Structured credit involves pooling various debt instruments to create marketable securities, often enhancing liquidity and risk distribution in financial markets. Project finance focuses on long-term financing of infrastructure and industrial projects, where repayment depends on the project's cash flow rather than the sponsors' balance sheets. Explore these financing strategies to understand their unique risk profiles and investment potentials.
Why it is important
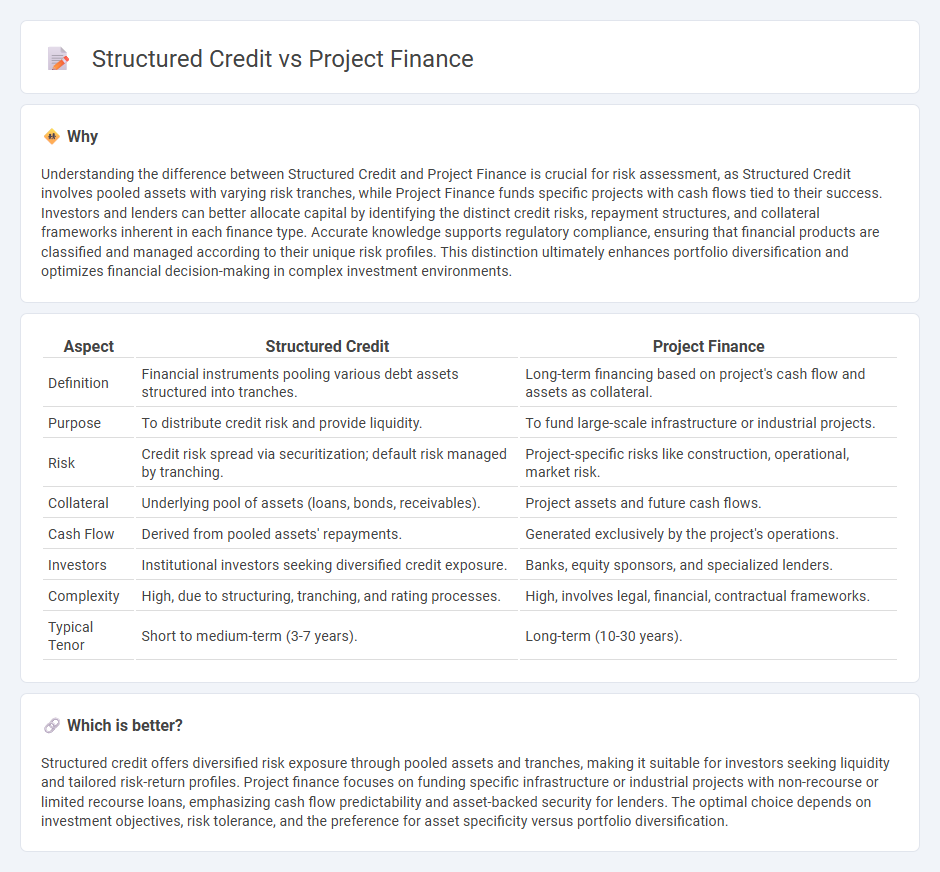
Understanding the difference between Structured Credit and Project Finance is crucial for risk assessment, as Structured Credit involves pooled assets with varying risk tranches, while Project Finance funds specific projects with cash flows tied to their success. Investors and lenders can better allocate capital by identifying the distinct credit risks, repayment structures, and collateral frameworks inherent in each finance type. Accurate knowledge supports regulatory compliance, ensuring that financial products are classified and managed according to their unique risk profiles. This distinction ultimately enhances portfolio diversification and optimizes financial decision-making in complex investment environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Structured Credit | Project Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial instruments pooling various debt assets structured into tranches. | Long-term financing based on project's cash flow and assets as collateral. |
| Purpose | To distribute credit risk and provide liquidity. | To fund large-scale infrastructure or industrial projects. |
| Risk | Credit risk spread via securitization; default risk managed by tranching. | Project-specific risks like construction, operational, market risk. |
| Collateral | Underlying pool of assets (loans, bonds, receivables). | Project assets and future cash flows. |
| Cash Flow | Derived from pooled assets' repayments. | Generated exclusively by the project's operations. |
| Investors | Institutional investors seeking diversified credit exposure. | Banks, equity sponsors, and specialized lenders. |
| Complexity | High, due to structuring, tranching, and rating processes. | High, involves legal, financial, contractual frameworks. |
| Typical Tenor | Short to medium-term (3-7 years). | Long-term (10-30 years). |
Which is better?
Structured credit offers diversified risk exposure through pooled assets and tranches, making it suitable for investors seeking liquidity and tailored risk-return profiles. Project finance focuses on funding specific infrastructure or industrial projects with non-recourse or limited recourse loans, emphasizing cash flow predictability and asset-backed security for lenders. The optimal choice depends on investment objectives, risk tolerance, and the preference for asset specificity versus portfolio diversification.
Connection
Structured credit and project finance intersect through the use of tailored financial instruments designed to manage risk and allocate capital efficiently in large-scale infrastructure or development projects. Structured credit products, such as asset-backed securities or collateralized loan obligations, often pool project finance assets to enhance liquidity and distribute credit risk among investors. This synergy enables project sponsors to secure long-term financing while providing investors diversified exposure to specific project cash flows and credit profiles.
Key Terms
**Project finance:**
Project finance centers on long-term, capital-intensive infrastructure and industrial projects where debt and equity are repaid from the project's cash flow, minimizing sponsor risk. It involves complex contractual frameworks, including off-take agreements and government guarantees, to ensure stable revenue streams and risk allocation. Discover more about how project finance structures enable large-scale investment and risk management strategies.
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
Project finance leverages a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) to isolate project assets and liabilities, enabling debt servicing solely from project cash flows while minimizing risk to sponsors. Structured credit uses SPVs to pool loans or assets, transforming them into marketable securities that distribute risk among investors through tranching and credit enhancement. Explore how SPVs uniquely drive risk management and financing structures in both domains.
Limited Recourse
Project finance involves raising funds primarily based on the future cash flows of a specific project, using limited recourse or non-recourse debt that restricts the lender's claims to project assets only. Structured credit, on the other hand, bundles various financial assets into securities with credit enhancements, often relying on the creditworthiness of the underlying assets rather than direct recourse to borrowers. Explore the nuances and risk allocation differences between project finance and structured credit to better understand limited recourse implications.
Source and External Links
Project finance - Wikipedia - Project finance is the long-term funding of infrastructure and industrial projects based on the project's projected cash flows rather than the sponsors' balance sheets, typically structured as non-recourse loans secured by project assets and revenue contracts.
Project Finance - Key Concepts - Public Private Partnership - A primary advantage of project financing is off-balance-sheet treatment for sponsors and governments, shifting project risks to lenders who, in turn, receive higher interest margins compared to standard corporate loans.
Project Finance Jobs: Recruiting, The Job, Salaries, Hours, and ... - Project finance professionals typically work in advisory or lending roles, structuring deals, modeling cash flows, and coordinating with multiple banks to raise the necessary debt for large infrastructure investments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com