Quantitative tightening involves reducing the central bank's balance sheet by selling assets or letting them mature, aiming to tighten monetary conditions and control inflation. Operation Twist refers to a specific policy where the central bank buys long-term securities while selling short-term ones to lower long-term interest rates without changing the overall balance sheet size. Explore more to understand how these tools influence financial markets and economic growth.
Why it is important
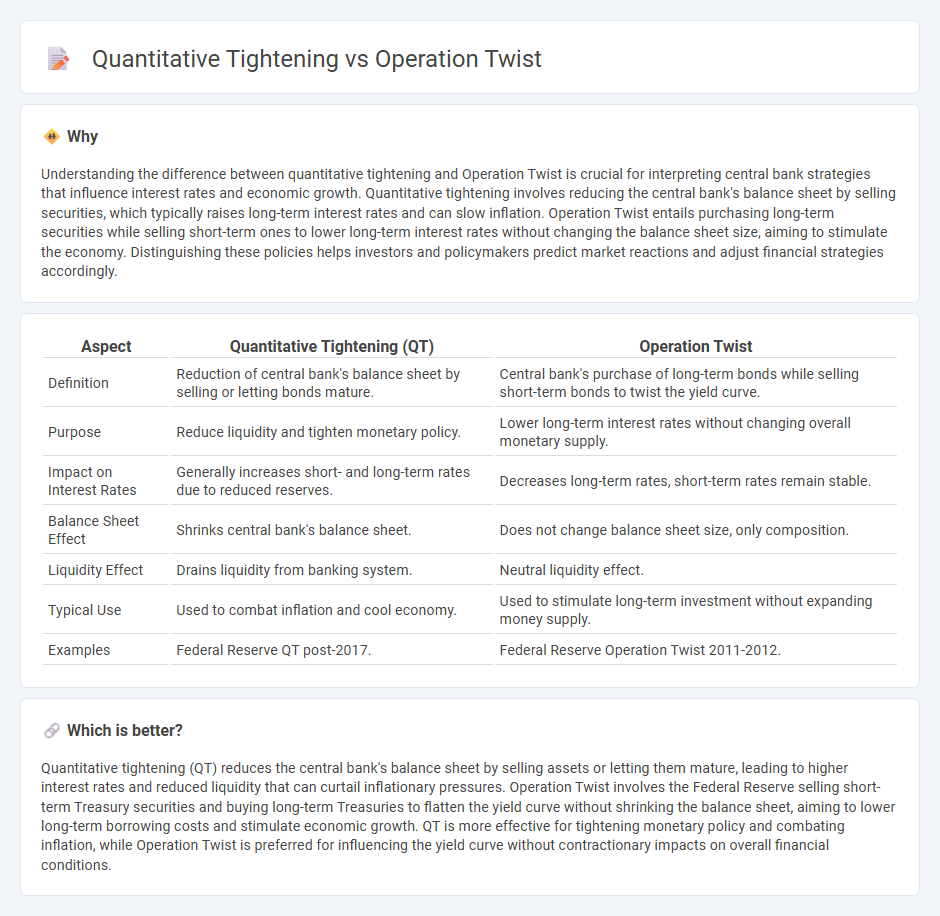
Understanding the difference between quantitative tightening and Operation Twist is crucial for interpreting central bank strategies that influence interest rates and economic growth. Quantitative tightening involves reducing the central bank's balance sheet by selling securities, which typically raises long-term interest rates and can slow inflation. Operation Twist entails purchasing long-term securities while selling short-term ones to lower long-term interest rates without changing the balance sheet size, aiming to stimulate the economy. Distinguishing these policies helps investors and policymakers predict market reactions and adjust financial strategies accordingly.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Tightening (QT) | Operation Twist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction of central bank's balance sheet by selling or letting bonds mature. | Central bank's purchase of long-term bonds while selling short-term bonds to twist the yield curve. |
| Purpose | Reduce liquidity and tighten monetary policy. | Lower long-term interest rates without changing overall monetary supply. |
| Impact on Interest Rates | Generally increases short- and long-term rates due to reduced reserves. | Decreases long-term rates, short-term rates remain stable. |
| Balance Sheet Effect | Shrinks central bank's balance sheet. | Does not change balance sheet size, only composition. |
| Liquidity Effect | Drains liquidity from banking system. | Neutral liquidity effect. |
| Typical Use | Used to combat inflation and cool economy. | Used to stimulate long-term investment without expanding money supply. |
| Examples | Federal Reserve QT post-2017. | Federal Reserve Operation Twist 2011-2012. |
Which is better?
Quantitative tightening (QT) reduces the central bank's balance sheet by selling assets or letting them mature, leading to higher interest rates and reduced liquidity that can curtail inflationary pressures. Operation Twist involves the Federal Reserve selling short-term Treasury securities and buying long-term Treasuries to flatten the yield curve without shrinking the balance sheet, aiming to lower long-term borrowing costs and stimulate economic growth. QT is more effective for tightening monetary policy and combating inflation, while Operation Twist is preferred for influencing the yield curve without contractionary impacts on overall financial conditions.
Connection
Quantitative tightening (QT) reduces the Federal Reserve's balance sheet by selling or allowing bonds to mature, which increases long-term interest rates and tightens financial conditions. Operation Twist involves the Fed buying long-term Treasuries while selling short-term securities to flatten the yield curve without changing the overall balance sheet size. Both strategies influence interest rate dynamics and monetary policy transmission by altering the supply and demand across different maturities of government debt.
Key Terms
Yield Curve
Operation Twist involves the Federal Reserve buying long-term Treasury securities while selling short-term ones to flatten the yield curve and stimulate economic growth. Quantitative tightening reduces the Fed's balance sheet by allowing securities to mature without reinvestment, generally leading to rising long-term yields and a steepening yield curve. Explore the detailed impacts of these monetary policies on the yield curve and financial markets.
Balance Sheet
Operation Twist involves selling short-term Treasury securities and purchasing long-term ones to reshape the Federal Reserve's balance sheet without changing its size, aiming to lower long-term interest rates. Quantitative tightening reduces the balance sheet by allowing securities to mature without reinvestment, decreasing the Fed's asset holdings and tightening monetary conditions. Explore the detailed impacts of these policies on financial markets and the economy.
Interest Rates
Operation Twist involves the Federal Reserve purchasing long-term Treasury securities while selling short-term ones to lower long-term interest rates and flatten the yield curve, aiming to stimulate economic growth without expanding the central bank's balance sheet. Quantitative tightening, in contrast, reduces the Fed's balance sheet by selling or letting mature securities, which tends to increase overall interest rates and tighten financial conditions. Explore the detailed impacts of these policies on interest rates and economic outlooks to understand their roles in monetary policy.
Source and External Links
History of Federal Open Market Committee actions - Wikipedia - Operation Twist was a Federal Reserve policy initiated in 1961 aimed at flattening the yield curve by selling short-term government debt and buying longer-term debt to lower long-term interest rates and promote capital inflows, though initially considered only marginally successful and later re-evaluated as more effective than first thought.
The Shout with Operation Twist - Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland - In 2011, the Federal Reserve implemented a version of Operation Twist by selling short-term Treasury securities and purchasing longer-term ones to lower long-term interest rates relative to short-term rates and support mortgage markets through adjusted reinvestment strategies.
Operation Twist and the Effect of Large-Scale Asset Purchases - Studies found that Operation Twist lowered long-term Treasury yields by about 13 to 16 basis points, confirming that the yield curve was twisted as intended, with spillover effects on agency and corporate bond yields as well.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com