Retail algorithmic trading uses computer algorithms to execute trades automatically based on predefined criteria, enabling faster and more efficient market participation. In contrast, arbitrage trading exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to generate risk-free profits by simultaneously buying low and selling high. Explore in-depth comparisons and strategies to enhance your trading expertise.
Why it is important
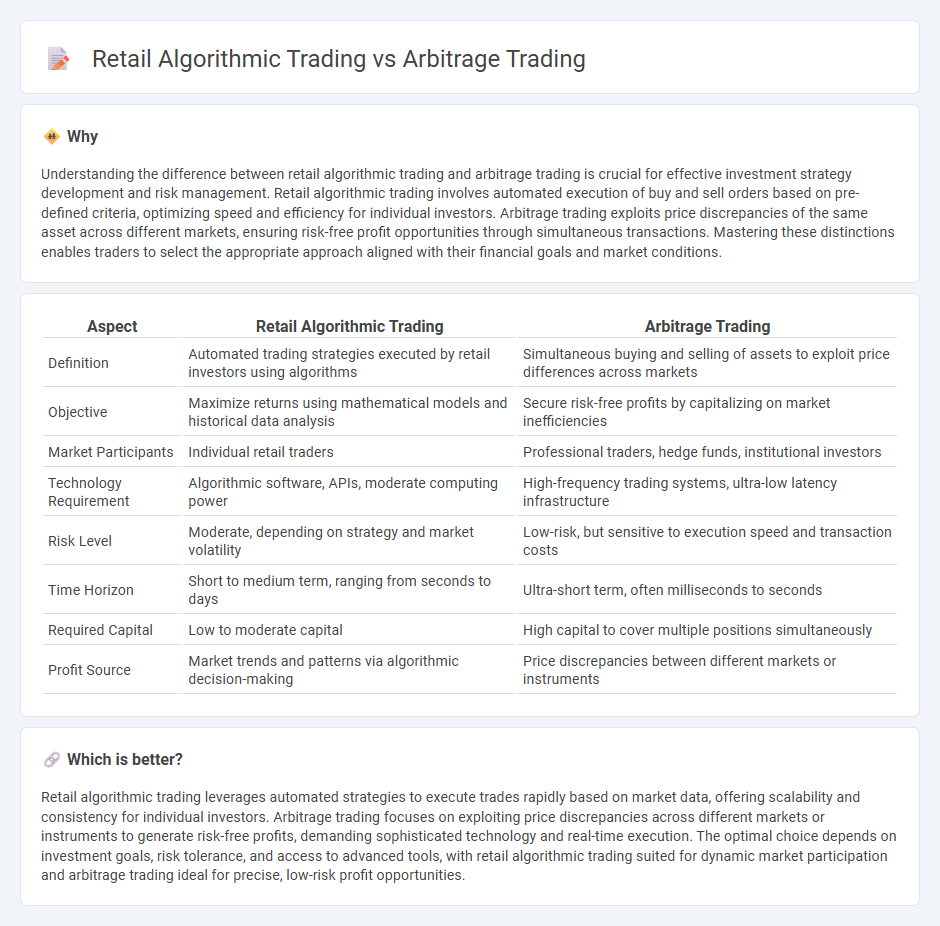
Understanding the difference between retail algorithmic trading and arbitrage trading is crucial for effective investment strategy development and risk management. Retail algorithmic trading involves automated execution of buy and sell orders based on pre-defined criteria, optimizing speed and efficiency for individual investors. Arbitrage trading exploits price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets, ensuring risk-free profit opportunities through simultaneous transactions. Mastering these distinctions enables traders to select the appropriate approach aligned with their financial goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Retail Algorithmic Trading | Arbitrage Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading strategies executed by retail investors using algorithms | Simultaneous buying and selling of assets to exploit price differences across markets |
| Objective | Maximize returns using mathematical models and historical data analysis | Secure risk-free profits by capitalizing on market inefficiencies |
| Market Participants | Individual retail traders | Professional traders, hedge funds, institutional investors |
| Technology Requirement | Algorithmic software, APIs, moderate computing power | High-frequency trading systems, ultra-low latency infrastructure |
| Risk Level | Moderate, depending on strategy and market volatility | Low-risk, but sensitive to execution speed and transaction costs |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, ranging from seconds to days | Ultra-short term, often milliseconds to seconds |
| Required Capital | Low to moderate capital | High capital to cover multiple positions simultaneously |
| Profit Source | Market trends and patterns via algorithmic decision-making | Price discrepancies between different markets or instruments |
Which is better?
Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated strategies to execute trades rapidly based on market data, offering scalability and consistency for individual investors. Arbitrage trading focuses on exploiting price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to generate risk-free profits, demanding sophisticated technology and real-time execution. The optimal choice depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and access to advanced tools, with retail algorithmic trading suited for dynamic market participation and arbitrage trading ideal for precise, low-risk profit opportunities.
Connection
Retail algorithmic trading and arbitrage trading are connected through their reliance on automated systems to identify and exploit market inefficiencies. Both strategies use algorithmic models to execute trades at high speeds, targeting price discrepancies across different markets or asset classes for profit. The integration of real-time data analytics and machine learning enhances the precision and profitability of these trading approaches in retail finance.
Key Terms
**Arbitrage Trading:**
Arbitrage trading exploits price discrepancies of identical or similar assets across different markets or exchanges, enabling traders to profit from risk-free price differentials. Key strategies include spatial arbitrage, triangular arbitrage, and statistical arbitrage, each relying on high-speed execution and advanced algorithms to capitalize on fleeting opportunities. Discover more about how arbitrage trading leverages market inefficiencies to drive consistent returns.
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage trading exploits price discrepancies between different markets or instruments by simultaneously buying low and selling high to secure risk-free profits. Retail algorithmic trading often uses automated strategies to identify and capitalize on short-term price inefficiencies, though it faces challenges like latency and transaction costs. Explore more on how these approaches leverage price discrepancies to maximize returns.
Market Efficiency
Arbitrage trading exploits price discrepancies across different markets to achieve risk-free profits, directly contributing to market efficiency by narrowing price gaps and ensuring asset prices reflect true values. Retail algorithmic trading uses automated strategies based on technical and fundamental data to optimize trade execution and capture small market inefficiencies, enhancing liquidity and price discovery. Explore further to understand how these approaches impact market dynamics and efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Arbitrage in Investing? (Risks, Types and Examples) - Indeed - Arbitrage is a financial process of simultaneously selling and buying the same asset in two different markets to profit from price differences, typically executed within seconds using algorithms or software to identify discrepancies.
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences of the same asset in different markets simultaneously to avoid market risk, with conditions requiring equality of prices across markets and highlighting the importance of simultaneous transactions to prevent exposure.
What is Arbitrage? | Definition, Calculation and Example - IG - Arbitrage trading is the practice of simultaneously buying and selling an asset to capitalize on price inefficiencies, with speed being critical for success and examples including trades across different exchanges exploiting small price differences.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com