Yield farming involves earning rewards by staking or lending cryptocurrencies in DeFi protocols, optimizing asset utilization for maximum returns. Liquidity provision focuses on supplying tokens to decentralized exchanges to facilitate trading while earning fees and incentives. Discover detailed insights and strategies to enhance your DeFi investments.
Why it is important
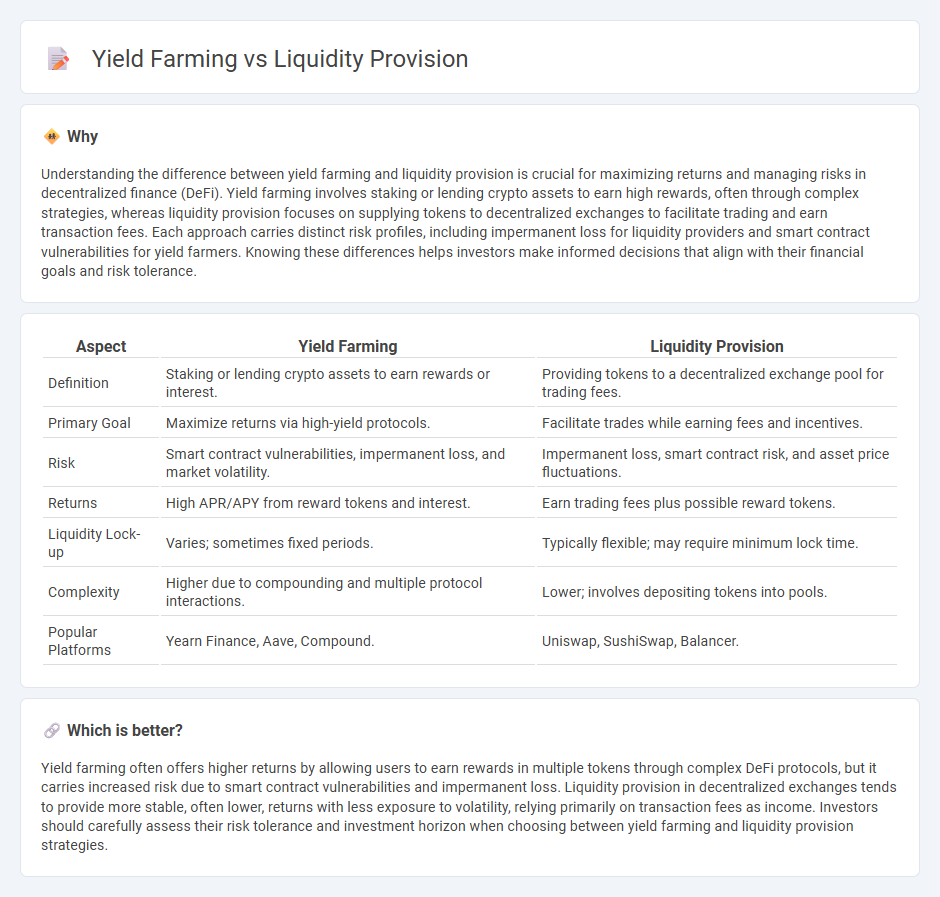
Understanding the difference between yield farming and liquidity provision is crucial for maximizing returns and managing risks in decentralized finance (DeFi). Yield farming involves staking or lending crypto assets to earn high rewards, often through complex strategies, whereas liquidity provision focuses on supplying tokens to decentralized exchanges to facilitate trading and earn transaction fees. Each approach carries distinct risk profiles, including impermanent loss for liquidity providers and smart contract vulnerabilities for yield farmers. Knowing these differences helps investors make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Yield Farming | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staking or lending crypto assets to earn rewards or interest. | Providing tokens to a decentralized exchange pool for trading fees. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize returns via high-yield protocols. | Facilitate trades while earning fees and incentives. |
| Risk | Smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss, and market volatility. | Impermanent loss, smart contract risk, and asset price fluctuations. |
| Returns | High APR/APY from reward tokens and interest. | Earn trading fees plus possible reward tokens. |
| Liquidity Lock-up | Varies; sometimes fixed periods. | Typically flexible; may require minimum lock time. |
| Complexity | Higher due to compounding and multiple protocol interactions. | Lower; involves depositing tokens into pools. |
| Popular Platforms | Yearn Finance, Aave, Compound. | Uniswap, SushiSwap, Balancer. |
Which is better?
Yield farming often offers higher returns by allowing users to earn rewards in multiple tokens through complex DeFi protocols, but it carries increased risk due to smart contract vulnerabilities and impermanent loss. Liquidity provision in decentralized exchanges tends to provide more stable, often lower, returns with less exposure to volatility, relying primarily on transaction fees as income. Investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment horizon when choosing between yield farming and liquidity provision strategies.
Connection
Yield farming and liquidity provision are interconnected through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms where liquidity providers supply tokens to liquidity pools, enabling seamless trading and earning transaction fees. Yield farming incentivizes liquidity provision by offering additional rewards in the form of governance tokens or interest, boosting overall yields for participants. This symbiotic relationship enhances market efficiency and liquidity depth while generating passive income opportunities for investors.
Key Terms
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Liquidity provision in Automated Market Makers (AMMs) involves depositing tokens into liquidity pools to facilitate decentralized trading, earning fees proportionally to the share provided. Yield farming leverages liquidity provision by optimizing token placements across multiple AMMs or DeFi protocols to maximize returns through additional incentives like governance tokens. Explore deeper strategies and risks associated with AMM liquidity provision and yield farming to enhance your DeFi participation.
Liquidity Pool
Liquidity provision involves supplying assets to a liquidity pool on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to facilitate trading and earn fees, contributing to market efficiency and reduced price slippage. Yield farming expands on this by using those liquidity pool tokens to earn additional rewards, often in the form of governance tokens or other incentives, increasing potential returns but also risk. Discover how liquidity pools function as the backbone of decentralized finance and optimize your crypto strategy.
Staking
Liquidity provision involves depositing tokens into decentralized exchange pools to facilitate trading and earn fees, while yield farming focuses on staking assets to generate additional rewards or interest. Staking in yield farming often requires locking tokens in smart contracts, enhancing network security and earning incentives based on protocol rules. Discover more about how staking strategies differ in DeFi ecosystems and optimize your returns.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Provision - Commercial Bank Financial Services - Liquidity provision involves a financial institution acting as an intermediary in securities markets to improve stock liquidity by increasing market depth and trading volumes.
Remarks on liquidity provision and on the economic outlook and ... - Central banks provide liquidity by standing ready to lend against good collateral to support financial stability and prevent market stress during crises.
DeFi Basics: Liquidity Provision - EMURGO - In DeFi, liquidity provision means users deposit tokens into pools allowing others to trade, earning fees as rewards, typically requiring a balanced supply of tokens in the pool.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com