Green bonds primarily finance environmentally sustainable projects such as renewable energy and conservation efforts, while social bonds fund initiatives that address social issues like affordable housing and healthcare access. Both instruments support impact investing by targeting specific Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to attract responsible investors. Discover how these bond types influence sustainable finance and impact investment strategies.
Why it is important
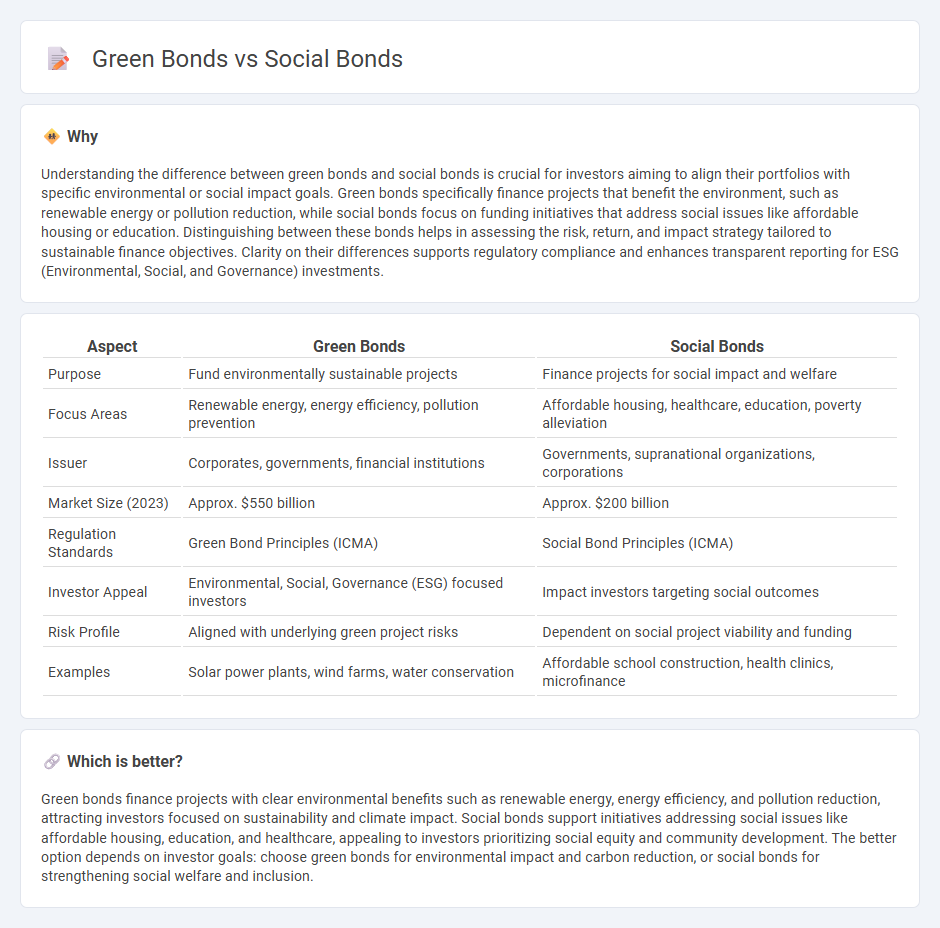
Understanding the difference between green bonds and social bonds is crucial for investors aiming to align their portfolios with specific environmental or social impact goals. Green bonds specifically finance projects that benefit the environment, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction, while social bonds focus on funding initiatives that address social issues like affordable housing or education. Distinguishing between these bonds helps in assessing the risk, return, and impact strategy tailored to sustainable finance objectives. Clarity on their differences supports regulatory compliance and enhances transparent reporting for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Bonds | Social Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Fund environmentally sustainable projects | Finance projects for social impact and welfare |
| Focus Areas | Renewable energy, energy efficiency, pollution prevention | Affordable housing, healthcare, education, poverty alleviation |
| Issuer | Corporates, governments, financial institutions | Governments, supranational organizations, corporations |
| Market Size (2023) | Approx. $550 billion | Approx. $200 billion |
| Regulation Standards | Green Bond Principles (ICMA) | Social Bond Principles (ICMA) |
| Investor Appeal | Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) focused investors | Impact investors targeting social outcomes |
| Risk Profile | Aligned with underlying green project risks | Dependent on social project viability and funding |
| Examples | Solar power plants, wind farms, water conservation | Affordable school construction, health clinics, microfinance |
Which is better?
Green bonds finance projects with clear environmental benefits such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction, attracting investors focused on sustainability and climate impact. Social bonds support initiatives addressing social issues like affordable housing, education, and healthcare, appealing to investors prioritizing social equity and community development. The better option depends on investor goals: choose green bonds for environmental impact and carbon reduction, or social bonds for strengthening social welfare and inclusion.
Connection
Green bonds and social bonds are both types of impact investing instruments designed to finance projects with positive environmental and social outcomes, respectively. They share a commitment to transparency and accountability through third-party verification and standardized reporting frameworks to ensure funds are used as intended. Investors increasingly view green and social bonds as complementary tools within sustainable finance strategies to address climate change and social inequality simultaneously.
Key Terms
Use of Proceeds
Social bonds primarily finance projects addressing social issues such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare, targeting measurable social benefits. Green bonds allocate proceeds exclusively to environmental initiatives like renewable energy, pollution prevention, and climate adaptation, ensuring projects contribute to sustainability goals. Explore detailed criteria and impact assessments to understand their distinct roles in sustainable finance.
Impact Reporting
Social bonds finance projects with positive social outcomes, such as affordable housing and education, while green bonds support environmentally sustainable initiatives like renewable energy and climate resilience. Both bond types emphasize Impact Reporting to provide transparency and measure the effectiveness of funded projects using key performance indicators aligned with social and environmental goals. Explore detailed Impact Reporting frameworks to understand how these bonds drive measurable change.
Eligible Projects
Social bonds primarily finance projects that deliver positive social outcomes, such as affordable housing, education, healthcare, and community development initiatives. Green bonds support projects with environmental benefits, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable waste management, and climate change mitigation efforts. Explore further to understand the distinct eligible project criteria and impact measurement for social and green bonds.
Source and External Links
Building Social Bonds | NIH News in Health - Strong social relationships with family, friends, and others can improve mental, emotional, and even physical health, reduce stress and heart-related risks, and are linked to a longer life, while loneliness and social isolation are associated with poorer health outcomes.
Social Bonds: Definition & Benefits - Nasdaq - Social bonds are fixed-income instruments issued to finance projects with direct, measurable social benefits such as affordable housing, healthcare, education, and job creation, and they follow strict guidelines to ensure transparency and accountability.
Social impact bond - Wikipedia - Social impact bonds are outcomes-based contracts where private investors fund social programs and are repaid by the government only if predetermined social outcomes are achieved, first implemented in the UK in 2010 for prisoner rehabilitation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com