Flash loan attacks exploit unsecured borrowing in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to manipulate asset prices momentarily and execute profitable trades without upfront capital. Price oracle manipulation involves feeding false or misleading price data into oracles, causing smart contracts to make erroneous financial decisions. Discover the mechanisms and risks behind these sophisticated exploits in blockchain finance.
Why it is important
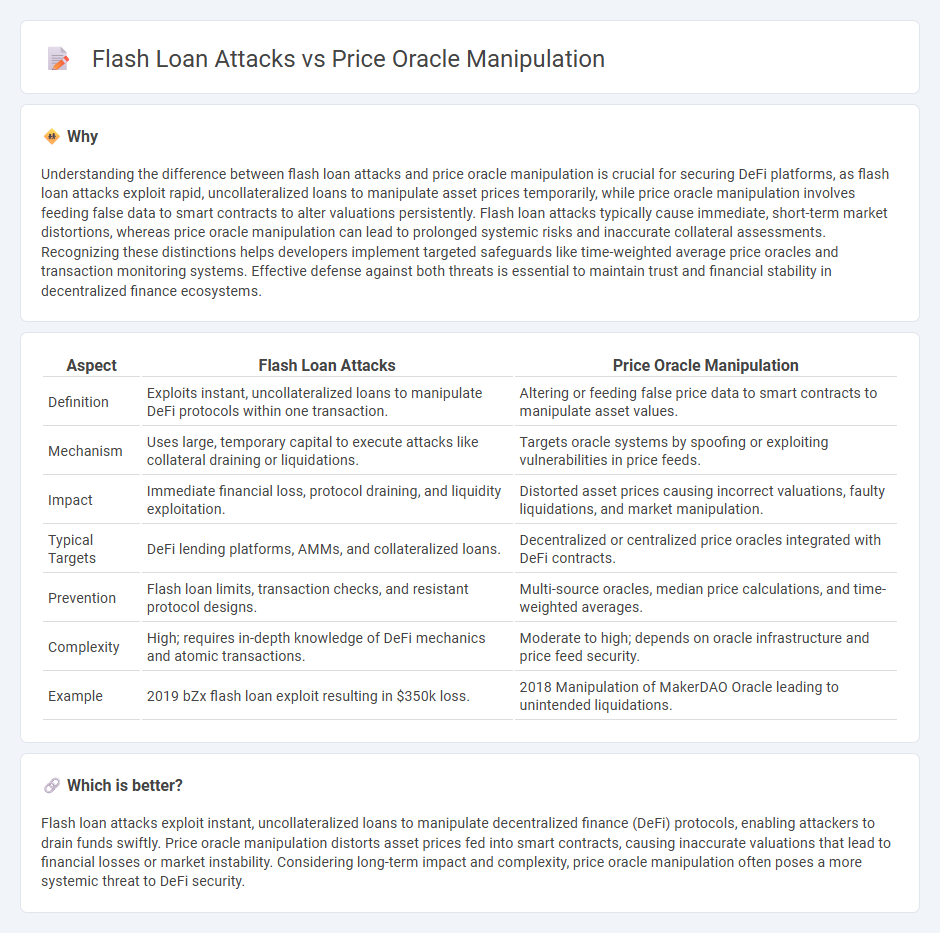
Understanding the difference between flash loan attacks and price oracle manipulation is crucial for securing DeFi platforms, as flash loan attacks exploit rapid, uncollateralized loans to manipulate asset prices temporarily, while price oracle manipulation involves feeding false data to smart contracts to alter valuations persistently. Flash loan attacks typically cause immediate, short-term market distortions, whereas price oracle manipulation can lead to prolonged systemic risks and inaccurate collateral assessments. Recognizing these distinctions helps developers implement targeted safeguards like time-weighted average price oracles and transaction monitoring systems. Effective defense against both threats is essential to maintain trust and financial stability in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flash Loan Attacks | Price Oracle Manipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploits instant, uncollateralized loans to manipulate DeFi protocols within one transaction. | Altering or feeding false price data to smart contracts to manipulate asset values. |
| Mechanism | Uses large, temporary capital to execute attacks like collateral draining or liquidations. | Targets oracle systems by spoofing or exploiting vulnerabilities in price feeds. |
| Impact | Immediate financial loss, protocol draining, and liquidity exploitation. | Distorted asset prices causing incorrect valuations, faulty liquidations, and market manipulation. |
| Typical Targets | DeFi lending platforms, AMMs, and collateralized loans. | Decentralized or centralized price oracles integrated with DeFi contracts. |
| Prevention | Flash loan limits, transaction checks, and resistant protocol designs. | Multi-source oracles, median price calculations, and time-weighted averages. |
| Complexity | High; requires in-depth knowledge of DeFi mechanics and atomic transactions. | Moderate to high; depends on oracle infrastructure and price feed security. |
| Example | 2019 bZx flash loan exploit resulting in $350k loss. | 2018 Manipulation of MakerDAO Oracle leading to unintended liquidations. |
Which is better?
