Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) offer a streamlined path for private companies to go public through a merger with a publicly listed shell company, bypassing the traditional IPO process. Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) enable startups to raise capital by issuing digital tokens on blockchain platforms, attracting investors seeking early access to innovative projects. Explore the distinctive mechanisms and regulatory landscapes of SPACs and ICOs to understand their roles in modern finance.
Why it is important
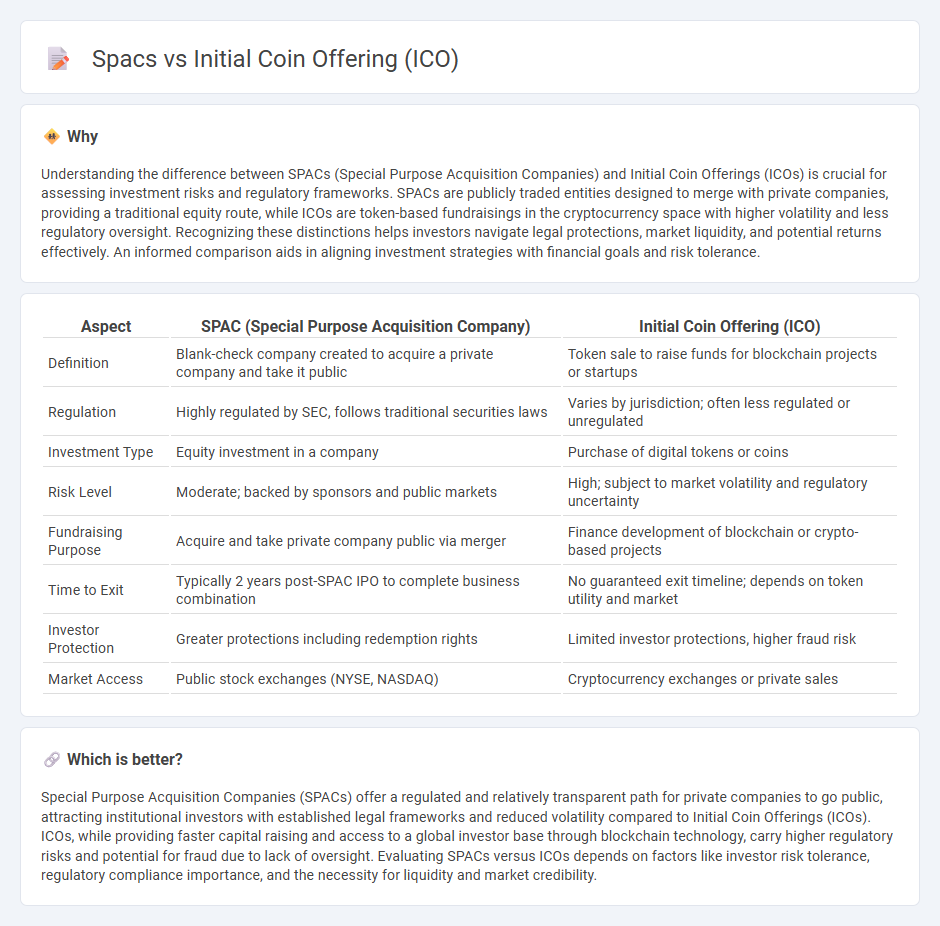
Understanding the difference between SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) is crucial for assessing investment risks and regulatory frameworks. SPACs are publicly traded entities designed to merge with private companies, providing a traditional equity route, while ICOs are token-based fundraisings in the cryptocurrency space with higher volatility and less regulatory oversight. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors navigate legal protections, market liquidity, and potential returns effectively. An informed comparison aids in aligning investment strategies with financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | SPAC (Special Purpose Acquisition Company) | Initial Coin Offering (ICO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blank-check company created to acquire a private company and take it public | Token sale to raise funds for blockchain projects or startups |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by SEC, follows traditional securities laws | Varies by jurisdiction; often less regulated or unregulated |
| Investment Type | Equity investment in a company | Purchase of digital tokens or coins |
| Risk Level | Moderate; backed by sponsors and public markets | High; subject to market volatility and regulatory uncertainty |
| Fundraising Purpose | Acquire and take private company public via merger | Finance development of blockchain or crypto-based projects |
| Time to Exit | Typically 2 years post-SPAC IPO to complete business combination | No guaranteed exit timeline; depends on token utility and market |
| Investor Protection | Greater protections including redemption rights | Limited investor protections, higher fraud risk |
| Market Access | Public stock exchanges (NYSE, NASDAQ) | Cryptocurrency exchanges or private sales |
Which is better?
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) offer a regulated and relatively transparent path for private companies to go public, attracting institutional investors with established legal frameworks and reduced volatility compared to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). ICOs, while providing faster capital raising and access to a global investor base through blockchain technology, carry higher regulatory risks and potential for fraud due to lack of oversight. Evaluating SPACs versus ICOs depends on factors like investor risk tolerance, regulatory compliance importance, and the necessity for liquidity and market credibility.
Connection
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are both innovative fundraising mechanisms reshaping finance by enabling companies to access capital markets outside traditional initial public offerings (IPOs). SPACs provide a faster route to public markets through a shell company merger, while ICOs utilize blockchain technology to raise funds by issuing digital tokens. Both methods attract speculative investment and regulatory scrutiny due to their potential for high returns and associated risks.
Key Terms
Tokenization
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) enable startups to raise capital by issuing digital tokens on blockchain networks, providing liquidity and fractional ownership through tokenization. Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) offer an alternative route to public markets via shell companies but lack the direct asset tokenization and decentralized features inherent in ICOs. Explore the transformative potential of tokenization in capital markets and how it reshapes fundraising strategies.
Shell Company
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) enable startups to raise capital by issuing digital tokens, whereas Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) act as shell companies formed to acquire or merge with existing firms, facilitating private companies' public market entry. SPACs provide a faster, more regulated path to public listing compared to ICOs, which face regulatory scrutiny and market volatility. Explore the distinct roles and regulatory environments of ICOs and SPACs in modern fundraising strategies.
Fundraising
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) leverage blockchain technology to raise capital quickly by issuing digital tokens directly to investors, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries. Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) provide an alternative fundraising method by allowing private companies to go public through a blank-check company, facilitating access to broader capital markets with regulatory oversight. Explore how these distinct mechanisms impact fundraising efficiency and investor opportunities in evolving financial landscapes.
Source and External Links
What are Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and how do they work? - Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are a cryptocurrency fundraising method where new tokens are distributed to participants, functioning similarly to initial public offerings (IPOs) but carry higher regulatory risks.
Initial coin offering - Wikipedia - ICOs are a type of crowdfunding in cryptocurrencies where tokens are sold to investors for capital, often avoiding traditional financial regulations but posing significant risks and a high failure rate for projects.
Initial Coin Offering (ICO) - Definition, Examples, Types - ICOs involve a company raising capital by creating and selling blockchain tokens that usually provide utility in a project rather than equity, requiring technology, legal, and financial knowledge to execute.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com