Climate-linked derivatives offer financial instruments that hedge risks associated with climate change by tying payouts to environmental variables such as temperature or carbon emissions. Responsible investment funds prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, channeling capital into companies with sustainable practices to promote long-term value. Explore deeper insights on how these finance innovations drive sustainable growth and risk management.
Why it is important
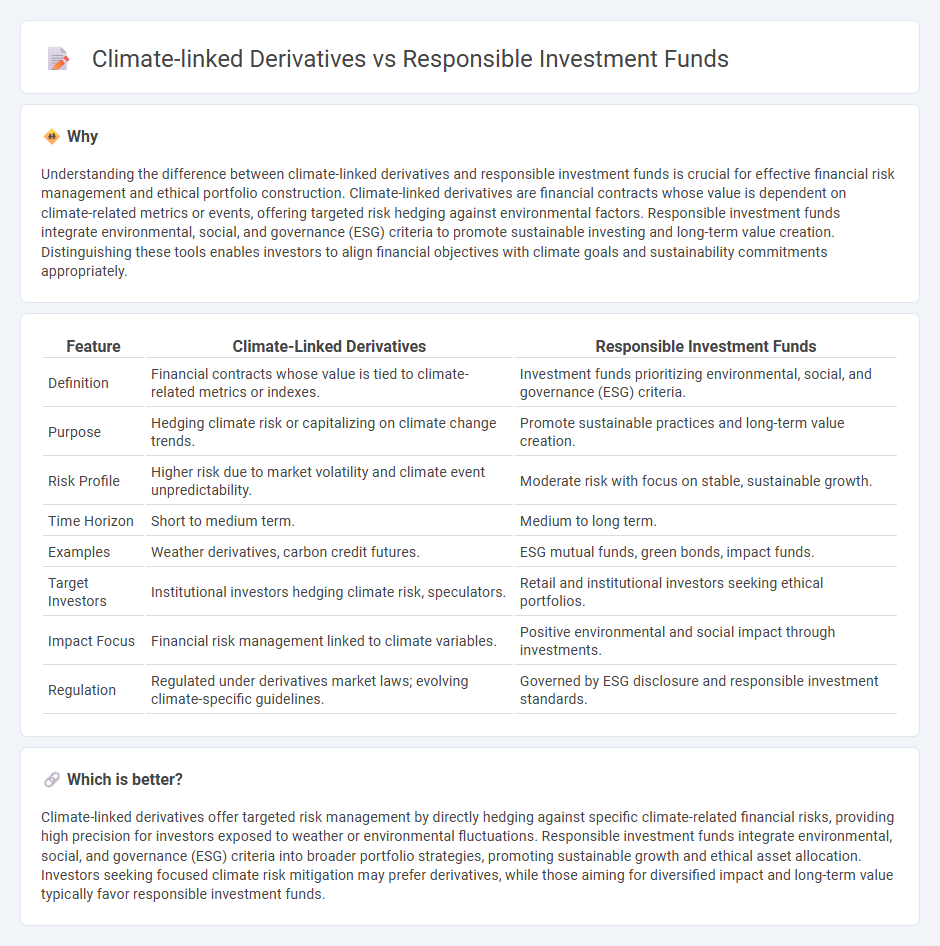
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and responsible investment funds is crucial for effective financial risk management and ethical portfolio construction. Climate-linked derivatives are financial contracts whose value is dependent on climate-related metrics or events, offering targeted risk hedging against environmental factors. Responsible investment funds integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote sustainable investing and long-term value creation. Distinguishing these tools enables investors to align financial objectives with climate goals and sustainability commitments appropriately.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Climate-Linked Derivatives | Responsible Investment Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial contracts whose value is tied to climate-related metrics or indexes. | Investment funds prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. |
| Purpose | Hedging climate risk or capitalizing on climate change trends. | Promote sustainable practices and long-term value creation. |
| Risk Profile | Higher risk due to market volatility and climate event unpredictability. | Moderate risk with focus on stable, sustainable growth. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term. | Medium to long term. |
| Examples | Weather derivatives, carbon credit futures. | ESG mutual funds, green bonds, impact funds. |
| Target Investors | Institutional investors hedging climate risk, speculators. | Retail and institutional investors seeking ethical portfolios. |
| Impact Focus | Financial risk management linked to climate variables. | Positive environmental and social impact through investments. |
| Regulation | Regulated under derivatives market laws; evolving climate-specific guidelines. | Governed by ESG disclosure and responsible investment standards. |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer targeted risk management by directly hedging against specific climate-related financial risks, providing high precision for investors exposed to weather or environmental fluctuations. Responsible investment funds integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into broader portfolio strategies, promoting sustainable growth and ethical asset allocation. Investors seeking focused climate risk mitigation may prefer derivatives, while those aiming for diversified impact and long-term value typically favor responsible investment funds.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives enable investors to hedge financial risks associated with climate change, enhancing portfolio resilience. Responsible investment funds integrate these derivatives to align investment strategies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This synergy supports sustainable finance by mitigating climate-related risks while promoting long-term value creation.
Key Terms
**Responsible investment funds:**
Responsible investment funds prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate sustainable, long-term financial returns while fostering positive societal impact. These funds integrate ESG factors into the investment process, targeting companies with strong sustainability practices and mitigating risks related to climate change and corporate responsibility. Explore how responsible investment funds can align your portfolio with global sustainability goals and ethical investing principles.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Responsible investment funds integrate ESG criteria directly into portfolio management, aiming to generate sustainable financial returns while supporting environmental, social, and governance goals. Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge or speculate on climate-related risks, offering dynamic risk management aligned with sustainability objectives. Explore how these financial tools shape ESG investing and mitigate climate impact effectively.
Screening
Responsible investment funds employ screening techniques such as exclusionary, positive, and norms-based screening to filter out companies with poor environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, ensuring alignment with sustainable and ethical criteria. Climate-linked derivatives, in contrast, use screening methods centered on climate risk metrics and indices to create financial instruments that hedge or gain exposure to temperature changes, carbon prices, or extreme weather events. Explore deeper insights into how screening mechanisms drive sustainable finance strategies in both asset management and risk mitigation contexts.
Source and External Links
Responsible investing - Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors with financial criteria to achieve long-term, resilient returns while managing risks such as climate impact and diversity, exemplified by organizations like TIAA committed to net zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Socially Responsible Investing - Socially responsible investing (SRI) aligns investment choices with personal values by targeting companies with strong ESG practices and avoiding those with poor social or environmental records, supported by rating systems like Green America's Heart Rating for mutual funds.
What is responsible investment? - Responsible investment involves incorporating ESG considerations into investment decisions and active ownership, aiming not only for financial returns but also positive social and environmental outcomes, guided by principles that promote ESG integration, transparency, and stewardship across the investment industry.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com