Carbon trading allows companies to buy and sell emission allowances to meet regulatory limits, creating a market-driven approach to reducing greenhouse gases. Green bonds finance environmentally sustainable projects by attracting investments aimed at renewable energy, clean transportation, and climate resilience. Discover how these financial tools drive global efforts toward a low-carbon economy.
Why it is important
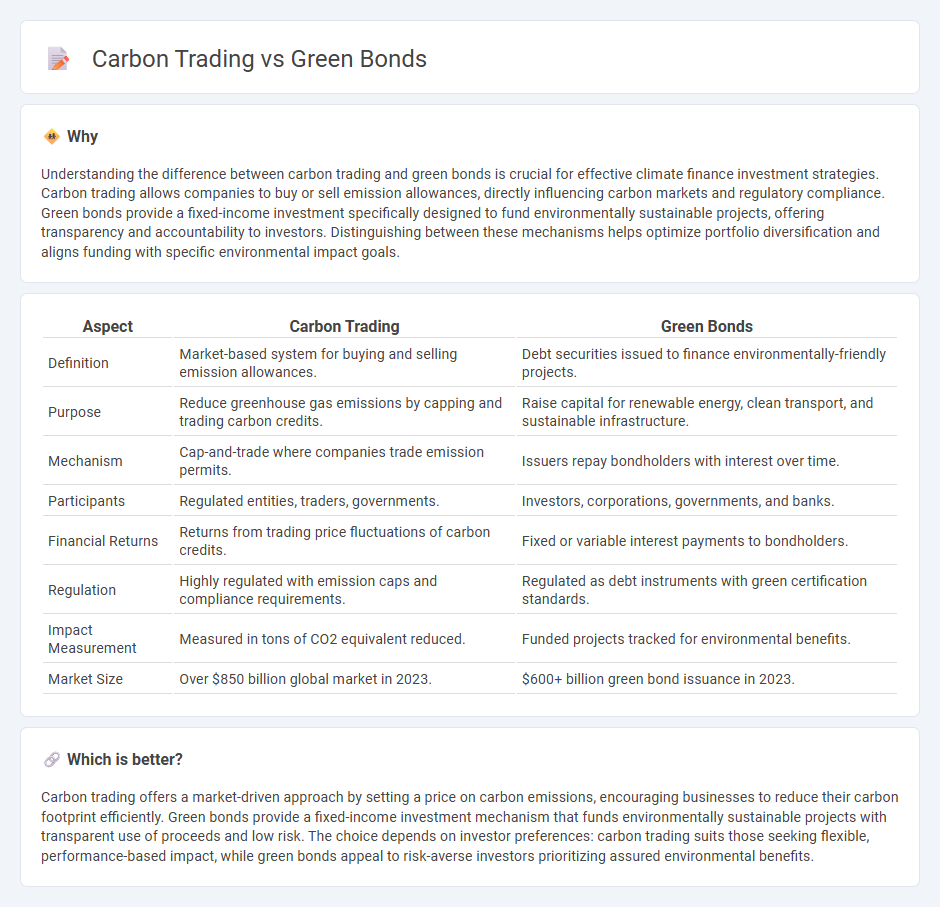
Understanding the difference between carbon trading and green bonds is crucial for effective climate finance investment strategies. Carbon trading allows companies to buy or sell emission allowances, directly influencing carbon markets and regulatory compliance. Green bonds provide a fixed-income investment specifically designed to fund environmentally sustainable projects, offering transparency and accountability to investors. Distinguishing between these mechanisms helps optimize portfolio diversification and aligns funding with specific environmental impact goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Trading | Green Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based system for buying and selling emission allowances. | Debt securities issued to finance environmentally-friendly projects. |
| Purpose | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capping and trading carbon credits. | Raise capital for renewable energy, clean transport, and sustainable infrastructure. |
| Mechanism | Cap-and-trade where companies trade emission permits. | Issuers repay bondholders with interest over time. |
| Participants | Regulated entities, traders, governments. | Investors, corporations, governments, and banks. |
| Financial Returns | Returns from trading price fluctuations of carbon credits. | Fixed or variable interest payments to bondholders. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated with emission caps and compliance requirements. | Regulated as debt instruments with green certification standards. |
| Impact Measurement | Measured in tons of CO2 equivalent reduced. | Funded projects tracked for environmental benefits. |
| Market Size | Over $850 billion global market in 2023. | $600+ billion green bond issuance in 2023. |
Which is better?
Carbon trading offers a market-driven approach by setting a price on carbon emissions, encouraging businesses to reduce their carbon footprint efficiently. Green bonds provide a fixed-income investment mechanism that funds environmentally sustainable projects with transparent use of proceeds and low risk. The choice depends on investor preferences: carbon trading suits those seeking flexible, performance-based impact, while green bonds appeal to risk-averse investors prioritizing assured environmental benefits.
Connection
Carbon trading and green bonds are interconnected financial mechanisms aimed at reducing environmental impact by incentivizing sustainable practices. Carbon trading creates a market for emission allowances, enabling companies to buy and sell carbon credits to meet regulatory targets, while green bonds provide capital specifically for projects that reduce carbon footprints, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency. Both tools mobilize investment toward climate mitigation, driving the transition to a low-carbon economy by aligning financial incentives with environmental goals.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Green bonds provide companies and governments with a sustainable financing method by raising capital specifically for environmentally beneficial projects, promoting transparency and accountability. Carbon trading enables entities to buy and sell emission allowances, creating a market-driven approach to reduce greenhouse gas emissions effectively. Explore deeper insights into how these tools drive sustainability and impact global climate goals.
Emissions Reduction
Green bonds finance projects that actively reduce emissions by supporting renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure. Carbon trading enables companies to buy or sell emission allowances, promoting cost-effective emissions reductions through market incentives. Explore further to understand which strategy best aligns with your emissions reduction goals.
Market Mechanisms
Green bonds are debt instruments designed to finance projects with environmental benefits, targeting investors seeking sustainable investment opportunities with fixed returns. Carbon trading involves the buying and selling of emission allowances or credits within cap-and-trade systems, incentivizing companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Explore how these market mechanisms drive climate finance and emissions reduction strategies.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - A green bond is a fixed-income financial instrument used to fund projects that have positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution control, allowing investors to support ESG goals through targeted environmental projects.
What are Green Bonds and what projects do they finance? - Iberdrola - Green bonds are debt instruments issued to finance sustainable and socially responsible environmental projects like renewable energy and clean transportation, promoting the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals related to affordable energy and climate action.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles provide voluntary guidelines that promote transparency, disclosure, and integrity in green bond issuance to support environmentally sound projects that foster a net-zero emissions economy and facilitate tracking of funds to sustainable outcomes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com