Basis trading exploits the price difference between a futures contract and its underlying asset to generate risk-free profits, often involving commodities, bonds, or indexes. Convertible arbitrage focuses on capitalizing on discrepancies between a convertible bond's price and the underlying stock, combining long equity and short bond positions for hedged returns. Explore detailed strategies and risk profiles to deepen your understanding of these advanced financial techniques.
Why it is important
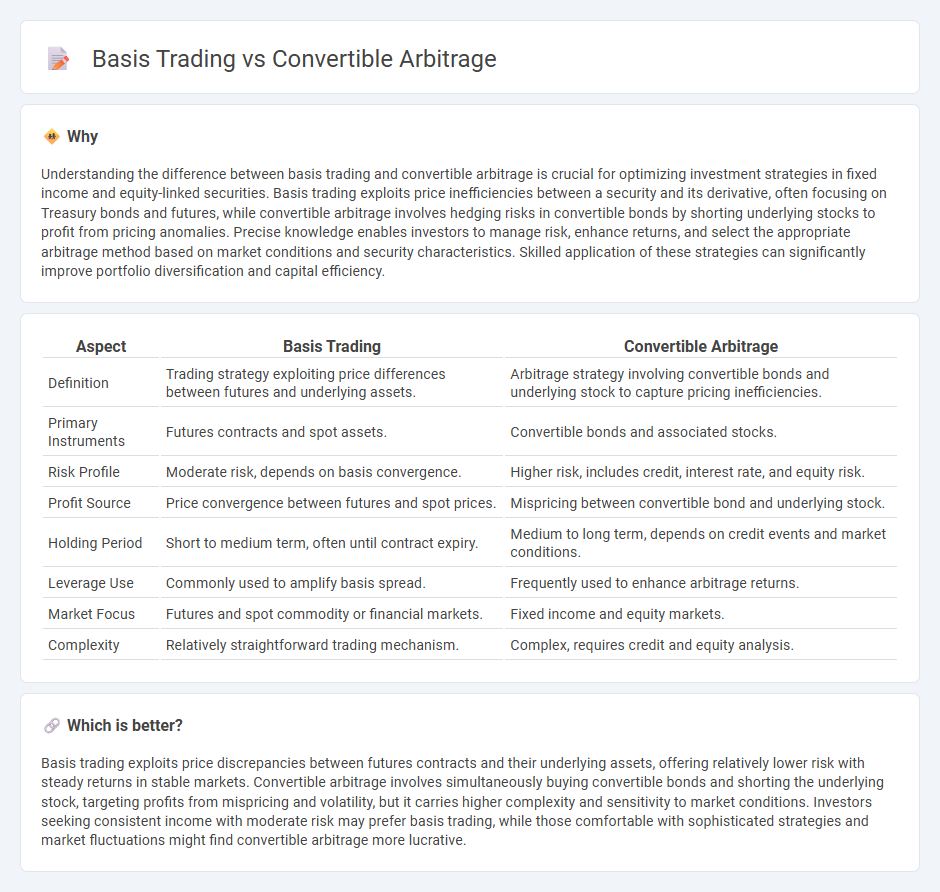
Understanding the difference between basis trading and convertible arbitrage is crucial for optimizing investment strategies in fixed income and equity-linked securities. Basis trading exploits price inefficiencies between a security and its derivative, often focusing on Treasury bonds and futures, while convertible arbitrage involves hedging risks in convertible bonds by shorting underlying stocks to profit from pricing anomalies. Precise knowledge enables investors to manage risk, enhance returns, and select the appropriate arbitrage method based on market conditions and security characteristics. Skilled application of these strategies can significantly improve portfolio diversification and capital efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Basis Trading | Convertible Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading strategy exploiting price differences between futures and underlying assets. | Arbitrage strategy involving convertible bonds and underlying stock to capture pricing inefficiencies. |
| Primary Instruments | Futures contracts and spot assets. | Convertible bonds and associated stocks. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk, depends on basis convergence. | Higher risk, includes credit, interest rate, and equity risk. |
| Profit Source | Price convergence between futures and spot prices. | Mispricing between convertible bond and underlying stock. |
| Holding Period | Short to medium term, often until contract expiry. | Medium to long term, depends on credit events and market conditions. |
| Leverage Use | Commonly used to amplify basis spread. | Frequently used to enhance arbitrage returns. |
| Market Focus | Futures and spot commodity or financial markets. | Fixed income and equity markets. |
| Complexity | Relatively straightforward trading mechanism. | Complex, requires credit and equity analysis. |
Which is better?
Basis trading exploits price discrepancies between futures contracts and their underlying assets, offering relatively lower risk with steady returns in stable markets. Convertible arbitrage involves simultaneously buying convertible bonds and shorting the underlying stock, targeting profits from mispricing and volatility, but it carries higher complexity and sensitivity to market conditions. Investors seeking consistent income with moderate risk may prefer basis trading, while those comfortable with sophisticated strategies and market fluctuations might find convertible arbitrage more lucrative.
Connection
Basis trading and convertible arbitrage are connected through their reliance on exploiting price discrepancies between related financial instruments. Basis trading focuses on the spread between the spot and futures prices of an asset, while convertible arbitrage capitalizes on mispricing between a convertible bond and its underlying equity. Both strategies involve hedging risks to profit from market inefficiencies in fixed income and equity-linked securities.
Key Terms
Convertible Bonds
Convertible arbitrage targets price inefficiencies between convertible bonds and underlying equities, exploiting volatility and mispricing through long convertible bond and short stock positions. Basis trading centers on the yield spread or price difference between convertible bonds and their synthetic equivalents, focusing on interest rate, credit, and liquidity factors impacting bond valuation. Explore convertible bond strategies to understand the nuances between arbitrage and basis trading for optimized portfolio diversification.
Credit Spread
Convertible arbitrage involves exploiting price inefficiencies between a company's convertible bonds and its underlying stock, focusing on credit spread to capture value from bond credit risk relative to equity volatility. Basis trading centers on the differential, or basis, between futures prices and spot prices of an asset, where monitoring credit spreads helps assess default risk impacting the basis in fixed income instruments. Explore the nuances of credit spread impact on these strategies to enhance your trading insights.
Futures Basis
Convertible arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between convertible bonds and the underlying stock, aiming to profit from mispricing and volatility. Basis trading, particularly futures basis trading, targets the difference between the futures contract price and the spot price of the underlying asset, seeking gains from the convergence at contract maturity. Explore the detailed mechanics and risk profiles of these strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Convertible arbitrage - Wikipedia - Convertible arbitrage is a market-neutral investment strategy used by hedge funds that involves buying convertible securities and short-selling the underlying common stock to exploit pricing inefficiencies while maintaining a delta-neutral position through dynamic rebalancing.
Convertible Arbitrage 101 - This strategy enhances income and reduces equity market risk by purchasing undervalued convertible bonds and short-selling the underlying stock, aiming to generate returns from yield, short interest credit, capital appreciation, and active rebalancing.
Convertible Arbitrage Hedge Funds: Full Guide - Convertible arbitrage is a relative value strategy that profits from pricing discrepancies between convertible bonds and underlying stock by exploiting volatility and credit factors, minimizing market risk with a hedged long convertible bond and short stock position.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com