Decentralized finance (DeFi) utilizes blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, offering greater transparency and lower costs compared to traditional banking systems that rely on central authorities and intermediaries for services like loans and deposits. Traditional banking provides established regulatory protections and a broad range of services but often involves slower transaction times and higher fees. Explore how DeFi and traditional banking impact the future of financial inclusion and efficiency.
Why it is important
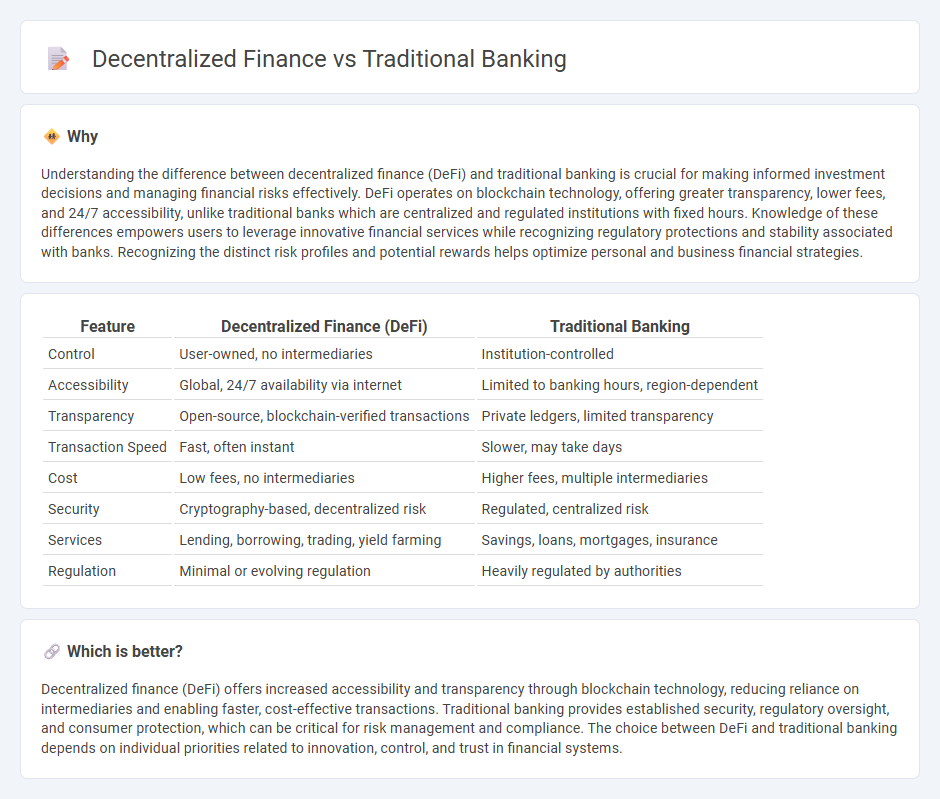
Understanding the difference between decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional banking is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing financial risks effectively. DeFi operates on blockchain technology, offering greater transparency, lower fees, and 24/7 accessibility, unlike traditional banks which are centralized and regulated institutions with fixed hours. Knowledge of these differences empowers users to leverage innovative financial services while recognizing regulatory protections and stability associated with banks. Recognizing the distinct risk profiles and potential rewards helps optimize personal and business financial strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Traditional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Control | User-owned, no intermediaries | Institution-controlled |
| Accessibility | Global, 24/7 availability via internet | Limited to banking hours, region-dependent |
| Transparency | Open-source, blockchain-verified transactions | Private ledgers, limited transparency |
| Transaction Speed | Fast, often instant | Slower, may take days |
| Cost | Low fees, no intermediaries | Higher fees, multiple intermediaries |
| Security | Cryptography-based, decentralized risk | Regulated, centralized risk |
| Services | Lending, borrowing, trading, yield farming | Savings, loans, mortgages, insurance |
| Regulation | Minimal or evolving regulation | Heavily regulated by authorities |
Which is better?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers increased accessibility and transparency through blockchain technology, reducing reliance on intermediaries and enabling faster, cost-effective transactions. Traditional banking provides established security, regulatory oversight, and consumer protection, which can be critical for risk management and compliance. The choice between DeFi and traditional banking depends on individual priorities related to innovation, control, and trust in financial systems.
Connection
Decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional banking intersect through their shared goal of facilitating financial services like lending, borrowing, and asset management. DeFi leverages blockchain technology to offer transparent, permissionless transactions, while traditional banks utilize centralized systems and regulatory oversight to ensure security and trust. Innovations such as tokenized assets and integration of stablecoins are bridging gaps, enabling interoperability between DeFi platforms and conventional financial institutions.
Key Terms
Intermediaries
Traditional banking relies heavily on intermediaries such as banks, clearinghouses, and payment processors to facilitate financial transactions and ensure regulatory compliance. Decentralized finance (DeFi) eliminates these middlemen by using blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer transactions with increased transparency and reduced costs. Explore how DeFi innovations are reshaping the role of intermediaries and transforming the financial ecosystem.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts in decentralized finance (DeFi) automate agreements through blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries present in traditional banking systems and thereby reducing costs and transaction times. Traditional banking relies heavily on centralized authorities to validate and enforce contracts, which can introduce delays and increase risks related to fraud or human error. Explore the transformative potential of smart contracts and how they are reshaping the future of financial transactions.
Custody
Traditional banking relies on centralized custody where financial institutions control user assets, offering security through regulatory oversight but exposing clients to centralized risks like insolvency or fraud. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology for self-custody, enabling users to hold and manage assets directly via smart contracts, reducing reliance on intermediaries but increasing responsibility for private key security. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how custody models impact asset control, security, and user empowerment in both systems.
Source and External Links
Online vs. Traditional Banking: Differences, Pros, and Cons | Brex - Traditional banking refers to financial institutions with physical branch locations and ATMs, offering in-person services, personal relationships with bankers, and a wide range of financial products under one roof.
Online Banking vs. Traditional Banking - Chase.com - Traditional banks provide a broader range of services--including cash deposits, access to extensive ATM networks, and in-person customer support--while often requiring certain transactions to be completed at a branch.
Online vs Traditional Banks: Pros, Cons, and More Explained - Traditional banks feature physical locations for face-to-face assistance and complex transactions, but typically charge higher fees and have limited operating hours compared to online banks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com