Synthetic risk transfer allows financial institutions to manage credit risk by using derivatives such as credit default swaps, transferring potential losses without selling the underlying loan assets. Loan sale involves the outright sale of loans, removing both the asset and associated risk from the balance sheet. Explore more to understand the strategic benefits and applications of these risk transfer methods.
Why it is important
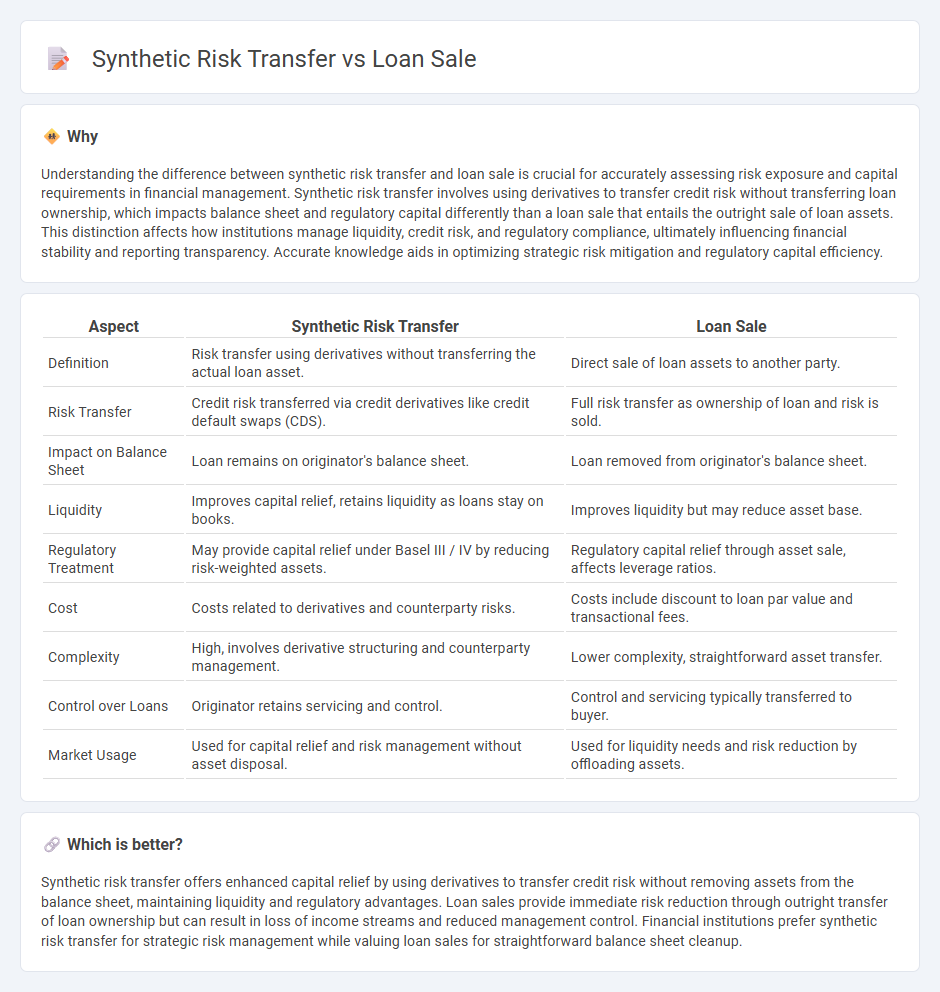
Understanding the difference between synthetic risk transfer and loan sale is crucial for accurately assessing risk exposure and capital requirements in financial management. Synthetic risk transfer involves using derivatives to transfer credit risk without transferring loan ownership, which impacts balance sheet and regulatory capital differently than a loan sale that entails the outright sale of loan assets. This distinction affects how institutions manage liquidity, credit risk, and regulatory compliance, ultimately influencing financial stability and reporting transparency. Accurate knowledge aids in optimizing strategic risk mitigation and regulatory capital efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Risk Transfer | Loan Sale |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk transfer using derivatives without transferring the actual loan asset. | Direct sale of loan assets to another party. |
| Risk Transfer | Credit risk transferred via credit derivatives like credit default swaps (CDS). | Full risk transfer as ownership of loan and risk is sold. |
| Impact on Balance Sheet | Loan remains on originator's balance sheet. | Loan removed from originator's balance sheet. |
| Liquidity | Improves capital relief, retains liquidity as loans stay on books. | Improves liquidity but may reduce asset base. |
| Regulatory Treatment | May provide capital relief under Basel III / IV by reducing risk-weighted assets. | Regulatory capital relief through asset sale, affects leverage ratios. |
| Cost | Costs related to derivatives and counterparty risks. | Costs include discount to loan par value and transactional fees. |
| Complexity | High, involves derivative structuring and counterparty management. | Lower complexity, straightforward asset transfer. |
| Control over Loans | Originator retains servicing and control. | Control and servicing typically transferred to buyer. |
| Market Usage | Used for capital relief and risk management without asset disposal. | Used for liquidity needs and risk reduction by offloading assets. |
Which is better?
Synthetic risk transfer offers enhanced capital relief by using derivatives to transfer credit risk without removing assets from the balance sheet, maintaining liquidity and regulatory advantages. Loan sales provide immediate risk reduction through outright transfer of loan ownership but can result in loss of income streams and reduced management control. Financial institutions prefer synthetic risk transfer for strategic risk management while valuing loan sales for straightforward balance sheet cleanup.
