Tax loss harvesting involves strategically selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income, enhancing after-tax returns. Asset location focuses on placing investments in specific account types, such as tax-advantaged or taxable accounts, to minimize taxes across various income streams. Explore how combining these strategies can optimize your overall tax efficiency and investment performance.
Why it is important
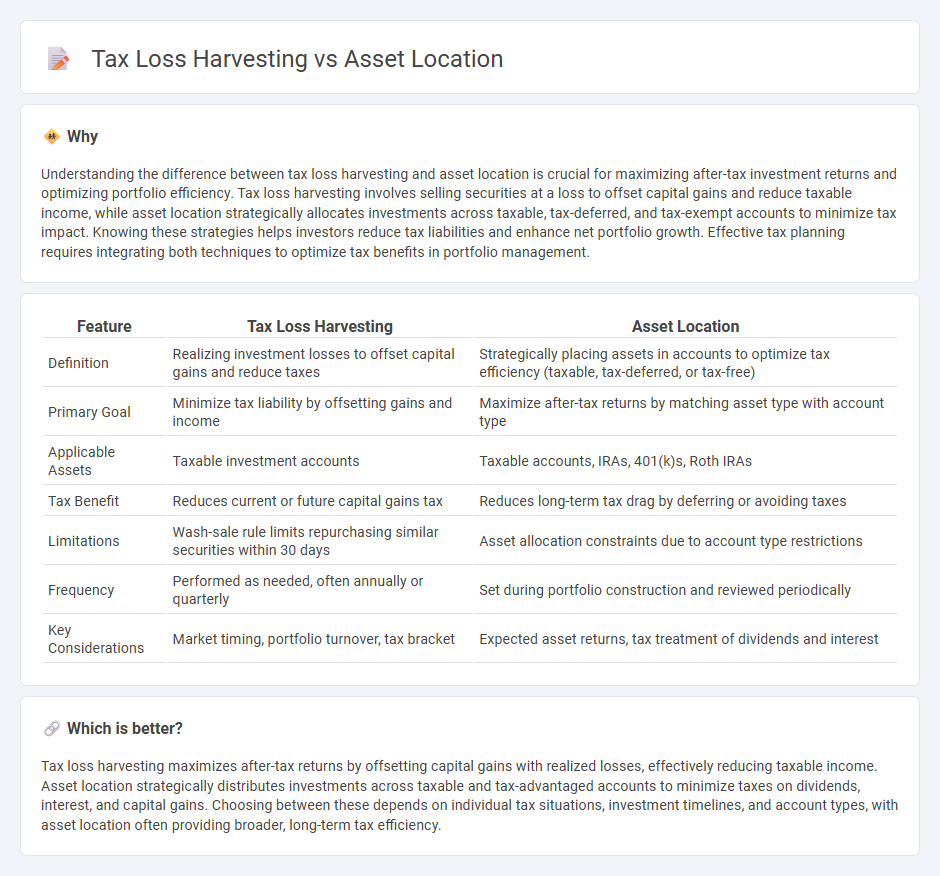
Understanding the difference between tax loss harvesting and asset location is crucial for maximizing after-tax investment returns and optimizing portfolio efficiency. Tax loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income, while asset location strategically allocates investments across taxable, tax-deferred, and tax-exempt accounts to minimize tax impact. Knowing these strategies helps investors reduce tax liabilities and enhance net portfolio growth. Effective tax planning requires integrating both techniques to optimize tax benefits in portfolio management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tax Loss Harvesting | Asset Location |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Realizing investment losses to offset capital gains and reduce taxes | Strategically placing assets in accounts to optimize tax efficiency (taxable, tax-deferred, or tax-free) |
| Primary Goal | Minimize tax liability by offsetting gains and income | Maximize after-tax returns by matching asset type with account type |
| Applicable Assets | Taxable investment accounts | Taxable accounts, IRAs, 401(k)s, Roth IRAs |
| Tax Benefit | Reduces current or future capital gains tax | Reduces long-term tax drag by deferring or avoiding taxes |
| Limitations | Wash-sale rule limits repurchasing similar securities within 30 days | Asset allocation constraints due to account type restrictions |
| Frequency | Performed as needed, often annually or quarterly | Set during portfolio construction and reviewed periodically |
| Key Considerations | Market timing, portfolio turnover, tax bracket | Expected asset returns, tax treatment of dividends and interest |
Which is better?
Tax loss harvesting maximizes after-tax returns by offsetting capital gains with realized losses, effectively reducing taxable income. Asset location strategically distributes investments across taxable and tax-advantaged accounts to minimize taxes on dividends, interest, and capital gains. Choosing between these depends on individual tax situations, investment timelines, and account types, with asset location often providing broader, long-term tax efficiency.
Connection
Tax loss harvesting strategically sells investments at a loss to offset capital gains, reducing taxable income. Asset location involves placing investments in accounts that maximize after-tax returns, such as holding tax-inefficient assets in tax-advantaged accounts. Combining tax loss harvesting with optimal asset location enhances portfolio tax efficiency and overall investment performance.
Key Terms
Tax Efficiency
Asset location strategically places investments in accounts based on their tax treatment to maximize after-tax returns, prioritizing tax-deferred or tax-exempt accounts for high-growth assets. Tax loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income within taxable accounts. Explore detailed strategies for enhancing tax efficiency through asset location and tax loss harvesting to optimize your investment portfolio.
Cost Basis
Asset location optimizes tax efficiency by placing investments in accounts with favorable tax treatments, such as holding bonds in tax-deferred accounts to reduce current taxable income. Tax loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains, thereby adjusting the cost basis and minimizing tax liabilities on future gains. Explore how strategic asset location combined with cost basis management through tax loss harvesting can maximize after-tax returns.
Account Type
Asset location strategies prioritize placing investments in tax-advantaged accounts such as IRAs and 401(k)s to maximize tax efficiency, while tax loss harvesting focuses on realizing losses in taxable accounts to offset gains and reduce tax liability. Account type critically influences the effectiveness of these strategies; tax-advantaged accounts offer deferral benefits that minimize the need for loss harvesting, whereas taxable accounts provide opportunities for strategic loss realization. Explore how aligning account types with these strategies can optimize overall tax outcomes.
Source and External Links
Asset location - Wikipedia - Asset location refers to how investors distribute their investments across various savings vehicles like taxable, tax-exempt, and tax-deferred accounts, aiming to optimize tax benefits and other personal objectives such as liquidity and privacy, distinct from asset allocation which focuses on what assets to hold.
Revisiting the conventional wisdom regarding asset location - Asset location is a strategic approach to placing assets in various investment accounts, like traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, and taxable accounts, to maximize after-tax returns, with research suggesting prioritizing bonds in traditional IRAs, then Roth IRAs, and lastly taxable accounts for most investors.
How Asset Location Can Help Save on Taxes - Charles Schwab - Asset location is a tax-efficiency strategy that matches different assets with suitable account types (taxable, tax-deferred, tax-exempt) to reduce taxes and potentially boost investment returns, particularly benefiting investors in higher tax brackets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com