Tokenized treasuries leverage blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership and seamless trading, enhancing liquidity and transparency in government debt markets. Repo agreements, traditional short-term borrowing arrangements involving the sale and repurchase of securities, provide secured financing but lack the immediacy and traceability offered by tokenized assets. Explore the evolving landscape of finance by understanding the differences between tokenized treasuries and repo agreements.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between tokenized treasuries and repo agreements is crucial for managing liquidity and risk in financial markets. Tokenized treasuries represent digital ownership of government debt securities that can be traded on blockchain platforms, enhancing transparency and settlement speed. Repo agreements involve short-term borrowing using securities as collateral, impacting interest rates and market stability. Distinguishing these instruments helps investors optimize portfolio strategies and comply with regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
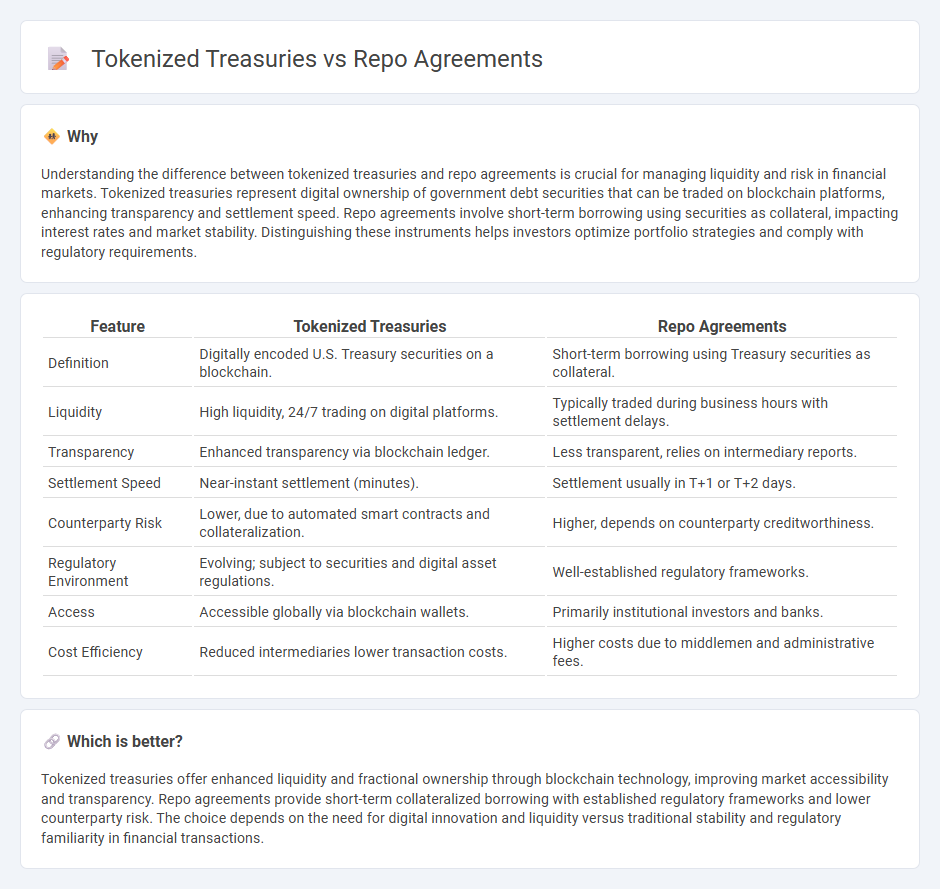
| Feature | Tokenized Treasuries | Repo Agreements |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally encoded U.S. Treasury securities on a blockchain. | Short-term borrowing using Treasury securities as collateral. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity, 24/7 trading on digital platforms. | Typically traded during business hours with settlement delays. |
| Transparency | Enhanced transparency via blockchain ledger. | Less transparent, relies on intermediary reports. |
| Settlement Speed | Near-instant settlement (minutes). | Settlement usually in T+1 or T+2 days. |
| Counterparty Risk | Lower, due to automated smart contracts and collateralization. | Higher, depends on counterparty creditworthiness. |
| Regulatory Environment | Evolving; subject to securities and digital asset regulations. | Well-established regulatory frameworks. |
| Access | Accessible globally via blockchain wallets. | Primarily institutional investors and banks. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced intermediaries lower transaction costs. | Higher costs due to middlemen and administrative fees. |
Which is better?
Tokenized treasuries offer enhanced liquidity and fractional ownership through blockchain technology, improving market accessibility and transparency. Repo agreements provide short-term collateralized borrowing with established regulatory frameworks and lower counterparty risk. The choice depends on the need for digital innovation and liquidity versus traditional stability and regulatory familiarity in financial transactions.
Connection
Tokenized treasuries enable the digitization of government debt instruments, allowing them to be traded more efficiently on blockchain platforms. Repo agreements use these tokenized treasuries as collateral, facilitating short-term borrowing with improved transparency and reduced settlement times. This integration enhances liquidity and streamlines the repo market by leveraging decentralized finance technology.
Key Terms
Collateral
Repo agreements involve short-term borrowing secured by collateral such as government bonds, providing liquidity with well-defined asset control and risk management. Tokenized treasuries use blockchain technology to represent ownership of treasury assets digitally, enabling fractionalization and enhanced transparency of collateral while reducing settlement friction. Explore the evolving landscape of collateral management through tokenized treasuries to understand their impact on market efficiency and risk mitigation.
Liquidity
Repo agreements provide short-term liquidity by allowing institutions to borrow cash using securities as collateral, ensuring quick access to funds without selling assets. Tokenized treasuries enhance liquidity through blockchain technology, enabling fractional ownership and 24/7 tradability of government securities in digital markets. Explore how these instruments redefine liquidity solutions in modern finance.
Settlement
Repo agreements facilitate short-term borrowing with collateral, typically involving the sale and repurchase of securities, enabling rapid settlement and enhancing liquidity in traditional financial markets. Tokenized treasuries leverage blockchain technology to represent ownership digitally, allowing near-instantaneous settlement, transparency, and reduced counterparty risk. Explore the intricacies of settlement processes in both models to understand their distinct advantages and potential integrations.
Source and External Links
Monitoring the Value of Securities in Repurchase Agreements - GFOA - A repo is a transaction where one party sells securities to another with a simultaneous agreement to repurchase them later at a higher price, with securities serving as collateral to manage default risk through margin maintenance.
1. What is a repo? - ICMA - A repo involves selling an asset and agreeing to buy it back later at a different price, functioning economically like secured lending where the asset acts as collateral to mitigate credit risk.
Repurchase agreement - Wikipedia - Repo transactions come in different forms such as specified delivery, tri-party, and hold-in-custody, with tri-party repos involving a third-party agent managing securities and payments to reduce risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com