Connection
Synthetic risk transfer and loan sales are both financial strategies used by banks to manage credit risk and improve balance sheet efficiency. Synthetic risk transfer involves using credit derivatives, such as credit default swaps, to transfer specific loan risks without transferring the actual loans, while loan sales involve outright selling loan assets to third parties, removing both risk and assets from the bank's books. Both mechanisms help financial institutions optimize capital allocation, comply with regulatory requirements, and enhance liquidity.
Key Terms
Credit Risk
Loan sale transfers credit risk by outright selling loans to investors, removing the risk from the lender's balance sheet, while synthetic risk transfer uses credit derivatives like credit default swaps to pass risk without transferring loan ownership. Loan sales provide complete risk removal but may face market liquidity constraints; synthetic transfers offer flexibility and retain borrower relationships, optimizing risk management efficiency. Explore in-depth comparisons to determine the best credit risk mitigation strategy for your portfolio needs.
True Sale
True Sale in loan sale involves the complete transfer of loan ownership and associated risks from the originator to the buyer, ensuring off-balance-sheet treatment and credit risk removal. Synthetic Risk Transfer (SRT) uses derivative structures, such as credit default swaps, to transfer credit risk without transferring the actual loan assets, allowing originators to retain ownership while achieving capital relief. Explore the distinctions and benefits of True Sale versus Synthetic Risk Transfer for optimized risk management strategies.
Credit Derivative
Loan sales transfer actual loan ownership from banks to investors, providing immediate risk reduction by removing credit exposure from the balance sheet. Synthetic risk transfer involves the use of credit derivatives, such as credit default swaps, allowing banks to retain loans while transferring credit risk to counterparties without altering loan ownership. Explore detailed mechanisms and market implications of credit derivatives in managing banking credit risk.
Source and External Links
Loan sale - Wikipedia - A loan sale is a contractual sale by a bank of all or part of the cash stream from a specific loan, removing it from the bank's balance sheet.
Office of Asset Sales | HUD.gov - HUD conducts competitive auctions to sell defaulted single-family mortgage loans, including reverse mortgages, to promote recoveries and avoid foreclosure expenses.
Loan Sale Advisory & Asset Resolutions - Newmark - Newmark offers specialized advisory services for performing and non-performing loan sales, helping clients maximize returns with targeted marketing to investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com