Quantitative tightening reduces the money supply by selling government bonds, while reserve requirements mandate the minimum reserves banks must hold, affecting lending capacity. Both tools are crucial for controlling inflation and stabilizing the economy through monetary policy. Explore these mechanisms to understand their impact on financial markets and economic growth.
Why it is important
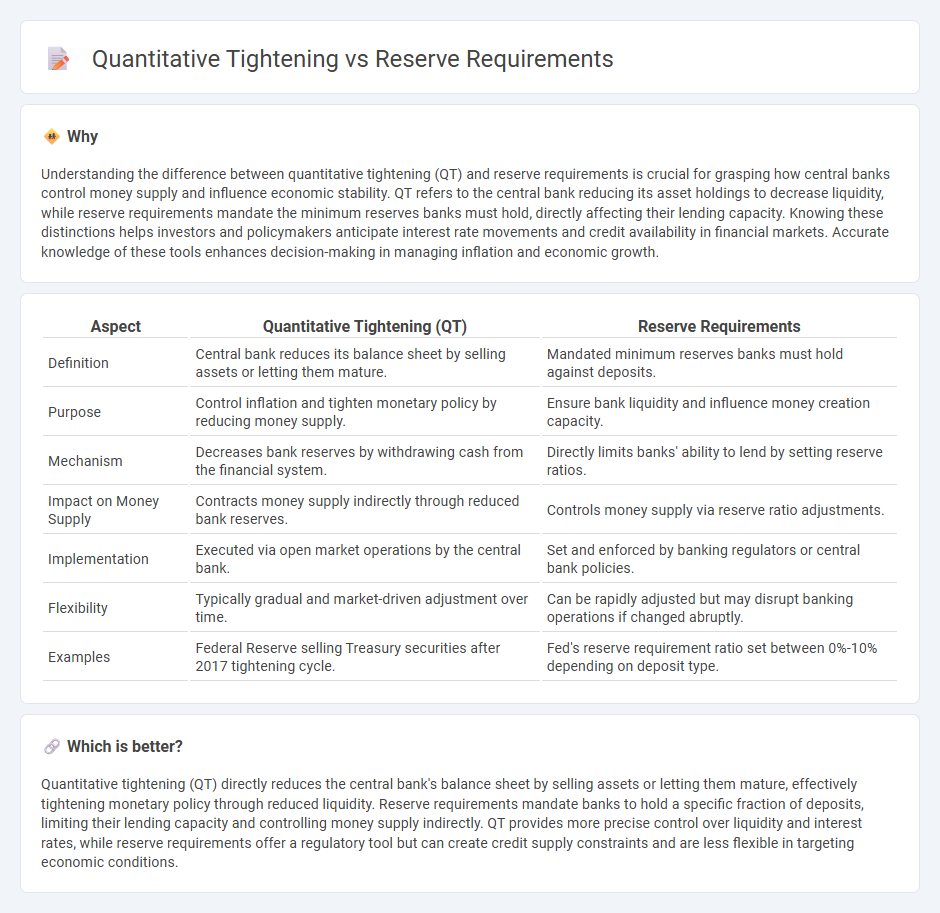
Understanding the difference between quantitative tightening (QT) and reserve requirements is crucial for grasping how central banks control money supply and influence economic stability. QT refers to the central bank reducing its asset holdings to decrease liquidity, while reserve requirements mandate the minimum reserves banks must hold, directly affecting their lending capacity. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and policymakers anticipate interest rate movements and credit availability in financial markets. Accurate knowledge of these tools enhances decision-making in managing inflation and economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Tightening (QT) | Reserve Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank reduces its balance sheet by selling assets or letting them mature. | Mandated minimum reserves banks must hold against deposits. |
| Purpose | Control inflation and tighten monetary policy by reducing money supply. | Ensure bank liquidity and influence money creation capacity. |
| Mechanism | Decreases bank reserves by withdrawing cash from the financial system. | Directly limits banks' ability to lend by setting reserve ratios. |
| Impact on Money Supply | Contracts money supply indirectly through reduced bank reserves. | Controls money supply via reserve ratio adjustments. |
| Implementation | Executed via open market operations by the central bank. | Set and enforced by banking regulators or central bank policies. |
| Flexibility | Typically gradual and market-driven adjustment over time. | Can be rapidly adjusted but may disrupt banking operations if changed abruptly. |
| Examples | Federal Reserve selling Treasury securities after 2017 tightening cycle. | Fed's reserve requirement ratio set between 0%-10% depending on deposit type. |
Which is better?
Quantitative tightening (QT) directly reduces the central bank's balance sheet by selling assets or letting them mature, effectively tightening monetary policy through reduced liquidity. Reserve requirements mandate banks to hold a specific fraction of deposits, limiting their lending capacity and controlling money supply indirectly. QT provides more precise control over liquidity and interest rates, while reserve requirements offer a regulatory tool but can create credit supply constraints and are less flexible in targeting economic conditions.
Connection
Quantitative tightening reduces the money supply by selling government securities or allowing them to mature, which directly impacts bank reserves. Reserve requirements dictate the minimum reserves banks must hold, influencing how much money banks can lend out, thereby affecting liquidity and credit availability. The interplay between quantitative tightening and reserve requirements shapes overall financial conditions by constraining or expanding bank lending capacity.
Key Terms
Central Bank Reserves
Reserve requirements mandate banks to hold a specific percentage of deposits as central bank reserves, directly influencing liquidity and credit availability in the economy. Quantitative tightening involves the central bank reducing its balance sheet by selling securities or letting them mature, which indirectly decreases reserve levels and tightens monetary conditions. Explore the detailed mechanisms and impacts of these tools on central bank reserves and economic policy.
Money Supply
Reserve requirements directly influence the money supply by dictating the minimum reserves banks must hold, thereby controlling their lending capacity and impacting overall liquidity. Quantitative tightening reduces money supply by central banks selling assets or letting them mature, which withdraws excess reserves from the banking system. Explore how these monetary policy tools shape economic stability and inflation management.
Interest Rates
Reserve requirements directly influence the amount of funds banks must hold, impacting liquidity and thus short-term interest rates by restricting or freeing up capital for lending. Quantitative tightening reduces central bank balance sheets by selling securities or letting them mature, leading to higher long-term interest rates through decreased market liquidity. Explore the effects of these monetary tools on interest rates to better understand their role in financial policy.
Source and External Links
Reserve Requirements | Economics Definition + Examples - Reserve requirements are central bank regulations that mandate a percentage of a depository institution's cash to be kept on hand rather than being lent or invested.
Reserve requirement - Reserve requirements are central bank regulations that set the minimum liquid assets a commercial bank must hold, often determined by a proportion of deposit liabilities.
History, Current Practice, and Potential Reform - This document discusses the history and current practices of reserve requirements in the context of monetary policy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com