Inflation swaps are derivative contracts allowing parties to exchange fixed payments for payments tied to inflation rates, providing protection against inflation risk. Interest rate swaps involve exchanging fixed-rate interest payments for floating-rate payments based on benchmarks like LIBOR, managing interest rate exposure. Explore the mechanisms and benefits of both swaps to enhance risk management strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between inflation swaps and interest rate swaps is crucial for effectively managing financial risks related to inflation and interest rate fluctuations. Inflation swaps help hedge against inflation risk by exchanging fixed payments for inflation-linked payments, while interest rate swaps focus on exchanging fixed and floating interest rate payments to manage exposure to interest rate volatility. Accurate differentiation allows investors and corporations to tailor their risk management strategies to specific economic conditions, optimizing portfolio performance. Mastery of these derivatives supports informed decision-making in dynamic financial markets.
Comparison Table
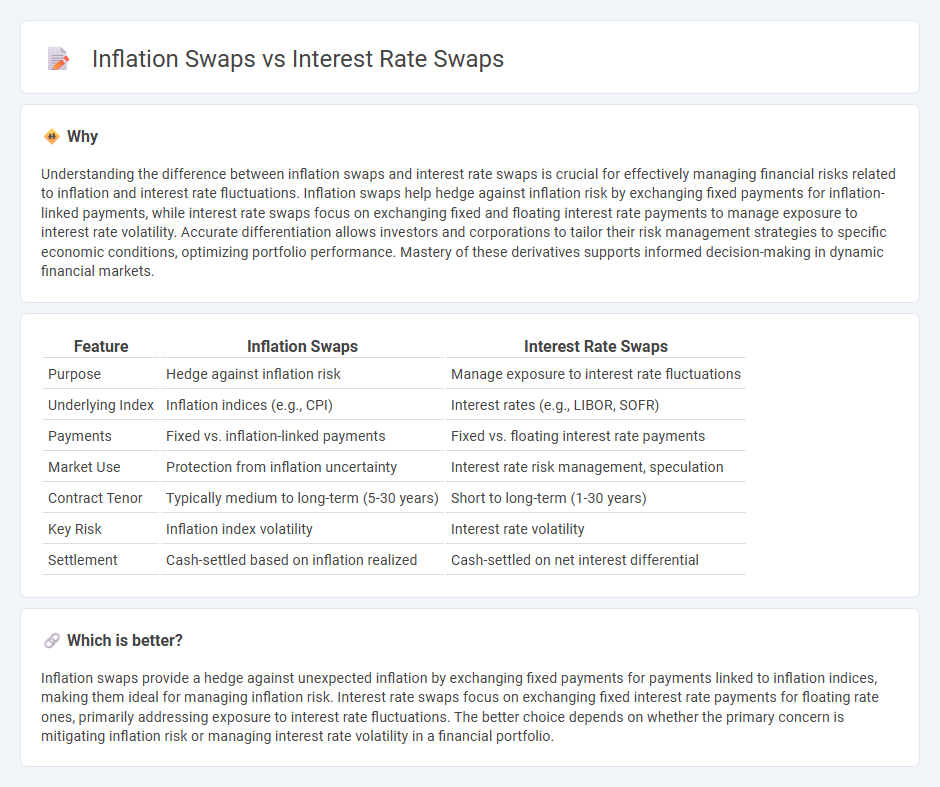
| Feature | Inflation Swaps | Interest Rate Swaps |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hedge against inflation risk | Manage exposure to interest rate fluctuations |
| Underlying Index | Inflation indices (e.g., CPI) | Interest rates (e.g., LIBOR, SOFR) |
| Payments | Fixed vs. inflation-linked payments | Fixed vs. floating interest rate payments |
| Market Use | Protection from inflation uncertainty | Interest rate risk management, speculation |
| Contract Tenor | Typically medium to long-term (5-30 years) | Short to long-term (1-30 years) |
| Key Risk | Inflation index volatility | Interest rate volatility |
| Settlement | Cash-settled based on inflation realized | Cash-settled on net interest differential |
Which is better?
Inflation swaps provide a hedge against unexpected inflation by exchanging fixed payments for payments linked to inflation indices, making them ideal for managing inflation risk. Interest rate swaps focus on exchanging fixed interest rate payments for floating rate ones, primarily addressing exposure to interest rate fluctuations. The better choice depends on whether the primary concern is mitigating inflation risk or managing interest rate volatility in a financial portfolio.
Connection
Inflation swaps and interest rate swaps are interconnected through their reliance on underlying interest rate benchmarks and inflation indices to manage financial risks. Both derivatives allow investors and institutions to hedge against uncertainties in inflation and interest rate fluctuations, often using LIBOR or SOFR rates as reference points. The pricing and valuation of inflation swaps frequently incorporate interest rate swap curves to reflect the time value of money and inflation expectations embedded in the market.
Key Terms
Notional Principal
Interest rate swaps and inflation swaps both use notional principal as a reference amount for calculating payments, but in interest rate swaps, the notional principal remains unchanged throughout the contract; it serves only as a basis to exchange fixed and floating interest payments. Inflation swaps, however, adjust the notional principal according to an inflation index, reflecting changes in inflation rates to protect against purchasing power risk. Learn more about how the role of notional principal varies and impacts swap contract valuation.
Source and External Links
Video An Overview Of Interest Rate Swaps - PNC Bank - Interest rate swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange a floating interest rate for a fixed interest rate, helping borrowers manage interest rate risk and budget with greater certainty by swapping uncertain floating payments for a predetermined fixed rate.
Interest Rate Swap (IRS) - Corporate Finance Institute - An interest rate swap is a derivative contract where two parties exchange interest payment streams, typically exchanging fixed-rate payments for floating-rate payments without exchanging underlying debt, to gain payment terms more suited to their risk preferences.
Interest rate swap - Wikipedia - Interest rate swaps are derivative contracts where counterparties exchange payments based on fixed and floating interest rates in order to hedge, speculate, or manage cashflows, with terms that specify notional amounts, payment schedules, and interest rate indices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com