Synthetic assets replicate the price movements of real financial instruments without requiring ownership of the underlying assets, offering traders flexibility and diversified exposure. Spot contracts involve the immediate purchase or sale of an asset at current market prices, facilitating straightforward and transparent transactions. Explore deeper insights into how synthetic assets and spot contracts can enhance your investment strategy.
Why it is important
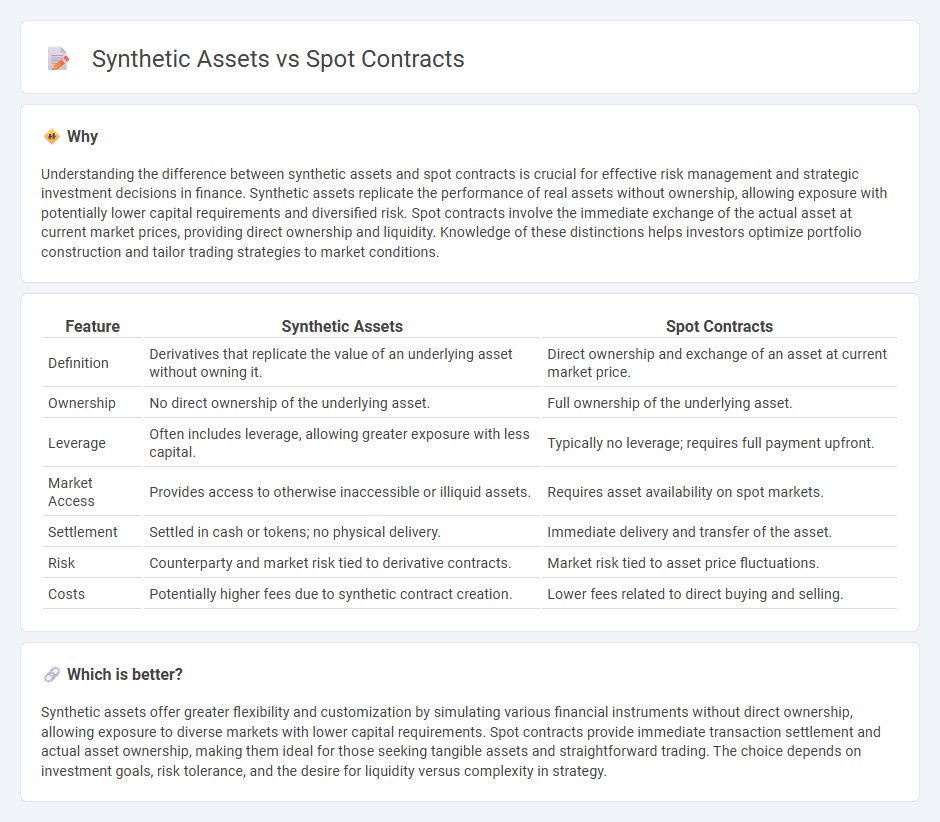
Understanding the difference between synthetic assets and spot contracts is crucial for effective risk management and strategic investment decisions in finance. Synthetic assets replicate the performance of real assets without ownership, allowing exposure with potentially lower capital requirements and diversified risk. Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of the actual asset at current market prices, providing direct ownership and liquidity. Knowledge of these distinctions helps investors optimize portfolio construction and tailor trading strategies to market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Synthetic Assets | Spot Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivatives that replicate the value of an underlying asset without owning it. | Direct ownership and exchange of an asset at current market price. |
| Ownership | No direct ownership of the underlying asset. | Full ownership of the underlying asset. |
| Leverage | Often includes leverage, allowing greater exposure with less capital. | Typically no leverage; requires full payment upfront. |
| Market Access | Provides access to otherwise inaccessible or illiquid assets. | Requires asset availability on spot markets. |
| Settlement | Settled in cash or tokens; no physical delivery. | Immediate delivery and transfer of the asset. |
| Risk | Counterparty and market risk tied to derivative contracts. | Market risk tied to asset price fluctuations. |
| Costs | Potentially higher fees due to synthetic contract creation. | Lower fees related to direct buying and selling. |
Which is better?
Synthetic assets offer greater flexibility and customization by simulating various financial instruments without direct ownership, allowing exposure to diverse markets with lower capital requirements. Spot contracts provide immediate transaction settlement and actual asset ownership, making them ideal for those seeking tangible assets and straightforward trading. The choice depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and the desire for liquidity versus complexity in strategy.
Connection
Synthetic assets replicate the value and performance of underlying financial instruments without requiring actual ownership, enabling investors to gain exposure to various markets such as stocks, commodities, or cryptocurrencies. Spot contracts involve the immediate purchase or sale of these underlying assets at current market prices, providing direct market access and liquidity. The connection lies in synthetic assets using spot contracts as reference points for pricing and settlement, allowing traders to hedge risks or speculate efficiently without holding the physical asset.
Key Terms
Underlying asset
Spot contracts involve the direct purchase or sale of the underlying asset, ensuring immediate ownership transfer and settlement based on the asset's current market price. Synthetic assets replicate the performance of the underlying asset through derivatives or financial instruments without requiring actual ownership, offering flexibility in exposure and risk management. Explore the key differences and applications of spot contracts and synthetic assets to enhance your trading strategy.
Derivative
Spot contracts involve the immediate purchase or sale of an asset at the current market price, ensuring direct ownership transfer without future obligations. Synthetic assets, created through derivatives such as options and futures, replicate the price movements of underlying assets without actual ownership, enabling strategic exposure and hedging. Explore deeper insights into derivative instruments to optimize trading strategies and risk management.
Settlement
Spot contracts involve the immediate settlement of asset transactions, typically within two business days, ensuring the actual delivery of the underlying asset. Synthetic assets, created through derivatives or smart contracts, settle based on the asset's price without transferring ownership, enabling exposure without physical delivery. Explore the nuances of settlement mechanisms to understand how these financial instruments impact risk and liquidity management.
Source and External Links
Spot contract - Wikipedia - A spot contract is a financial agreement to buy or sell a commodity, security, or currency for immediate settlement, typically within two business days, contrasting with forward or futures contracts which settle in the future.
What is Spot contract - Capital.com - Spot contracts are "buy now, pay now" deals mostly used in foreign exchange and commodities markets, involving immediate delivery and payment at the spot price, unlike futures or forward contracts settled later.
Forward Contracts Spot Contracts - TD Securities - A spot contract is an agreement to buy or sell currency at the current spot exchange rate with settlement usually within two business days, offering liquidity and price transparency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com