Altcoin staking involves locking digital assets in a blockchain network to support operations and earn rewards, emphasizing security and passive income. Yield farming maximizes returns by strategically providing liquidity across DeFi platforms, often with higher risk and complexity. Explore the benefits and risks of both to optimize your cryptocurrency investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between altcoin staking and yield farming is crucial for maximizing investment returns in decentralized finance (DeFi). Altcoin staking involves locking up coins to support blockchain operations and earn rewards, while yield farming focuses on providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges for interest or token incentives. Knowing these distinctions helps investors manage risks, optimize passive income, and select strategies aligned with market volatility and tokenomics. Detailed knowledge of smart contract mechanisms and reward structures ensures safer, more profitable crypto asset management.
Comparison Table
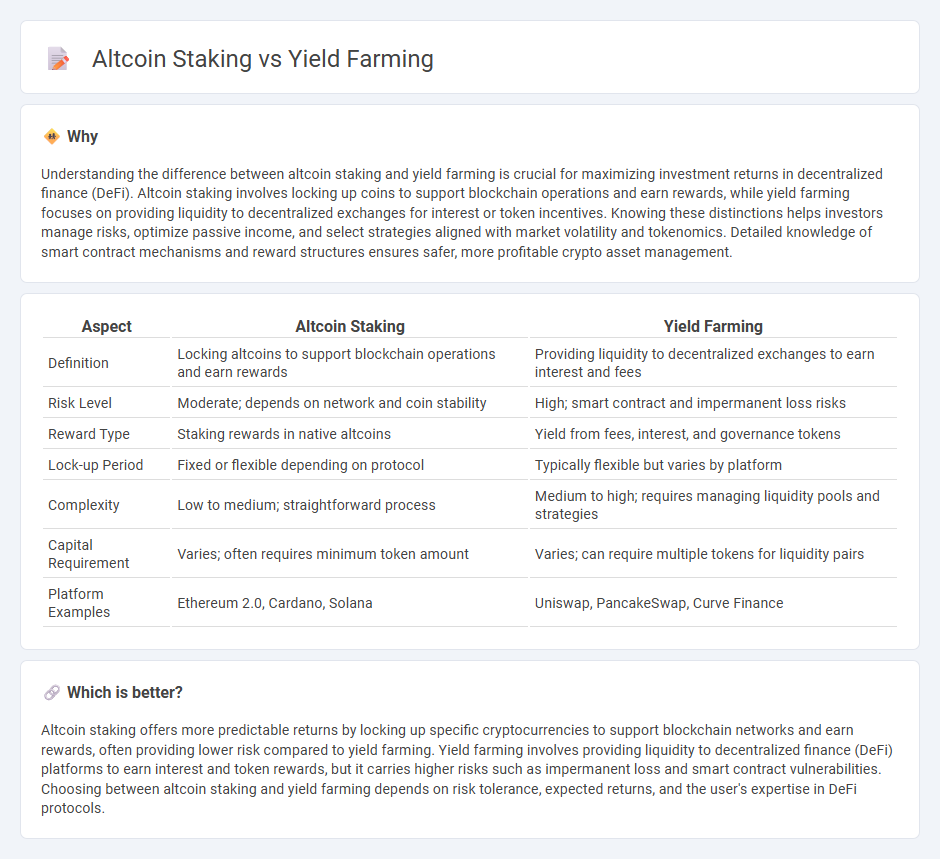
| Aspect | Altcoin Staking | Yield Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking altcoins to support blockchain operations and earn rewards | Providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges to earn interest and fees |
| Risk Level | Moderate; depends on network and coin stability | High; smart contract and impermanent loss risks |
| Reward Type | Staking rewards in native altcoins | Yield from fees, interest, and governance tokens |
| Lock-up Period | Fixed or flexible depending on protocol | Typically flexible but varies by platform |
| Complexity | Low to medium; straightforward process | Medium to high; requires managing liquidity pools and strategies |
| Capital Requirement | Varies; often requires minimum token amount | Varies; can require multiple tokens for liquidity pairs |
| Platform Examples | Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, Solana | Uniswap, PancakeSwap, Curve Finance |
Which is better?
Altcoin staking offers more predictable returns by locking up specific cryptocurrencies to support blockchain networks and earn rewards, often providing lower risk compared to yield farming. Yield farming involves providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to earn interest and token rewards, but it carries higher risks such as impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities. Choosing between altcoin staking and yield farming depends on risk tolerance, expected returns, and the user's expertise in DeFi protocols.
Connection
Altcoin staking and yield farming both involve locking cryptocurrencies to earn passive income, but they function differently within decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems. Staking requires participants to hold and delegate coins to support blockchain security and validate transactions, often earning staking rewards in the native token. Yield farming involves providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges or lending platforms, earning returns through interest, trading fees, or governance tokens, thereby optimizing capital efficiency in DeFi markets.
Key Terms
APY (Annual Percentage Yield)
Yield farming often offers higher APY by leveraging liquidity pools and automated market maker protocols, resulting in variable but potentially lucrative returns. Altcoin staking provides more stable and predictable APY since it involves locking tokens in a blockchain's proof-of-stake network to secure the system and earn rewards. Explore detailed comparisons and latest APY trends to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Liquidity Pools
Yield farming involves providing assets to liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap or SushiSwap to earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and governance tokens. Altcoin staking, on the other hand, requires locking up specific cryptocurrency assets such as Ethereum 2.0 or Cardano to secure the network and receive staking rewards. Explore the differences between liquidity pool participation and staking mechanisms to maximize your crypto portfolio's passive income.
Lock-up Period
Yield farming typically involves short to medium lock-up periods, often ranging from days to weeks, allowing for more flexibility in asset management compared to altcoin staking. Altcoin staking usually requires longer lock-up intervals, which can span from several weeks to months, providing network security and earning staking rewards but limiting immediate liquidity. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which approach aligns best with your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
What Is Yield Farming? Meaning and Definition - Chainlink - Yield farming, or liquidity mining, is a DeFi strategy rewarding users who provide liquidity or other value to protocols, typically paying them in native tokens to bootstrap liquidity and fairly distribute governance tokens, thus growing and securing the ecosystem.
What is yield farming and how does it work? - Coinbase - Yield farming is the process where users allocate their digital assets into DeFi protocols to earn rewards, usually governance tokens, by providing liquidity that is locked in smart contracts which pay out yields often expressed as an annual percentage yield (APY).
Yield Farming Explained: Your Complete Beginner's Guide - Kraken - Yield farming involves providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges or lending protocols to earn rewards through transaction fees and governance tokens, requiring active management to optimize returns while managing risks like impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com