Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) offers consumers the option to purchase goods immediately while deferring payments through interest-free installments, enhancing short-term affordability. Rent-to-Own (RTO) agreements allow customers to use and eventually own products by making periodic rental payments, often with higher overall costs due to fees and interest. Explore the key differences and financial implications between BNPL and RTO to make informed purchasing decisions.
Why it is important
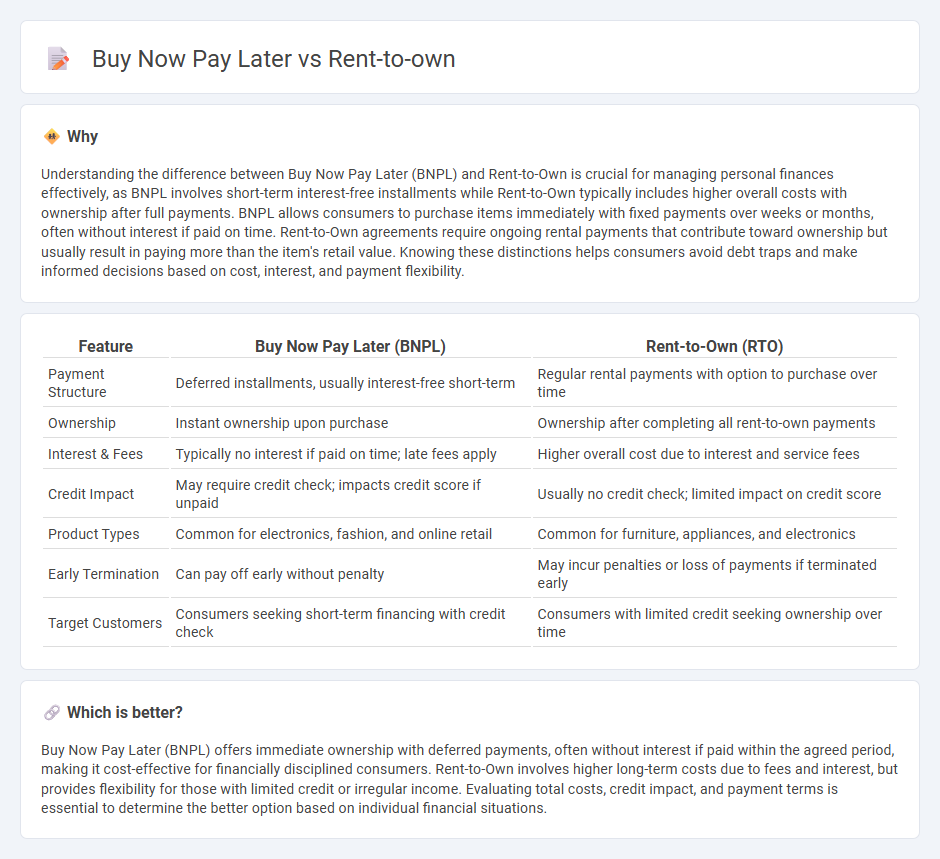
Understanding the difference between Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) and Rent-to-Own is crucial for managing personal finances effectively, as BNPL involves short-term interest-free installments while Rent-to-Own typically includes higher overall costs with ownership after full payments. BNPL allows consumers to purchase items immediately with fixed payments over weeks or months, often without interest if paid on time. Rent-to-Own agreements require ongoing rental payments that contribute toward ownership but usually result in paying more than the item's retail value. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers avoid debt traps and make informed decisions based on cost, interest, and payment flexibility.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) | Rent-to-Own (RTO) |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | Deferred installments, usually interest-free short-term | Regular rental payments with option to purchase over time |
| Ownership | Instant ownership upon purchase | Ownership after completing all rent-to-own payments |
| Interest & Fees | Typically no interest if paid on time; late fees apply | Higher overall cost due to interest and service fees |
| Credit Impact | May require credit check; impacts credit score if unpaid | Usually no credit check; limited impact on credit score |
| Product Types | Common for electronics, fashion, and online retail | Common for furniture, appliances, and electronics |
| Early Termination | Can pay off early without penalty | May incur penalties or loss of payments if terminated early |
| Target Customers | Consumers seeking short-term financing with credit check | Consumers with limited credit seeking ownership over time |
Which is better?
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) offers immediate ownership with deferred payments, often without interest if paid within the agreed period, making it cost-effective for financially disciplined consumers. Rent-to-Own involves higher long-term costs due to fees and interest, but provides flexibility for those with limited credit or irregular income. Evaluating total costs, credit impact, and payment terms is essential to determine the better option based on individual financial situations.
Connection
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) and Rent-to-Own (RTO) models both enable consumers to acquire products without immediate full payment, increasing purchasing power and cash flow flexibility. BNPL typically divides the purchase amount into interest-free installments over a short term, while RTO allows ownership after a series of rent payments over a longer period, often including interest or fees. Both financing options target consumers with limited upfront capital, impacting credit behavior and retail sales strategies.
Key Terms
Ownership
Rent-to-own agreements provide a clear path to ownership by allowing consumers to make installment payments on products like furniture or electronics until full ownership is achieved. Buy now pay later (BNPL) services offer short-term financing options without transferring ownership until the total amount is paid off, often leading to quicker access but no initial ownership rights. Explore the key differences in commitment and financial implications to decide which option fits your needs best.
Payment Structure
Rent-to-own involves regular rental payments with the option to purchase the item after a set period, often leading to ownership once all payments are complete. Buy now pay later divides the total purchase cost into installments without interest, typically due within a few months, but ownership is immediate. Explore more to understand which payment structure aligns best with your financial goals.
Interest/Fees
Rent-to-own agreements often carry higher interest rates and fees compared to traditional buy now pay later (BNPL) options, leading to increased overall costs for consumers. BNPL typically offers lower or zero-interest plans when payments are made on time, making it a more cost-effective choice for short-term financing. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which option aligns better with your financial goals and budget.
Source and External Links
How Does Rent-To-Own Work? - Rent-to-own allows tenants to rent a house or condo with an option or requirement to buy it later, combining leasing with a path to ownership.
Rent-to-own - Rent-to-own is a legally documented transaction leasing tangible property in exchange for payments, with an option to purchase during the lease, applying to goods and often real estate.
What You Need to Know About Rent-to-Own in Illinois | IL - Rent-to-own agreements can be lease-option or lease-purchase, allowing tenants to buy the home after a rental period but with risks like losing option fees or being obligated to buy depending on the agreement type.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com