Flash loan attacks exploit instant, uncollateralized loans to manipulate decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, enabling attackers to drain funds swiftly. Price oracle manipulation distorts asset prices fed into smart contracts, causing inaccurate valuations that lead to financial losses or market instability. Considering long-term impact and complexity, price oracle manipulation often poses a more systemic threat to DeFi security.
Connection
Flash loan attacks exploit the instantaneous, uncollateralized borrowing of large asset amounts, enabling attackers to manipulate decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols by artificially inflating or deflating asset prices on price oracles. Price oracle manipulation occurs when attackers feed false or manipulated data to these oracles, causing inaccurate asset valuation that can trigger flawed contract executions. The connection between flash loan attacks and price oracle manipulation lies in attackers using borrowed funds to distort oracle prices, enabling profitable exploits such as asset liquidation, collateral theft, or protocol draining.
Key Terms
Decentralized Price Oracle
Decentralized price oracles are critical components in blockchain ecosystems, providing real-time, tamper-resistant asset price data essential for DeFi protocols. Price oracle manipulation exploits vulnerabilities by feeding false price information to smart contracts, often orchestrated through flash loan attacks that temporarily amass large capital to influence market prices without long-term risk. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how decentralized price oracles safeguard integrity against such exploits and the evolving defense mechanisms in DeFi security.
Flash Loan
Flash loan attacks exploit uncollateralized loans to borrow large sums instantly, enabling attackers to manipulate price oracles by artificially inflating or deflating asset values within decentralized finance protocols. These attacks often cause severe financial damage by triggering erroneous liquidations or draining liquidity pools due to manipulated price feeds. Explore the mechanisms and prevention strategies of flash loan attacks to safeguard decentralized ecosystems.
Collateral Liquidation
Price oracle manipulation exploits vulnerabilities in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols by providing false asset valuations, leading to erroneous collateral liquidation events. Flash loan attacks leverage instantaneous uncollateralized loans to manipulate price or liquidity conditions, triggering forced liquidations and destabilizing lending platforms. Explore how advanced oracle designs and real-time monitoring can mitigate these collateral liquidation risks.
Source and External Links
What are Price Oracle Manipulation Attacks in DeFi? - Halborn - Price oracle manipulation attacks trick smart contracts into using incorrect token valuations, allowing attackers to profit by exploiting the difference between real and perceived token values in DeFi protocols.
Automated Detection of Price Oracle Manipulations via LLM-Driven ... - Price oracle manipulation (POM) occurs when attackers manipulate price data from on-chain or off-chain oracles, for instance by using flash loans to distort on-chain prices temporarily, enabling financial exploits.
Oracle Manipulation Attacks - Smart Contract Security Field Guide - On-chain price oracles that rely on a single data source, such as a decentralized exchange's spot price, can be manipulated via flash loans, causing smart contracts to act on false price data and enabling attacks like arbitrage or wrongful liquidations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com