Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain while maintaining security through on-chain data availability, significantly reducing network congestion and fees. Hybrid blockchain architectures combine public and private chains to leverage transparency and confidentiality, optimizing performance for enterprise applications. Explore the differences and benefits of these innovative solutions to transform your blockchain strategy.
Why it is important
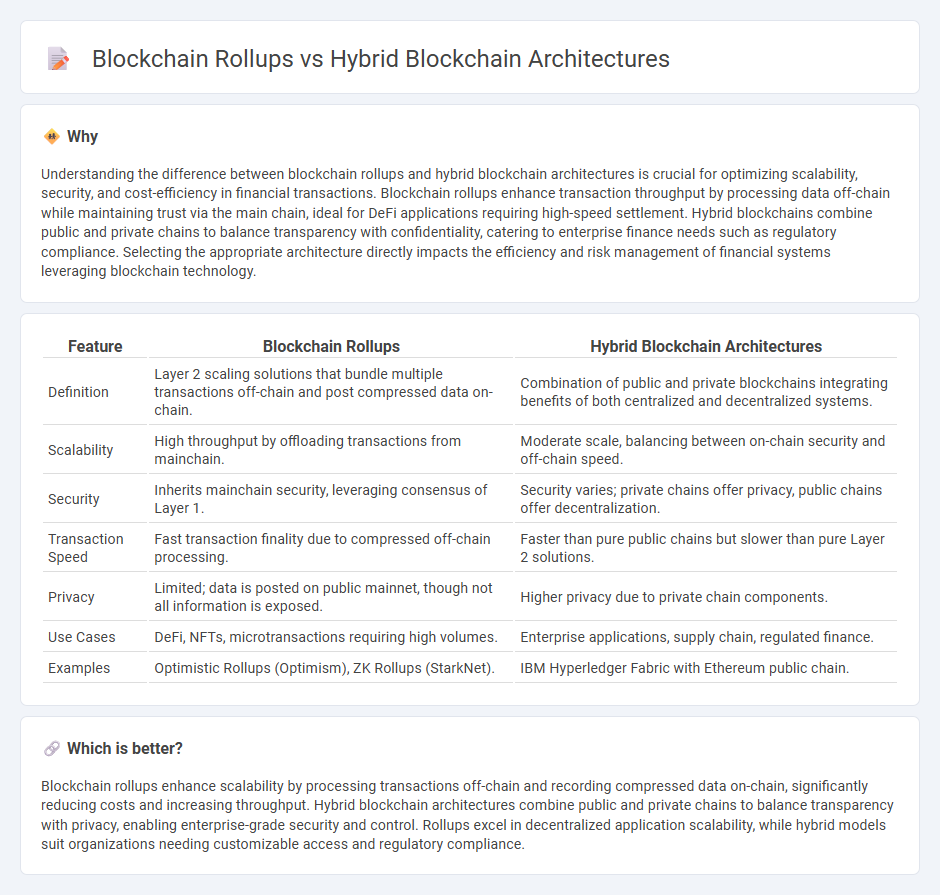
Understanding the difference between blockchain rollups and hybrid blockchain architectures is crucial for optimizing scalability, security, and cost-efficiency in financial transactions. Blockchain rollups enhance transaction throughput by processing data off-chain while maintaining trust via the main chain, ideal for DeFi applications requiring high-speed settlement. Hybrid blockchains combine public and private chains to balance transparency with confidentiality, catering to enterprise finance needs such as regulatory compliance. Selecting the appropriate architecture directly impacts the efficiency and risk management of financial systems leveraging blockchain technology.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Rollups | Hybrid Blockchain Architectures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layer 2 scaling solutions that bundle multiple transactions off-chain and post compressed data on-chain. | Combination of public and private blockchains integrating benefits of both centralized and decentralized systems. |
| Scalability | High throughput by offloading transactions from mainchain. | Moderate scale, balancing between on-chain security and off-chain speed. |
| Security | Inherits mainchain security, leveraging consensus of Layer 1. | Security varies; private chains offer privacy, public chains offer decentralization. |
| Transaction Speed | Fast transaction finality due to compressed off-chain processing. | Faster than pure public chains but slower than pure Layer 2 solutions. |
| Privacy | Limited; data is posted on public mainnet, though not all information is exposed. | Higher privacy due to private chain components. |
| Use Cases | DeFi, NFTs, microtransactions requiring high volumes. | Enterprise applications, supply chain, regulated finance. |
| Examples | Optimistic Rollups (Optimism), ZK Rollups (StarkNet). | IBM Hyperledger Fabric with Ethereum public chain. |
Which is better?
Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain and recording compressed data on-chain, significantly reducing costs and increasing throughput. Hybrid blockchain architectures combine public and private chains to balance transparency with privacy, enabling enterprise-grade security and control. Rollups excel in decentralized application scalability, while hybrid models suit organizations needing customizable access and regulatory compliance.
Connection
Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain while maintaining security through on-chain data verification, which aligns with hybrid blockchain architectures that combine public and private chains to optimize performance and privacy. Hybrid architectures utilize rollups to efficiently manage transaction loads and reduce congestion on public blockchains. This integration leverages the decentralized security of public chains with the customized control of private chains, enabling faster and cost-effective financial services.
Key Terms
On-chain vs. off-chain data
Hybrid blockchain architectures combine on-chain and off-chain components to enhance scalability and flexibility, storing critical data on-chain while processing less sensitive information off-chain. Blockchain rollups, especially optimistic and zk-rollups, aggregate numerous transactions off-chain and submit compressed proofs on-chain, optimizing data throughput and reducing gas costs. Explore the detailed nuances and performance metrics of these technologies to understand their impact on blockchain scalability.
Trust assumptions
Hybrid blockchain architectures combine public and private chains to balance trust assumptions by allowing sensitive data to remain on permissioned networks while leveraging public chains for transparency and security. Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain and submitting cryptographic proofs on-chain, reducing trust requirements by relying primarily on the validity of the underlying blockchain. Explore deeper insights into how these trust models impact security, decentralization, and performance in evolving blockchain ecosystems.
Scalability
Hybrid blockchain architectures combine public and private chains to enhance scalability by restricting sensitive data to private networks while leveraging the security of public chains for transaction validation. Blockchain rollups achieve scalability by bundling multiple transactions off-chain and submitting a single compressed proof to the main chain, significantly reducing on-chain congestion and fees. Explore how these innovative solutions address scalability challenges in modern blockchain systems.
Source and External Links
Hybrid Blockchain Models - Hybrid blockchain architectures combine the strengths of public and private blockchains by balancing transparency and decentralization with controlled access and privacy, enabling secure data exchange, interoperability between networks, and scalability for handling large volumes of transactions efficiently.
Exploring the Different Types of Blockchain Architecture - PlasBit - Hybrid blockchains operate with two interfaces: one public allowing broad participation, and one private with permissioned, controlled access, providing organizations improved control, security, and transparency while reducing energy consumption compared to fully public blockchains.
Hybrid Blockchain - GeeksforGeeks - Hybrid blockchain technology offers benefits like lower transaction costs, protection against external 51% attacks due to a closed environment, flexible new rule policies, increased decentralized access as needed, and more transparent transaction handling compared to private blockchains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com