Quantamental investing integrates quantitative analysis with fundamental research to identify investment opportunities using data-driven models alongside traditional valuation metrics. Value investing focuses on purchasing undervalued stocks based on intrinsic value assessments, often emphasizing financial statements and market sentiment. Explore the strengths and strategies of both approaches to optimize your investment decisions.
Why it is important
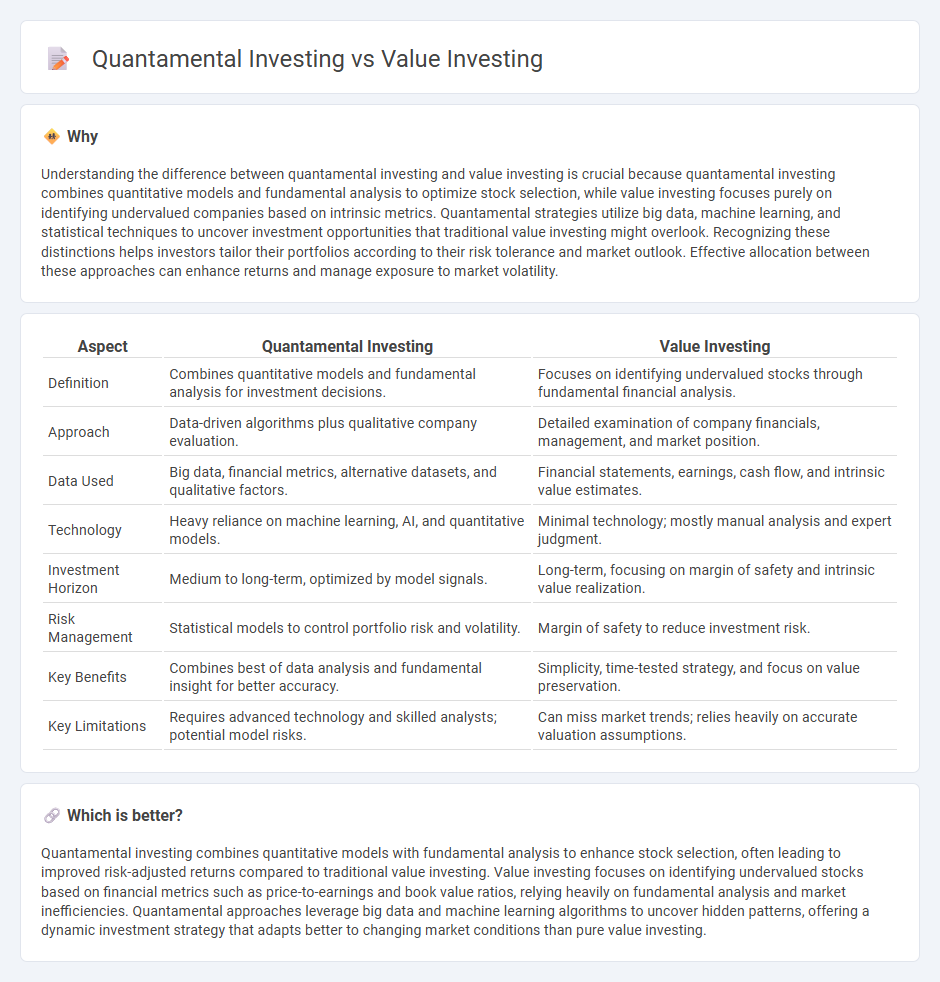
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing and value investing is crucial because quantamental investing combines quantitative models and fundamental analysis to optimize stock selection, while value investing focuses purely on identifying undervalued companies based on intrinsic metrics. Quantamental strategies utilize big data, machine learning, and statistical techniques to uncover investment opportunities that traditional value investing might overlook. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors tailor their portfolios according to their risk tolerance and market outlook. Effective allocation between these approaches can enhance returns and manage exposure to market volatility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative models and fundamental analysis for investment decisions. | Focuses on identifying undervalued stocks through fundamental financial analysis. |
| Approach | Data-driven algorithms plus qualitative company evaluation. | Detailed examination of company financials, management, and market position. |
| Data Used | Big data, financial metrics, alternative datasets, and qualitative factors. | Financial statements, earnings, cash flow, and intrinsic value estimates. |
| Technology | Heavy reliance on machine learning, AI, and quantitative models. | Minimal technology; mostly manual analysis and expert judgment. |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term, optimized by model signals. | Long-term, focusing on margin of safety and intrinsic value realization. |
| Risk Management | Statistical models to control portfolio risk and volatility. | Margin of safety to reduce investment risk. |
| Key Benefits | Combines best of data analysis and fundamental insight for better accuracy. | Simplicity, time-tested strategy, and focus on value preservation. |
| Key Limitations | Requires advanced technology and skilled analysts; potential model risks. | Can miss market trends; relies heavily on accurate valuation assumptions. |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to enhance stock selection, often leading to improved risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional value investing. Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks based on financial metrics such as price-to-earnings and book value ratios, relying heavily on fundamental analysis and market inefficiencies. Quantamental approaches leverage big data and machine learning algorithms to uncover hidden patterns, offering a dynamic investment strategy that adapts better to changing market conditions than pure value investing.
Connection
Quantamental investing integrates quantitative analysis with fundamental research to identify undervalued stocks, leveraging data-driven models alongside traditional value investing principles. Both strategies focus on buying securities trading below their intrinsic value, aiming to capitalize on market inefficiencies and long-term growth potential. By combining algorithmic precision with fundamental valuation metrics, quantamental investing enhances decision-making processes in value investing portfolios.
Key Terms
Value Investing:
Value investing centers on identifying undervalued stocks by analyzing fundamental metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios, book value, and dividend yields to uncover long-term growth potential. This strategy relies on deep financial analysis and market psychology to buy quality assets below their intrinsic worth, aiming for capital appreciation and margin of safety. Discover more about the principles and techniques that make value investing a proven approach to wealth creation.
Intrinsic Value
Value investing centers on determining a company's intrinsic value through fundamental analysis of financial statements and market conditions, aiming to purchase stocks undervalued by the market. Quantamental investing integrates quantitative models and fundamental analysis to enhance stock selection, using data-driven techniques alongside intrinsic value assessments. Explore detailed strategies and key differences to deepen your understanding of intrinsic value approaches in investing.
Margin of Safety
Value investing emphasizes a strong margin of safety by purchasing undervalued stocks with significant intrinsic value gaps, reducing downside risk. Quantamental investing blends quantitative models and fundamental analysis, applying data-driven signals to identify securities with robust margin of safety while considering market and financial metrics. Explore deeper insights into how margin of safety shapes these investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Value investing - Wikipedia - Value investing is an investment strategy focused on buying securities that appear underpriced based on fundamental analysis, aiming to purchase stocks at less than their intrinsic value for a margin of safety.
What is value investing? | iShares - BlackRock - Value investing targets stocks trading below their real worth, using metrics like price-to-book and price-to-earnings ratios to identify undervalued companies historically outperforming the broad market.
The Value of Value Investing - Brown Advisory - The goal is to find companies not only undervalued but also positioned to regain fair value over time, often characterized by steady profits, strong fundamentals, and higher dividend yields.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com