Deepfake insurance provides coverage against financial losses and reputational damage caused by AI-generated synthetic media used maliciously to impersonate individuals or manipulate content. Data breach insurance focuses on protecting organizations from costs associated with unauthorized access to sensitive information, including legal fees, notification expenses, and remediation efforts. Explore the key differences and benefits of deepfake insurance versus data breach insurance to safeguard your digital assets effectively.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between deepfake insurance and data breach insurance is crucial because deepfake insurance specifically protects against financial losses caused by synthetic media fraud, while data breach insurance covers costs related to unauthorized access and exposure of sensitive information. Deepfake insurance addresses risks from AI-generated content manipulation, which can damage reputation and lead to fraud. Data breach insurance provides coverage for incident response, legal fees, and notification expenses after a cybersecurity breach. Identifying the correct insurance type ensures appropriate risk management and financial protection tailored to specific digital threats.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Deepfake Insurance | Data Breach Insurance |
|---|---|---|
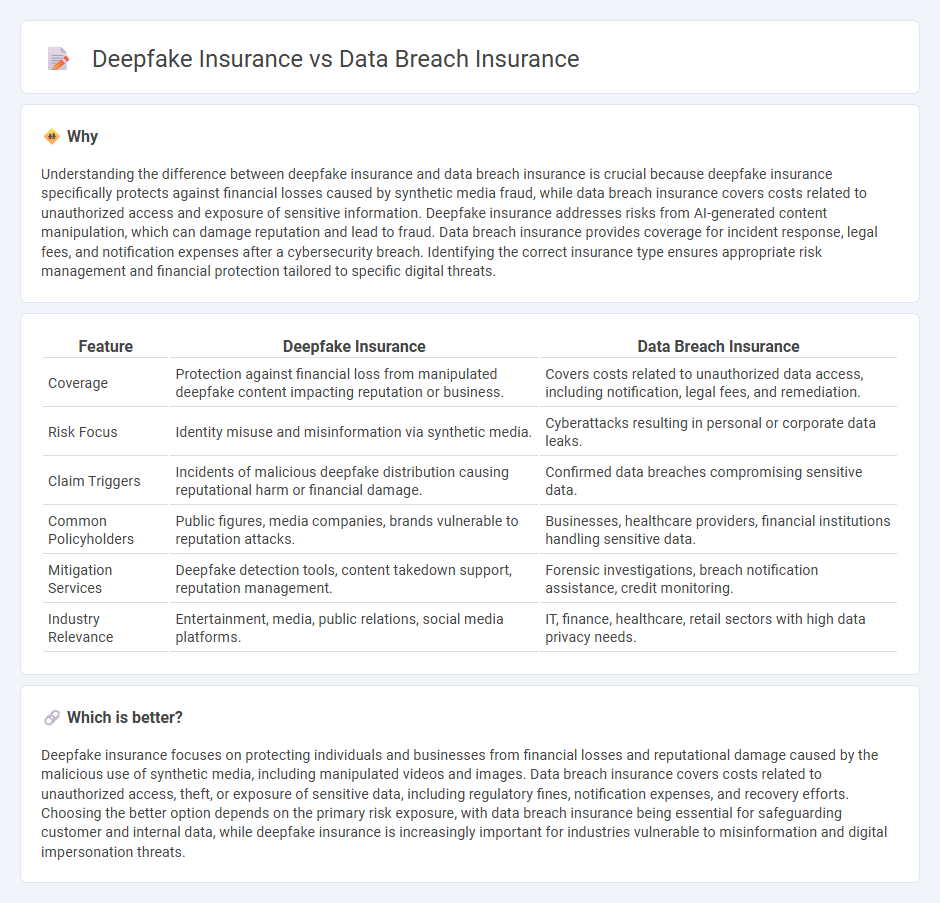
| Coverage | Protection against financial loss from manipulated deepfake content impacting reputation or business. | Covers costs related to unauthorized data access, including notification, legal fees, and remediation. |
| Risk Focus | Identity misuse and misinformation via synthetic media. | Cyberattacks resulting in personal or corporate data leaks. |
| Claim Triggers | Incidents of malicious deepfake distribution causing reputational harm or financial damage. | Confirmed data breaches compromising sensitive data. |
| Common Policyholders | Public figures, media companies, brands vulnerable to reputation attacks. | Businesses, healthcare providers, financial institutions handling sensitive data. |
| Mitigation Services | Deepfake detection tools, content takedown support, reputation management. | Forensic investigations, breach notification assistance, credit monitoring. |
| Industry Relevance | Entertainment, media, public relations, social media platforms. | IT, finance, healthcare, retail sectors with high data privacy needs. |
Which is better?
Deepfake insurance focuses on protecting individuals and businesses from financial losses and reputational damage caused by the malicious use of synthetic media, including manipulated videos and images. Data breach insurance covers costs related to unauthorized access, theft, or exposure of sensitive data, including regulatory fines, notification expenses, and recovery efforts. Choosing the better option depends on the primary risk exposure, with data breach insurance being essential for safeguarding customer and internal data, while deepfake insurance is increasingly important for industries vulnerable to misinformation and digital impersonation threats.
Connection
Deepfake insurance mitigates financial losses from synthetic media fraud, while data breach insurance covers damages from unauthorized data exposure; both policies address risks linked to advanced cyber threats and identity manipulation. The intersection lies in their protection against the exploitation of personal and organizational data, as deepfakes often result from compromised information used maliciously. By integrating these insurances, companies can safeguard against reputational harm, regulatory fines, and operational disruptions caused by cyber-attacks involving synthetic identity fraud and data breaches.
Key Terms
**Data Breach Insurance:**
Data breach insurance provides coverage against financial losses resulting from unauthorized access to sensitive data, including customer information, trade secrets, and personal records. This insurance helps cover costs associated with data recovery, legal fees, regulatory fines, and reputational damage caused by cyberattacks or hacking incidents. Explore detailed insights on how data breach insurance safeguards businesses and mitigates cybersecurity risks.
Notification Costs
Notification costs in data breach insurance typically cover expenses related to informing affected individuals, regulatory bodies, and credit monitoring services following unauthorized access to personal or financial information. Deepfake insurance's notification costs concentrate on alerting victims and relevant stakeholders about fraudulent synthetic media incidents, often necessitating specialized communication strategies due to reputational risks. Explore the distinctions in notification cost coverage between these policies to better understand protection against evolving digital threats.
Data Restoration
Data breach insurance primarily covers costs associated with restoring compromised data, including expenses for forensic analysis, data recovery, and notification to affected parties. Deepfake insurance focuses on protecting individuals and organizations against reputational damage and financial losses caused by synthetic media, emphasizing identity verification and digital restoration techniques rather than raw data recovery. Explore the distinctions and specialized coverage options to better safeguard your digital assets.
Source and External Links
Cyber Insurance & Data Breach Insurance Differences - Business.com - Data breach insurance covers direct costs from a breach, such as lost revenue and credit monitoring, especially when personally identifiable information is exposed, whether via hacking, theft, or employee negligence.
Cyber Insurance & Data Breach Coverage for Business - biBERK - Data breach insurance, often an add-on to other policies, helps cover expenses from system hacks or data security breaches, including incident response, credit monitoring, identity restoration, and legal defense for affected individuals.
cyber and privacy insurance - IRMI - Cyber and privacy insurance covers a business's liability for data breaches involving customer personal information, including notification costs, credit monitoring, regulatory fines, legal defense, and losses from identity theft.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com