Green bonds are fixed-income securities issued to fund environmentally friendly projects, offering investors a way to support sustainability. The greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, often reflected in lower yields. Explore the dynamics of greenium and green bonds to understand their impact on sustainable finance and investment strategies.
Why it is important
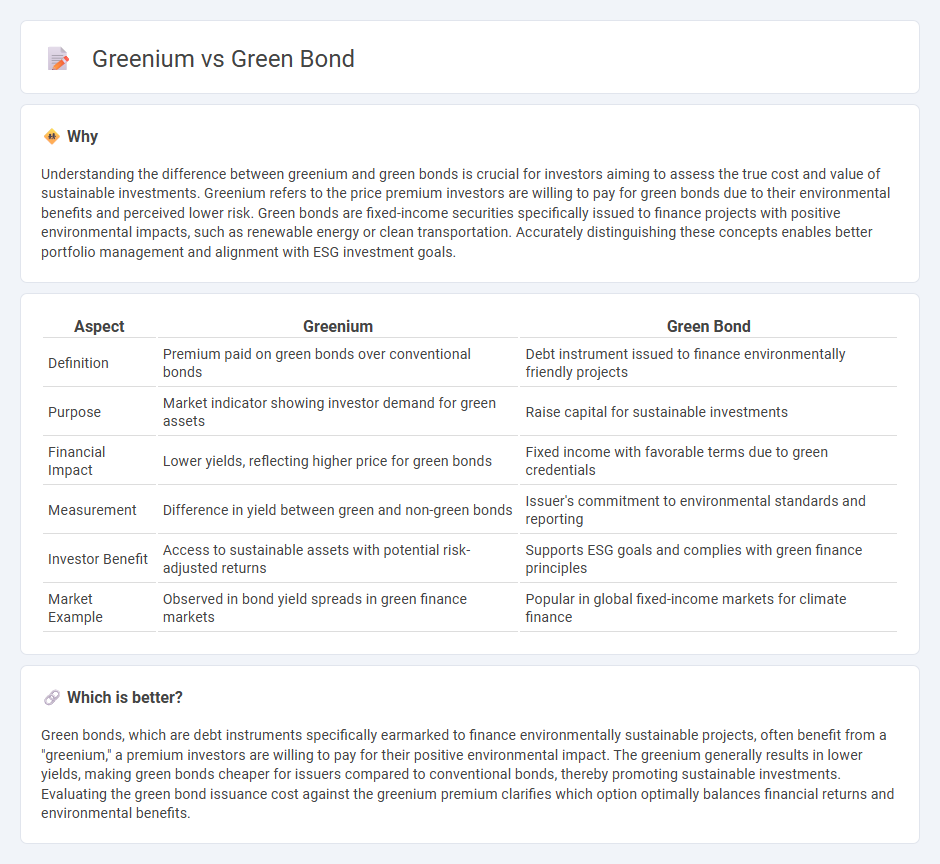
Understanding the difference between greenium and green bonds is crucial for investors aiming to assess the true cost and value of sustainable investments. Greenium refers to the price premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds due to their environmental benefits and perceived lower risk. Green bonds are fixed-income securities specifically issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or clean transportation. Accurately distinguishing these concepts enables better portfolio management and alignment with ESG investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenium | Green Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Premium paid on green bonds over conventional bonds | Debt instrument issued to finance environmentally friendly projects |
| Purpose | Market indicator showing investor demand for green assets | Raise capital for sustainable investments |
| Financial Impact | Lower yields, reflecting higher price for green bonds | Fixed income with favorable terms due to green credentials |
| Measurement | Difference in yield between green and non-green bonds | Issuer's commitment to environmental standards and reporting |
| Investor Benefit | Access to sustainable assets with potential risk-adjusted returns | Supports ESG goals and complies with green finance principles |
| Market Example | Observed in bond yield spreads in green finance markets | Popular in global fixed-income markets for climate finance |
Which is better?
Green bonds, which are debt instruments specifically earmarked to finance environmentally sustainable projects, often benefit from a "greenium," a premium investors are willing to pay for their positive environmental impact. The greenium generally results in lower yields, making green bonds cheaper for issuers compared to conventional bonds, thereby promoting sustainable investments. Evaluating the green bond issuance cost against the greenium premium clarifies which option optimally balances financial returns and environmental benefits.
Connection
Greenium refers to the pricing premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds due to their environmental benefits, resulting in lower yields compared to conventional bonds. Green bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or sustainable infrastructure. The connection lies in greenium reflecting investor demand and confidence in the environmental credentials and long-term value of green bonds.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Green bonds are debt instruments specifically issued to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, driving sustainability financing by attracting investors committed to eco-friendly initiatives. Greenium refers to the premium price investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, reflecting increased demand for sustainable investments and a lower yield for issuers. Explore the dynamics between green bonds and greenium to better understand their pivotal role in advancing global sustainability goals.
Yield
Green bonds typically offer competitive yields that reflect their environmentally friendly projects, while greenium represents the premium investors accept, often resulting in slightly lower yields due to higher demand for sustainable assets. The yield differential between standard bonds and green bonds, or greenium, highlights the market's valuation of environmental benefits alongside financial returns. Discover more about the impact of greenium on bond investment strategies and yield outcomes.
Premium
Green bonds are fixed-income securities designed to fund environmentally sustainable projects, offering investors a way to support eco-friendly initiatives. Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, driven by growing demand for sustainable investments and the positive environmental impact. Explore how the greenium influences bond pricing and market dynamics to understand the premium's role in green finance.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - A green bond is a fixed-income financial instrument used specifically to fund projects with positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, pollution control, and climate adaptation, enabling investors to support ESG goals while being repaid by the issuer.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles provide voluntary guidelines promoting transparency, disclosure, and integrity for financing environmentally sustainable projects that foster a net-zero emissions economy, ensuring investors can track the use and impact of green bond proceeds.
Green Bonds | International Finance Corporation (IFC) - IFC's green bonds mobilize private sector investment to combat climate change through climate-smart projects, having issued $14.8 billion in green bonds supporting renewable energy, clean transportation, and biodiversity conservation globally as of early 2025.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com