Laddered bond ETFs invest in bonds with staggered maturities, providing predictable income streams and reducing reinvestment risk, while floating rate bond funds hold bonds with variable interest rates that adjust according to market benchmarks, offering protection against rising interest rates. Laddered bond ETFs suit investors seeking steady returns and lower volatility, whereas floating rate bond funds appeal to those aiming to benefit from increasing rates and mitigate duration risk. Explore the differences between these bond investment strategies to optimize your fixed-income portfolio.
Why it is important
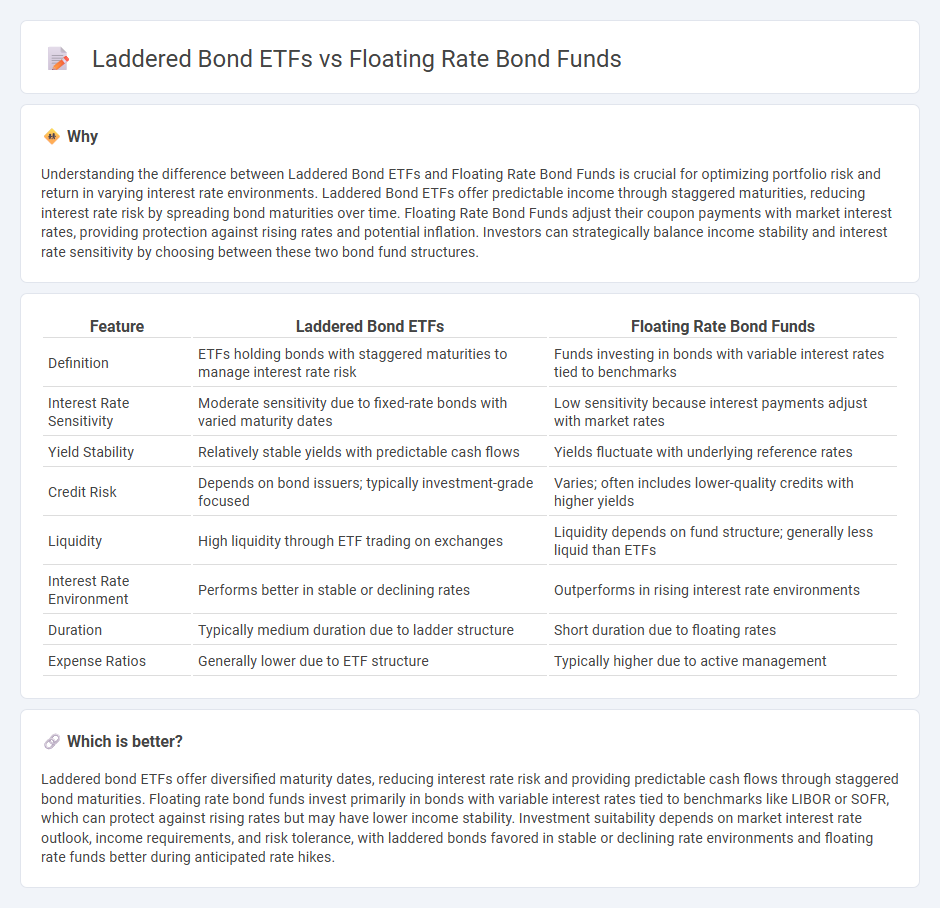
Understanding the difference between Laddered Bond ETFs and Floating Rate Bond Funds is crucial for optimizing portfolio risk and return in varying interest rate environments. Laddered Bond ETFs offer predictable income through staggered maturities, reducing interest rate risk by spreading bond maturities over time. Floating Rate Bond Funds adjust their coupon payments with market interest rates, providing protection against rising rates and potential inflation. Investors can strategically balance income stability and interest rate sensitivity by choosing between these two bond fund structures.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Laddered Bond ETFs | Floating Rate Bond Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | ETFs holding bonds with staggered maturities to manage interest rate risk | Funds investing in bonds with variable interest rates tied to benchmarks |
| Interest Rate Sensitivity | Moderate sensitivity due to fixed-rate bonds with varied maturity dates | Low sensitivity because interest payments adjust with market rates |
| Yield Stability | Relatively stable yields with predictable cash flows | Yields fluctuate with underlying reference rates |
| Credit Risk | Depends on bond issuers; typically investment-grade focused | Varies; often includes lower-quality credits with higher yields |
| Liquidity | High liquidity through ETF trading on exchanges | Liquidity depends on fund structure; generally less liquid than ETFs |
| Interest Rate Environment | Performs better in stable or declining rates | Outperforms in rising interest rate environments |
| Duration | Typically medium duration due to ladder structure | Short duration due to floating rates |
| Expense Ratios | Generally lower due to ETF structure | Typically higher due to active management |
Which is better?
Laddered bond ETFs offer diversified maturity dates, reducing interest rate risk and providing predictable cash flows through staggered bond maturities. Floating rate bond funds invest primarily in bonds with variable interest rates tied to benchmarks like LIBOR or SOFR, which can protect against rising rates but may have lower income stability. Investment suitability depends on market interest rate outlook, income requirements, and risk tolerance, with laddered bonds favored in stable or declining rate environments and floating rate funds better during anticipated rate hikes.
Connection
Laddered bond ETFs and floating rate bond funds both aim to manage interest rate risk but do so through different strategies; laddered bond ETFs invest in bonds with staggered maturities to provide steady income and reduce reinvestment risk. Floating rate bond funds hold bonds with variable interest rates that adjust with market rates, offering protection against rising interest rates. Together, these investment vehicles offer diversification in fixed income portfolios by balancing income stability and inflation sensitivity.
Key Terms
Interest Rate Risk
Floating Rate Bond Funds adjust their coupon payments based on prevailing interest rates, effectively reducing interest rate risk during rising rate environments. Laddered bond ETFs involve staggered maturities to spread out reinvestment risk and provide a predictable income stream, but remain more sensitive to fluctuating interest rates overall. Explore the differences further to optimize fixed income strategies amid changing market conditions.
Yield
Floating rate bond funds adjust their interest payments based on prevailing short-term rates, often providing higher yields during rising interest rate environments compared to laddered bond ETFs, which invest in fixed-rate bonds staggered across maturities to mitigate interest rate risk. Laddered bond ETFs typically offer more stability and predictable income through diversified maturities but may lag in yield when rates climb. Explore detailed yield comparisons and risk profiles to determine the best fit for your investment strategy.
Maturity Structure
Floating Rate Bond Funds adjust interest payments based on short-term rates, offering protection against rising interest rates, while laddered bond ETFs hold bonds with staggered maturities, balancing interest rate risk and liquidity by spreading out bond maturities over time. The maturity structure in laddered bond ETFs creates a predictable cash flow and reduces reinvestment risk, contrasting with the flexible rate resets in floating rate funds that respond to market rate changes. Explore detailed analyses to determine which maturity strategy aligns best with your investment goals.
Source and External Links
A primer on floating-rate bond funds - Floating-rate bond funds invest primarily in speculative-grade loans (credit quality typically BB to B), offering low interest rate risk due to their short duration, but carry high credit risk similar to high-yield bond funds.
Floating Rate Funds - These funds pay variable interest rates that reset frequently (typically every 30-90 days), providing potential protection against rising rates, but are considered aggressive-income investments with risk levels comparable to high-yield bonds.
A Guide to Understanding Floating Rate Securities - Floating-rate securities adjust their interest payments periodically based on a predetermined benchmark (such as LIBOR or CPI), offering investors protection against rising interest rates while exposing them to credit risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com