Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data transmission to execute trades faster than competitors, capitalizing on price differences before they adjust. Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models analyzing historical price patterns and correlations to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies across assets. Discover more about how these advanced trading strategies impact financial markets and investment performance.
Why it is important
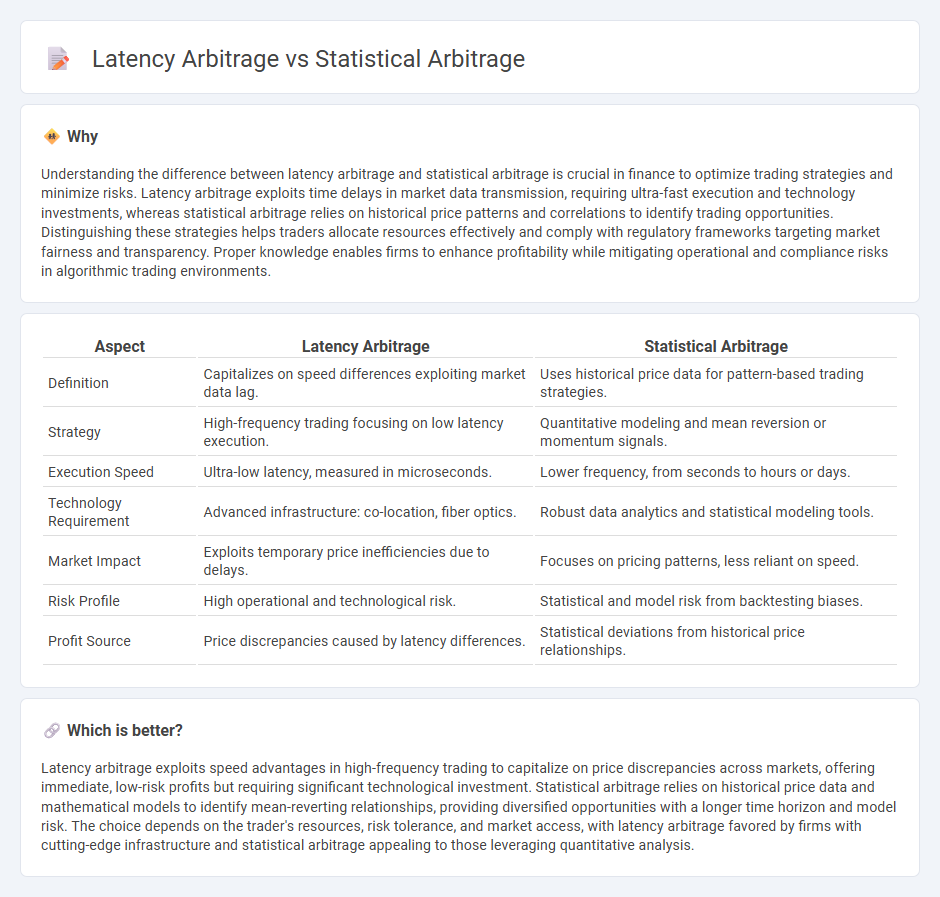
Understanding the difference between latency arbitrage and statistical arbitrage is crucial in finance to optimize trading strategies and minimize risks. Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data transmission, requiring ultra-fast execution and technology investments, whereas statistical arbitrage relies on historical price patterns and correlations to identify trading opportunities. Distinguishing these strategies helps traders allocate resources effectively and comply with regulatory frameworks targeting market fairness and transparency. Proper knowledge enables firms to enhance profitability while mitigating operational and compliance risks in algorithmic trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Latency Arbitrage | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Capitalizes on speed differences exploiting market data lag. | Uses historical price data for pattern-based trading strategies. |
| Strategy | High-frequency trading focusing on low latency execution. | Quantitative modeling and mean reversion or momentum signals. |
| Execution Speed | Ultra-low latency, measured in microseconds. | Lower frequency, from seconds to hours or days. |
| Technology Requirement | Advanced infrastructure: co-location, fiber optics. | Robust data analytics and statistical modeling tools. |
| Market Impact | Exploits temporary price inefficiencies due to delays. | Focuses on pricing patterns, less reliant on speed. |
| Risk Profile | High operational and technological risk. | Statistical and model risk from backtesting biases. |
| Profit Source | Price discrepancies caused by latency differences. | Statistical deviations from historical price relationships. |
Which is better?
Latency arbitrage exploits speed advantages in high-frequency trading to capitalize on price discrepancies across markets, offering immediate, low-risk profits but requiring significant technological investment. Statistical arbitrage relies on historical price data and mathematical models to identify mean-reverting relationships, providing diversified opportunities with a longer time horizon and model risk. The choice depends on the trader's resources, risk tolerance, and market access, with latency arbitrage favored by firms with cutting-edge infrastructure and statistical arbitrage appealing to those leveraging quantitative analysis.
Connection
Latency arbitrage exploits milliseconds-level market data delays to execute trades faster than competitors, while statistical arbitrage relies on mathematical models to identify price discrepancies across assets. Both strategies depend on high-frequency trading technology and quantitative analytics to capitalize on market inefficiencies. Their connection lies in leveraging real-time data and algorithmic execution to gain competitive advantages in financial markets.
Key Terms
Statistical Arbitrage:
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price data and advanced quantitative models to identify and exploit relative price inefficiencies across correlated assets, often employing mean reversion strategies. It relies on large datasets, machine learning algorithms, and high-frequency trading systems to execute numerous trades with small expected profits, minimizing risk through diversification. Explore deeper insights into statistical arbitrage strategies and their market impact to enhance your trading acumen.
Mean Reversion
Mean reversion in statistical arbitrage exploits predictable price corrections by identifying overbought or oversold assets, enabling traders to profit from price normalization in equity pairs or index spreads. Latency arbitrage capitalizes on speed advantages to exploit temporary price discrepancies caused by delayed market data transmission, often prioritizing millisecond-level execution over traditional mean reversion signals. Explore detailed strategies and risk profiles to better understand how mean reversion techniques differ in these arbitrage approaches.
Pairs Trading
Pairs trading, a popular form of statistical arbitrage, exploits historical price correlations between two securities to identify relative mispricings, executing simultaneous buy and sell positions to profit from convergence. Latency arbitrage leverages ultra-fast market data and execution speeds to capitalize on price discrepancies between venues before they disappear, often requiring advanced technology infrastructure. Explore further to understand how paired securities insights and high-frequency systems impact returns and risk management strategies in modern trading.
Source and External Links
The Power of Statistical Arbitrage in Finance - PyQuant News - Statistical arbitrage (stat arb) is a quantitative trading strategy that exploits temporary price discrepancies between related financial instruments based on mean reversion and involves data collection, model development, and trade execution phases.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage is a class of short-term, beta-neutral trading strategies employing mean reversion and multi-factor statistical models over diversified portfolios, often implemented via automated high-frequency trading systems.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? | CQF - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative finance strategy exploiting pricing deviations or unexpected statistical relationships between related securities for profitable trades based on rigorous modeling.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com