Silent cyber coverage addresses cyber risks not explicitly covered or excluded in traditional insurance policies, filling critical gaps in protection for businesses facing evolving cyber threats. Exclusionary language in policies often omits coverage for cyber incidents, leaving policyholders vulnerable to financial losses caused by cyberattacks or data breaches. Explore the nuances between silent cyber coverage and exclusionary language to better understand the scope and limitations of your insurance protection.
Why it is important
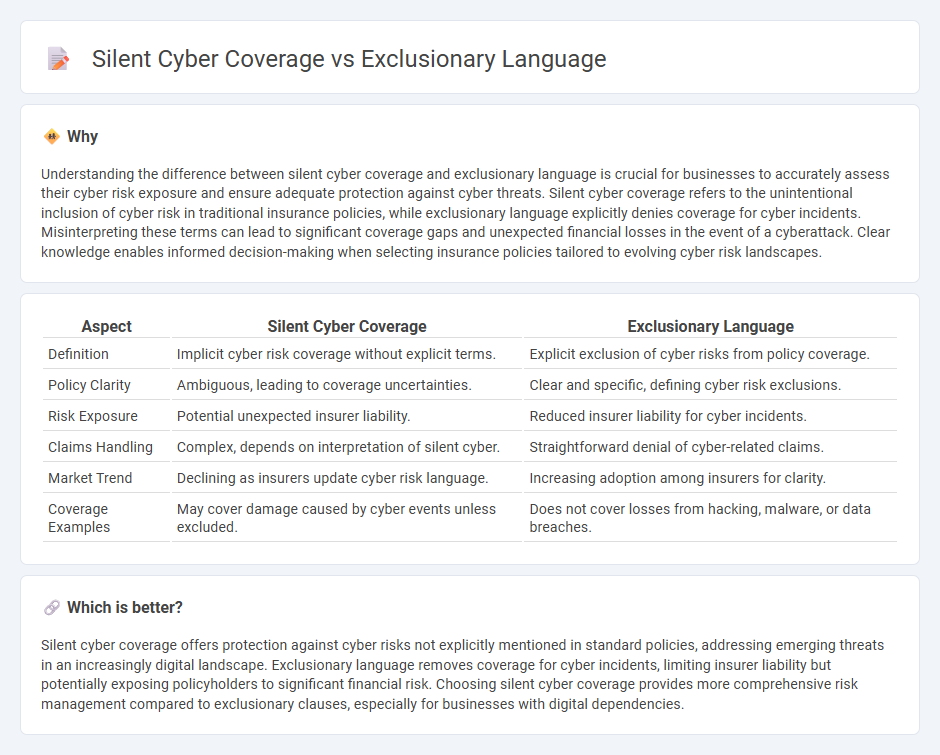
Understanding the difference between silent cyber coverage and exclusionary language is crucial for businesses to accurately assess their cyber risk exposure and ensure adequate protection against cyber threats. Silent cyber coverage refers to the unintentional inclusion of cyber risk in traditional insurance policies, while exclusionary language explicitly denies coverage for cyber incidents. Misinterpreting these terms can lead to significant coverage gaps and unexpected financial losses in the event of a cyberattack. Clear knowledge enables informed decision-making when selecting insurance policies tailored to evolving cyber risk landscapes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Silent Cyber Coverage | Exclusionary Language |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Implicit cyber risk coverage without explicit terms. | Explicit exclusion of cyber risks from policy coverage. |
| Policy Clarity | Ambiguous, leading to coverage uncertainties. | Clear and specific, defining cyber risk exclusions. |
| Risk Exposure | Potential unexpected insurer liability. | Reduced insurer liability for cyber incidents. |
| Claims Handling | Complex, depends on interpretation of silent cyber. | Straightforward denial of cyber-related claims. |
| Market Trend | Declining as insurers update cyber risk language. | Increasing adoption among insurers for clarity. |
| Coverage Examples | May cover damage caused by cyber events unless excluded. | Does not cover losses from hacking, malware, or data breaches. |
Which is better?
Silent cyber coverage offers protection against cyber risks not explicitly mentioned in standard policies, addressing emerging threats in an increasingly digital landscape. Exclusionary language removes coverage for cyber incidents, limiting insurer liability but potentially exposing policyholders to significant financial risk. Choosing silent cyber coverage provides more comprehensive risk management compared to exclusionary clauses, especially for businesses with digital dependencies.
Connection
Silent cyber coverage arises when insurance policies unintentionally provide protection for cyber risks due to vague or exclusionary language. Exclusionary language aims to limit coverage for cyber incidents but often leads to ambiguity, causing disputes over whether cyber losses are covered. Clear and precise wording in insurance contracts is essential to define the scope of cyber risk coverage and avoid coverage gaps or unintended liability.
Key Terms
Policy Exclusions
Policy exclusions in cyber insurance often use exclusionary language to clearly define what types of cyber incidents are not covered, such as acts of war or intentional breaches. Silent cyber refers to cyber risks that are unintentionally covered under traditional property and casualty policies due to the absence of explicit exclusions. To understand how insurers manage these risks and protect your business, explore the nuances of exclusionary language and silent cyber coverage in policy documents.
Affirmative Coverage
Exclusionary language in cyber insurance policies explicitly denies coverage for silent cyber risks, whereas affirmative coverage specifically includes these cyber-related losses even if not expressly mentioned. Affirmative silent cyber coverage addresses evolving cyber threats by clearly outlining insurer obligations, providing greater risk certainty for insured parties. Explore the nuances of affirmative silent cyber coverage to enhance your organization's cyber risk management strategy.
Non-affirmative (Silent) Risk
Exclusionary language in insurance policies explicitly denies coverage for silent cyber risks, leaving non-affirmative exposures uninsured and increasing potential financial vulnerability for businesses. Silent cyber coverage addresses these gaps by encompassing cyber-related losses not expressly covered or excluded, providing essential protection against emerging cyber threats that traditional policies often overlook. Explore how insurers are evolving underwriting practices to manage silent cyber risks and safeguard organizations in this dynamic landscape.
Source and External Links
Inclusive Language vs Exclusive Language - This article discusses the contrast between inclusive and exclusive language, highlighting how exclusive language can marginalize individuals based on their identities and reinforce harmful biases.
25 of the Most-Used Exclusionary Words - This piece identifies common exclusionary words in job ads that fall under biases such as race, age, and sexual orientation, and suggests replacing them with inclusive alternatives.
Terminology, Power, and Exclusionary Language - This document argues for using more inclusive language in technical contexts, such as replacing metaphors like "master-slave" to promote broader participation and respect.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com