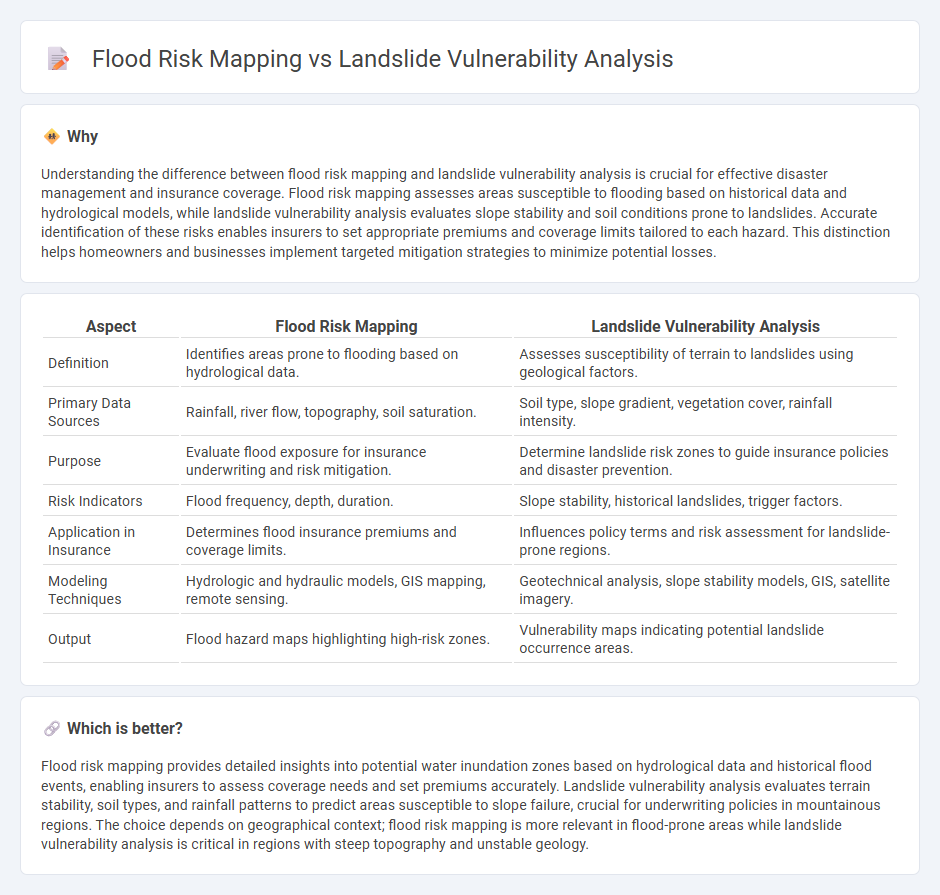
Understanding the difference between flood risk mapping and landslide vulnerability analysis is crucial for effective disaster management and insurance coverage. Flood risk mapping assesses areas susceptible to flooding based on historical data and hydrological models, while landslide vulnerability analysis evaluates slope stability and soil conditions prone to landslides. Accurate identification of these risks enables insurers to set appropriate premiums and coverage limits tailored to each hazard. This distinction helps homeowners and businesses implement targeted mitigation strategies to minimize potential losses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flood Risk Mapping | Landslide Vulnerability Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifies areas prone to flooding based on hydrological data. | Assesses susceptibility of terrain to landslides using geological factors. |
| Primary Data Sources | Rainfall, river flow, topography, soil saturation. | Soil type, slope gradient, vegetation cover, rainfall intensity. |
| Purpose | Evaluate flood exposure for insurance underwriting and risk mitigation. | Determine landslide risk zones to guide insurance policies and disaster prevention. |
| Risk Indicators | Flood frequency, depth, duration. | Slope stability, historical landslides, trigger factors. |
| Application in Insurance | Determines flood insurance premiums and coverage limits. | Influences policy terms and risk assessment for landslide-prone regions. |
| Modeling Techniques | Hydrologic and hydraulic models, GIS mapping, remote sensing. | Geotechnical analysis, slope stability models, GIS, satellite imagery. |
| Output | Flood hazard maps highlighting high-risk zones. | Vulnerability maps indicating potential landslide occurrence areas. |
Which is better?
Flood risk mapping provides detailed insights into potential water inundation zones based on hydrological data and historical flood events, enabling insurers to assess coverage needs and set premiums accurately. Landslide vulnerability analysis evaluates terrain stability, soil types, and rainfall patterns to predict areas susceptible to slope failure, crucial for underwriting policies in mountainous regions. The choice depends on geographical context; flood risk mapping is more relevant in flood-prone areas while landslide vulnerability analysis is critical in regions with steep topography and unstable geology.
Connection
Flood risk mapping and landslide vulnerability analysis are interconnected through their focus on assessing and mitigating natural hazard impacts on land stability and water flow patterns. Both use geospatial data, topographic analysis, and rainfall metrics to identify high-risk zones that influence property insurance risk profiles. Integrating these analyses enhances insurance underwriting by providing comprehensive risk assessments for flood and landslide-prone areas.
Key Terms
Hazard Assessment
Landslide vulnerability analysis evaluates slope stability factors such as soil type, vegetation cover, and rainfall intensity to identify areas susceptible to mass movements. Flood risk mapping employs hydrological models and historical flood data to delineate zones prone to inundation and estimate potential damage. Explore detailed methodologies to enhance hazard assessment accuracy in both contexts.
Exposure Mapping
Landslide vulnerability analysis and flood risk mapping both rely heavily on exposure mapping to identify areas susceptible to hazards based on population density, infrastructure, and land use patterns. Exposure mapping for landslides emphasizes slope steepness, soil type, and proximity to fault lines, while flood risk mapping prioritizes floodplain delineation, rainfall intensity, and drainage network analysis. Explore further to understand how these exposure metrics improve disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Loss Estimation
Landslide vulnerability analysis evaluates terrain stability and assesses potential damage to infrastructure, considering factors like soil properties, slope angle, and historical landslide data to estimate loss. Flood risk mapping integrates hydrological models, rainfall intensity, and floodplain data to quantify probable flood depths and affected populations for effective loss estimation. Explore detailed methodologies and comparative insights on loss estimation in natural hazards for enhanced disaster preparedness.
Source and External Links
Assessment of landslide susceptibility, exposure, vulnerability, and risk in Shahpur valley - This study assesses landslide vulnerability by creating maps that show elements at risk and their vulnerability to landslide occurrences in the Shahpur valley.
Landslide Risk Assessment - This resource explains how landslide risk assessment involves analyzing vulnerability by gathering data on how susceptible elements at risk are to landslide damage.
Landslide Hazard and Risk Assessment - This document outlines the process of assessing societal vulnerability to landslides, which involves setting priorities and analyzing trends to empower risk management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com