Algorithmic trading in retail finance leverages advanced software to execute high-frequency trades based on complex market data, aiming to maximize short-term profits. Passive investing involves long-term strategies focused on low-cost index funds or ETFs, prioritizing steady growth and minimal management. Explore the nuances and benefits of these investment approaches to optimize your portfolio.
Why it is important
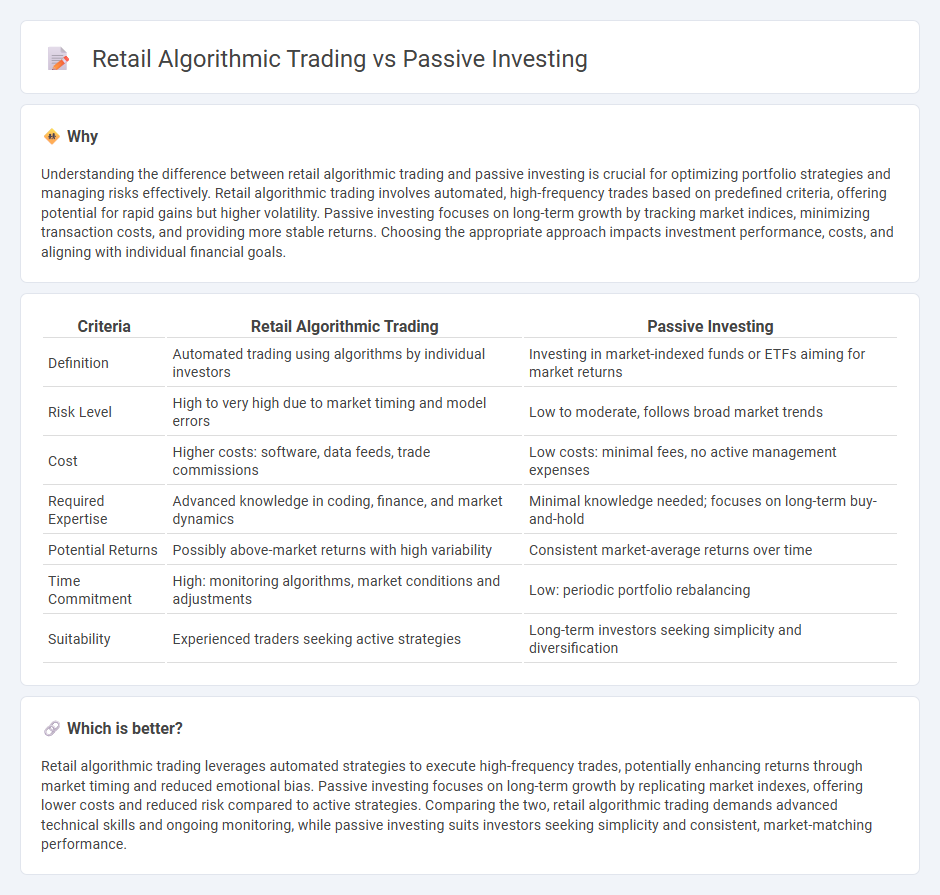
Understanding the difference between retail algorithmic trading and passive investing is crucial for optimizing portfolio strategies and managing risks effectively. Retail algorithmic trading involves automated, high-frequency trades based on predefined criteria, offering potential for rapid gains but higher volatility. Passive investing focuses on long-term growth by tracking market indices, minimizing transaction costs, and providing more stable returns. Choosing the appropriate approach impacts investment performance, costs, and aligning with individual financial goals.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Retail Algorithmic Trading | Passive Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading using algorithms by individual investors | Investing in market-indexed funds or ETFs aiming for market returns |
| Risk Level | High to very high due to market timing and model errors | Low to moderate, follows broad market trends |
| Cost | Higher costs: software, data feeds, trade commissions | Low costs: minimal fees, no active management expenses |
| Required Expertise | Advanced knowledge in coding, finance, and market dynamics | Minimal knowledge needed; focuses on long-term buy-and-hold |
| Potential Returns | Possibly above-market returns with high variability | Consistent market-average returns over time |
| Time Commitment | High: monitoring algorithms, market conditions and adjustments | Low: periodic portfolio rebalancing |
| Suitability | Experienced traders seeking active strategies | Long-term investors seeking simplicity and diversification |
Which is better?
Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated strategies to execute high-frequency trades, potentially enhancing returns through market timing and reduced emotional bias. Passive investing focuses on long-term growth by replicating market indexes, offering lower costs and reduced risk compared to active strategies. Comparing the two, retail algorithmic trading demands advanced technical skills and ongoing monitoring, while passive investing suits investors seeking simplicity and consistent, market-matching performance.
Connection
Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated systems to execute trades based on predefined criteria, enhancing efficiency and reducing emotional bias. Passive investing focuses on replicating market indices to achieve steady growth with minimal active management. Both strategies utilize algorithmic processes to optimize portfolio performance while minimizing transaction costs and human intervention.
Key Terms
Index Funds
Index funds represent a core strategy in passive investing, offering diversified exposure to market benchmarks with minimal management fees. Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated systems and data-driven strategies to execute trades, often seeking short-term market inefficiencies. Explore how combining these approaches can optimize portfolio performance and risk management.
Automated Trading Systems
Automated Trading Systems (ATS) play a crucial role in retail algorithmic trading by executing pre-programmed instructions at high speeds to capitalize on market opportunities, contrasting with passive investing's long-term, low-maintenance approach that tracks market indices. Retail algorithmic trading leverages ATS for their ability to analyze vast data sets and implement quantitative strategies with minimal human intervention, enhancing trade precision and response times. Explore the advantages and mechanisms of ATS in revolutionizing retail algorithmic trading for a deeper understanding.
Liquidity
Passive investing relies on broad market indices and offers high liquidity due to continuous trading of large-cap securities, enabling quick entry and exit. Retail algorithmic trading may experience variable liquidity depending on strategy and market conditions, with algorithms exploiting short-term price disparities. Explore in-depth liquidity dynamics for both methods to enhance your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
What is Passive Investing & How it Works? - Passive investing is a long-term strategy focusing on buying and holding a diversified portfolio that mimics a market index, aiming to build wealth gradually while minimizing transaction costs and management fees compared to active investing.
Passive management - Passive investing tracks market-weighted indexes through vehicles like index funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and index futures, aiming to replicate index returns with low fees and minimal trading activity.
Active vs. Passive Investing - Passive investing involves a "buy and hold" approach that leverages the market's long-term upward trend, primarily through index funds, requiring less hands-on management compared to the frequent trading seen in active investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com