Alternative data encompasses non-traditional sources such as social media activity, satellite imagery, and transaction logs, offering unique insights beyond conventional financial metrics. Structured data, typically found in databases and spreadsheets, consists of organized, easily searchable information like financial statements and stock prices. Explore the impact of both data types on investment strategies and market analysis.
Why it is important
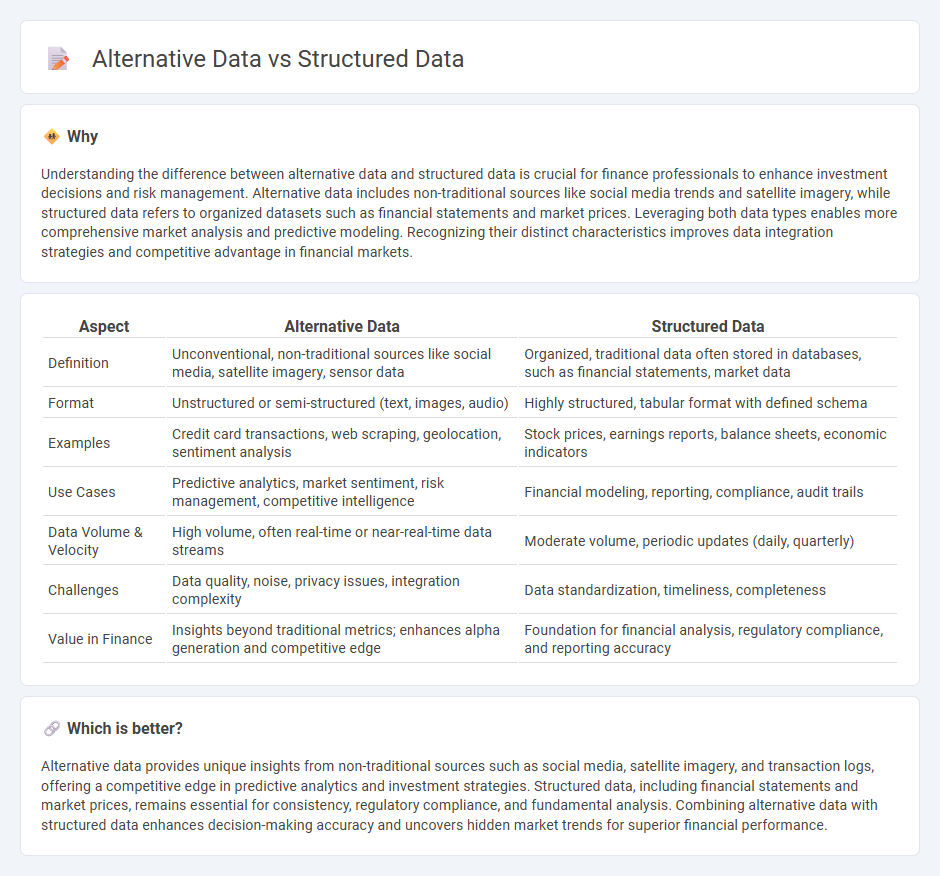
Understanding the difference between alternative data and structured data is crucial for finance professionals to enhance investment decisions and risk management. Alternative data includes non-traditional sources like social media trends and satellite imagery, while structured data refers to organized datasets such as financial statements and market prices. Leveraging both data types enables more comprehensive market analysis and predictive modeling. Recognizing their distinct characteristics improves data integration strategies and competitive advantage in financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Data | Structured Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unconventional, non-traditional sources like social media, satellite imagery, sensor data | Organized, traditional data often stored in databases, such as financial statements, market data |
| Format | Unstructured or semi-structured (text, images, audio) | Highly structured, tabular format with defined schema |
| Examples | Credit card transactions, web scraping, geolocation, sentiment analysis | Stock prices, earnings reports, balance sheets, economic indicators |
| Use Cases | Predictive analytics, market sentiment, risk management, competitive intelligence | Financial modeling, reporting, compliance, audit trails |
| Data Volume & Velocity | High volume, often real-time or near-real-time data streams | Moderate volume, periodic updates (daily, quarterly) |
| Challenges | Data quality, noise, privacy issues, integration complexity | Data standardization, timeliness, completeness |
| Value in Finance | Insights beyond traditional metrics; enhances alpha generation and competitive edge | Foundation for financial analysis, regulatory compliance, and reporting accuracy |
Which is better?
Alternative data provides unique insights from non-traditional sources such as social media, satellite imagery, and transaction logs, offering a competitive edge in predictive analytics and investment strategies. Structured data, including financial statements and market prices, remains essential for consistency, regulatory compliance, and fundamental analysis. Combining alternative data with structured data enhances decision-making accuracy and uncovers hidden market trends for superior financial performance.
Connection
Alternative data, such as social media activity, satellite imagery, and transaction records, complements structured financial data by providing unconventional insights that traditional datasets may miss. Integrating these diverse data types enhances predictive analytics, allowing firms to identify market trends, credit risks, and investment opportunities with greater accuracy. Leveraging both alternative and structured data enables a comprehensive, data-driven approach to financial decision-making and risk management.
Key Terms
Financial Statements
Structured data in financial statements includes organized information like balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, providing precise numeric values and standardized formats for analysis. Alternative data comprises unstructured or semi-structured information such as social media sentiment, satellite imagery, or transaction data, offering insights beyond traditional financial metrics. Discover how integrating both data types can enhance investment strategies and risk assessment.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery serves as a powerful source of alternative data, capturing real-time visual information from Earth's surface that structured data, such as databases and spreadsheets, cannot provide. Unlike structured data's organized and categorical format, satellite imagery offers unstructured, high-resolution spatial data that enables unique insights into environmental changes, urban development, and agricultural trends. Explore how satellite imagery enhances decision-making by complementing traditional structured datasets.
Web Scraping
Structured data, such as databases and spreadsheets, offers organized and easily searchable information, whereas alternative data extracted through web scraping includes unstructured content like social media posts, reviews, and news articles. Web scraping enables the collection of diverse alternative data from various online sources, providing real-time insights for market analysis, sentiment tracking, and competitive intelligence. Explore how web scraping transforms alternative data into actionable business intelligence by learning more about its methods and applications.
Source and External Links
What Is Structured Data? - Structured data is information organized in a predefined and consistent format, such as rows and columns in a database, making it easy to search, sort, and analyze.
What is Structured Data? - Structured data is data with a standardized, typically tabular format (rows and columns), allowing both software and humans to efficiently access and analyze it--common examples include SQL databases and Excel files.
About Structured Data - Structured data is data divided into standardized, identifiable pieces (like numbers, dates, or text segments) that are accessible and analyzable by both humans and computers, often using formats such as XBRL, XML, or JSON.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com