Zero day options represent contracts set to expire on the day of purchase, offering high-risk, high-reward trading opportunities with immediate time decay. Swaptions, or swap options, grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to enter into an interest rate swap at a future date, providing strategic hedging against interest rate fluctuations. Explore more to understand how these derivatives fit into sophisticated financial strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero day options and swaptions is crucial for managing risk and optimizing investment strategies in finance. Zero day options, expiring on the same day they are traded, offer high leverage but also high risk and volatility. Swaptions grant the right to enter into an interest rate swap agreement, providing strategic interest rate exposure for hedging or speculation. Correctly differentiating these instruments helps investors tailor their portfolios to specific time horizons and financial goals.
Comparison Table
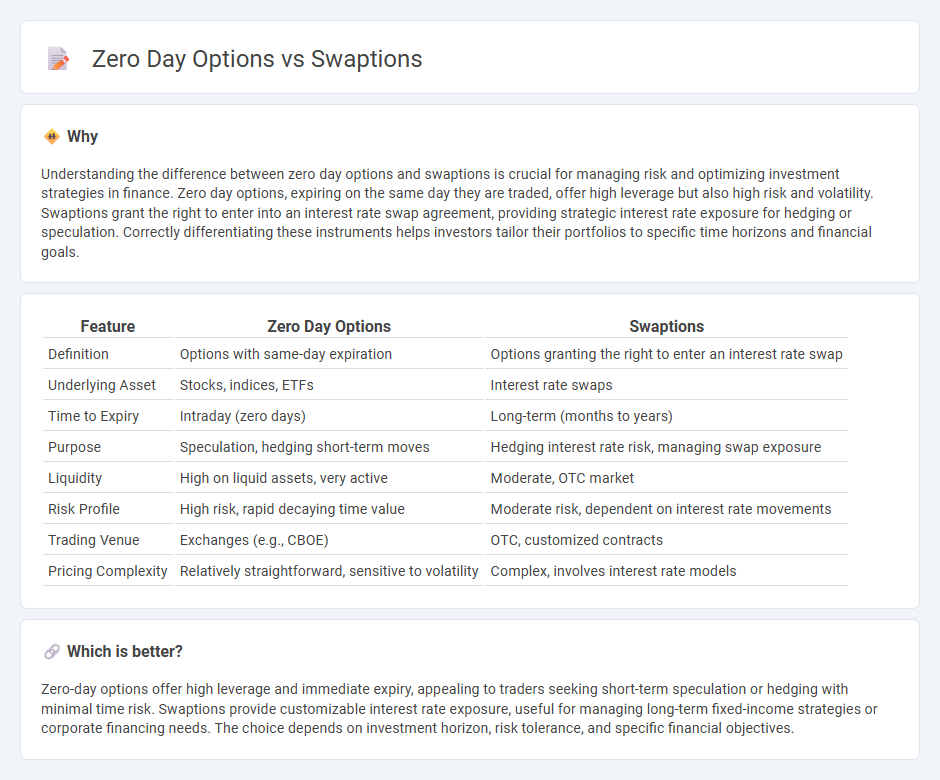
| Feature | Zero Day Options | Swaptions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Options with same-day expiration | Options granting the right to enter an interest rate swap |
| Underlying Asset | Stocks, indices, ETFs | Interest rate swaps |
| Time to Expiry | Intraday (zero days) | Long-term (months to years) |
| Purpose | Speculation, hedging short-term moves | Hedging interest rate risk, managing swap exposure |
| Liquidity | High on liquid assets, very active | Moderate, OTC market |
| Risk Profile | High risk, rapid decaying time value | Moderate risk, dependent on interest rate movements |
| Trading Venue | Exchanges (e.g., CBOE) | OTC, customized contracts |
| Pricing Complexity | Relatively straightforward, sensitive to volatility | Complex, involves interest rate models |
Which is better?
Zero-day options offer high leverage and immediate expiry, appealing to traders seeking short-term speculation or hedging with minimal time risk. Swaptions provide customizable interest rate exposure, useful for managing long-term fixed-income strategies or corporate financing needs. The choice depends on investment horizon, risk tolerance, and specific financial objectives.
Connection
Zero day options and swaptions are connected through their role in managing financial risk and enhancing market liquidity. Zero day options, expiring on the same day they are traded, offer traders rapid hedging opportunities, while swaptions grant the right to enter into interest rate swaps, providing flexibility in interest rate exposure management. Both instruments are integral in derivatives markets, supporting sophisticated strategies for interest rate risk and short-term volatility management.
Key Terms
Interest Rate Derivatives
Swaptions provide the holder the right but not the obligation to enter into an interest rate swap at a predetermined date and rate, functioning as key tools for managing interest rate risk and hedging in fixed income portfolios. Zero day options, expiring on the same day, are highly sensitive to intraday interest rate movements and used for short-term speculation or hedging in the interest rate derivatives market. Explore the nuances and strategic applications of swaptions and zero day options to optimize your interest rate risk management.
Expiry/Maturity
Swaptions grant the right to enter into an interest rate swap on a specified future date, with expiry determining when this option can be exercised, typically ranging from months to years. Zero day options expire on the same day they are traded, providing immediate exposure to underlying asset movements and emphasizing intra-day strategies. Explore the key differences and strategic uses of swaptions and zero day options for effective risk management.
Volatility
Swaptions exhibit higher volatility sensitivity due to their longer time horizon and underlying interest rate dynamics compared to zero day options, which experience extreme gamma and rapid time decay as expiration approaches. Volatility in swaptions impacts the premium more significantly, reflecting changes in interest rate expectations, while zero day options primarily react to immediate price movements and short-term volatility spikes. Explore deeper insights into volatility behavior by comparing these derivatives for strategic trading and risk management.
Source and External Links
Swaption - A swaption is an option granting the owner the right, but not obligation, to enter into an interest rate swap, typically classified into payer and receiver swaptions, settled either physically or in cash at expiry.
Swaption - Definition, Types, Styles, and Examples - A swaption is an OTC option contract allowing its holder to enter a predetermined swap in exchange for a premium, with customizable contract features including swap notional, fixed and floating leg specifications.
What Is a Swaption? Guide to Understanding Swap Options - A swaption gives the buyer the right to enter an interest rate swap as either payer (pay fixed, receive floating) or receiver (receive fixed, pay floating), useful for managing exposure to interest rate movements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com