Perpetual futures and options contracts serve as essential derivatives in finance, enabling traders to hedge risks or speculate on asset price movements without owning the underlying asset. Perpetual futures feature no expiration date and closely track the spot price through funding rates, while options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price by a specific date. Explore the detailed mechanics and strategic uses of these instruments to enhance your trading and risk management expertise.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between perpetual futures and options contracts is crucial in finance for effective risk management and investment strategy. Perpetual futures provide continuous exposure without an expiration date, enabling traders to maintain positions indefinitely with funding rate considerations. Options contracts grant the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before expiration, offering strategic flexibility. Mastering these distinctions helps investors optimize leverage, hedge assets, and navigate market volatility efficiently.
Comparison Table
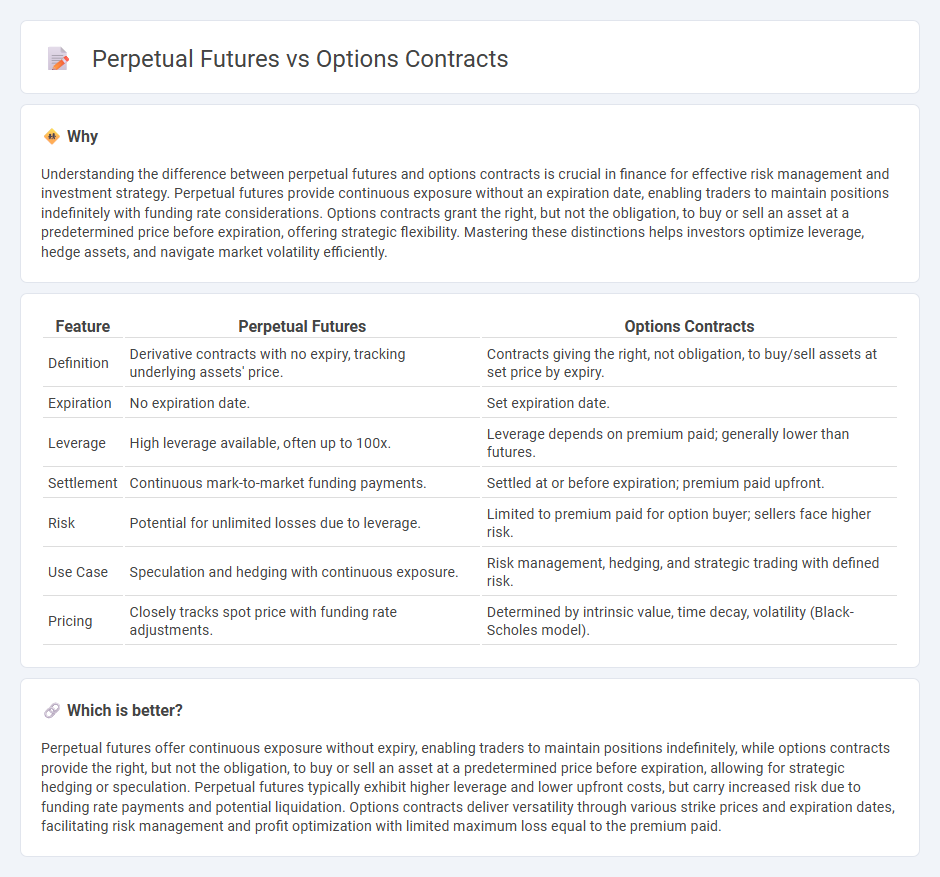
| Feature | Perpetual Futures | Options Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivative contracts with no expiry, tracking underlying assets' price. | Contracts giving the right, not obligation, to buy/sell assets at set price by expiry. |
| Expiration | No expiration date. | Set expiration date. |
| Leverage | High leverage available, often up to 100x. | Leverage depends on premium paid; generally lower than futures. |
| Settlement | Continuous mark-to-market funding payments. | Settled at or before expiration; premium paid upfront. |
| Risk | Potential for unlimited losses due to leverage. | Limited to premium paid for option buyer; sellers face higher risk. |
| Use Case | Speculation and hedging with continuous exposure. | Risk management, hedging, and strategic trading with defined risk. |
| Pricing | Closely tracks spot price with funding rate adjustments. | Determined by intrinsic value, time decay, volatility (Black-Scholes model). |
Which is better?
Perpetual futures offer continuous exposure without expiry, enabling traders to maintain positions indefinitely, while options contracts provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before expiration, allowing for strategic hedging or speculation. Perpetual futures typically exhibit higher leverage and lower upfront costs, but carry increased risk due to funding rate payments and potential liquidation. Options contracts deliver versatility through various strike prices and expiration dates, facilitating risk management and profit optimization with limited maximum loss equal to the premium paid.
Connection
Perpetual futures and options contracts are both derivative instruments used in finance to hedge risk and speculate on asset price movements. Perpetual futures provide continuous exposure with no expiry, allowing traders to maintain positions indefinitely, while options contracts offer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before expiration. Both contracts derive their value from underlying assets such as stocks, commodities, or cryptocurrencies, and their pricing is influenced by factors including volatility, time decay, and market sentiment.
Key Terms
Expiry Date
Options contracts have a fixed expiry date, requiring traders to exercise or sell the option before this deadline to realize profits or limit losses, while perpetual futures lack an expiry and allow positions to be held indefinitely with funding rates applied to maintain price alignment with the underlying asset. This time constraint in options introduces strategic considerations such as time decay (theta), impacting option premiums as the expiration approaches, whereas perpetual futures emphasize continuous market exposure and funding fee dynamics. Explore the detailed mechanisms and trading strategies of options and perpetual futures to optimize your derivatives portfolio.
Leverage
Options contracts offer leverage by allowing traders to control larger positions with a fraction of the underlying asset's price, often requiring only a premium as an upfront cost. Perpetual futures provide continuous leverage opportunities without expiration dates, enabling traders to maintain leveraged positions indefinitely by posting margin and managing funding rates. Explore more to understand how different leverage mechanisms impact risk and potential returns in these derivatives.
Settlement
Options contracts settle either upon expiration or when the holder exercises the option, with settlement involving the transfer of the underlying asset or cash based on the strike price. Perpetual futures feature no fixed expiration date and settle continuously through a funding rate mechanism that aligns contract prices with the spot market. Explore more to understand how these settlement mechanisms impact trading strategies and risk management.
Source and External Links
Options | FINRA.org - Options contracts give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a strike price within a set period, with calls granting the right to buy and puts the right to sell; sellers take on corresponding obligations if assigned.
Option (finance) - Wikipedia - Options can be exchange-traded with standardized contracts or customized over-the-counter, allowing holders to buy or sell assets at specified strike prices before expiration, with various types including stock options, index options, and currency options.
What are options, and how do they work? - Fidelity Investments - Options are legal contracts granting the right to buy (call) or sell (put) an asset at a specific price by a certain time, with buyers being "long" and sellers "short" on the expected asset performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com