Liquidity staking offers flexible asset management by allowing investors to earn rewards while maintaining access to their crypto holdings, unlike fixed income securities which lock capital for predetermined periods in exchange for steady interest payments. Fixed income securities provide predictable returns and lower volatility, making them suitable for risk-averse investors seeking consistent income streams. Explore the advantages and trade-offs between liquidity staking and fixed income securities to optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
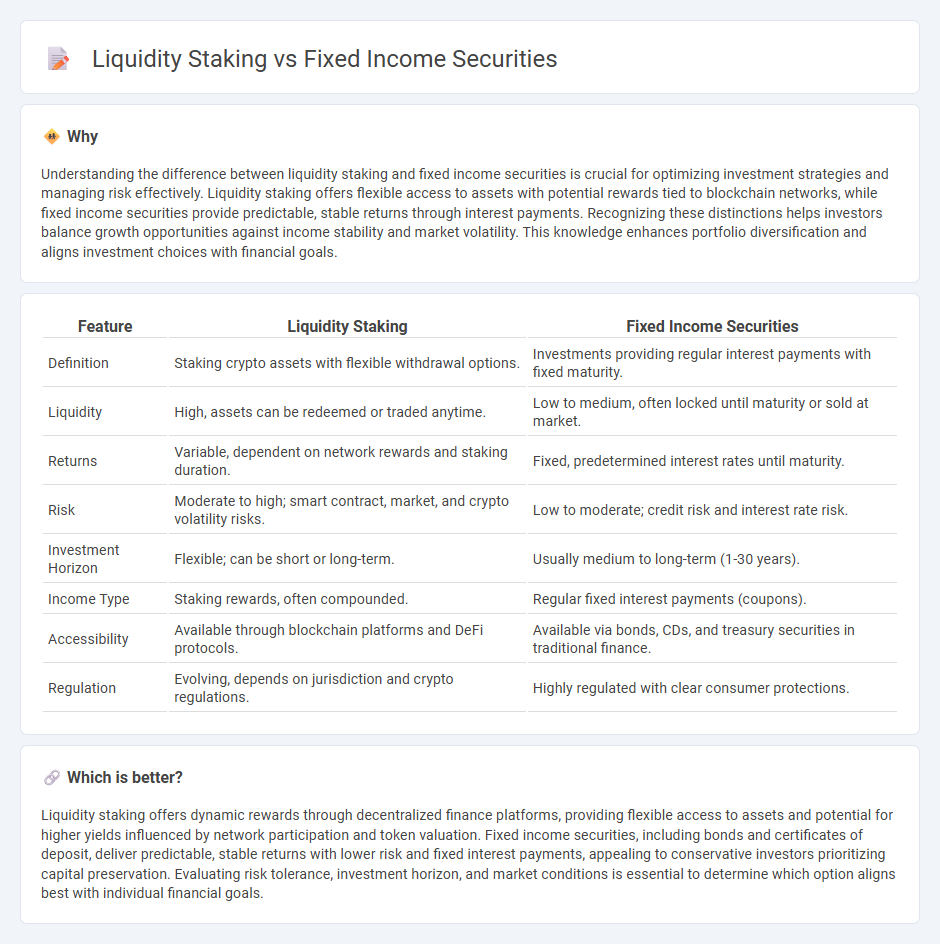
Understanding the difference between liquidity staking and fixed income securities is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and managing risk effectively. Liquidity staking offers flexible access to assets with potential rewards tied to blockchain networks, while fixed income securities provide predictable, stable returns through interest payments. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors balance growth opportunities against income stability and market volatility. This knowledge enhances portfolio diversification and aligns investment choices with financial goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Staking | Fixed Income Securities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staking crypto assets with flexible withdrawal options. | Investments providing regular interest payments with fixed maturity. |
| Liquidity | High, assets can be redeemed or traded anytime. | Low to medium, often locked until maturity or sold at market. |
| Returns | Variable, dependent on network rewards and staking duration. | Fixed, predetermined interest rates until maturity. |
| Risk | Moderate to high; smart contract, market, and crypto volatility risks. | Low to moderate; credit risk and interest rate risk. |
| Investment Horizon | Flexible; can be short or long-term. | Usually medium to long-term (1-30 years). |
| Income Type | Staking rewards, often compounded. | Regular fixed interest payments (coupons). |
| Accessibility | Available through blockchain platforms and DeFi protocols. | Available via bonds, CDs, and treasury securities in traditional finance. |
| Regulation | Evolving, depends on jurisdiction and crypto regulations. | Highly regulated with clear consumer protections. |
Which is better?
Liquidity staking offers dynamic rewards through decentralized finance platforms, providing flexible access to assets and potential for higher yields influenced by network participation and token valuation. Fixed income securities, including bonds and certificates of deposit, deliver predictable, stable returns with lower risk and fixed interest payments, appealing to conservative investors prioritizing capital preservation. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market conditions is essential to determine which option aligns best with individual financial goals.
Connection
Liquidity staking enhances capital efficiency by allowing investors to earn staking rewards while simultaneously accessing liquid assets, thus complementing fixed income securities that provide steady, predictable cash flows through interest payments. Both strategies aim to optimize risk-adjusted returns by balancing yield generation with liquidity management in portfolio construction. Integrating liquidity staking with fixed income instruments supports diversified income streams and improved portfolio resilience against market volatility.
Key Terms
Coupon Rate
Fixed income securities offer a predetermined coupon rate, providing investors with regular interest payments and predictable income streams. Liquidity staking typically yields variable returns based on network rewards and transaction fees, leading to less predictable earnings compared to fixed coupon payments. Explore the differences further to determine which strategy aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Yield
Fixed income securities offer predictable yields through interest payments, providing stability and often higher returns compared to typical savings accounts. Liquidity staking generates variable yields by enabling asset holders to earn rewards while maintaining liquidity in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. Explore more to understand how yield dynamics differ between these investment strategies.
Lock-up Period
Fixed income securities such as bonds typically have predefined lock-up periods during which investors cannot sell or redeem their holdings without penalty, impacting liquidity and capital accessibility. In contrast, liquidity staking in decentralized finance often features flexible or shorter lock-up periods to encourage participation in protocols while earning staking rewards, balancing returns with access to funds. Explore more to understand how lock-up durations influence investment strategies and portfolio management.
Source and External Links
Fixed Income Securities | Definition + Examples - Wall Street Prep - Fixed income securities are investments where capital is provided to governments or corporations for a set term, offering regular interest payments and return of principal at maturity, with a focus on capital preservation and steady income.
Definition and Examples of Fixed Income Securities - Corporate Finance Institute - Fixed income securities are highly liquid debt instruments like bonds, delivering predictable interest payments (coupons) and principal repayment at maturity, issued by governments and corporations to finance operations.
Fixed Income Securities and Economics | EBSCO Research Starters - Fixed income securities provide regular interest and principal at maturity, influenced by interest rate fluctuations and monetary policy, serving as stable investment options especially government-issued bonds considered nearly risk-free.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com