Crowdlending connects numerous individual investors directly with borrowers, enabling medium-sized enterprises to access finance quickly and with fewer intermediaries. Public bond issuance involves companies raising capital from institutional and retail investors through regulated markets, often requiring extensive disclosure and longer timelines. Discover how these financing methods differ in risk, cost, and accessibility to determine the best option for your investment or business needs.
Why it is important
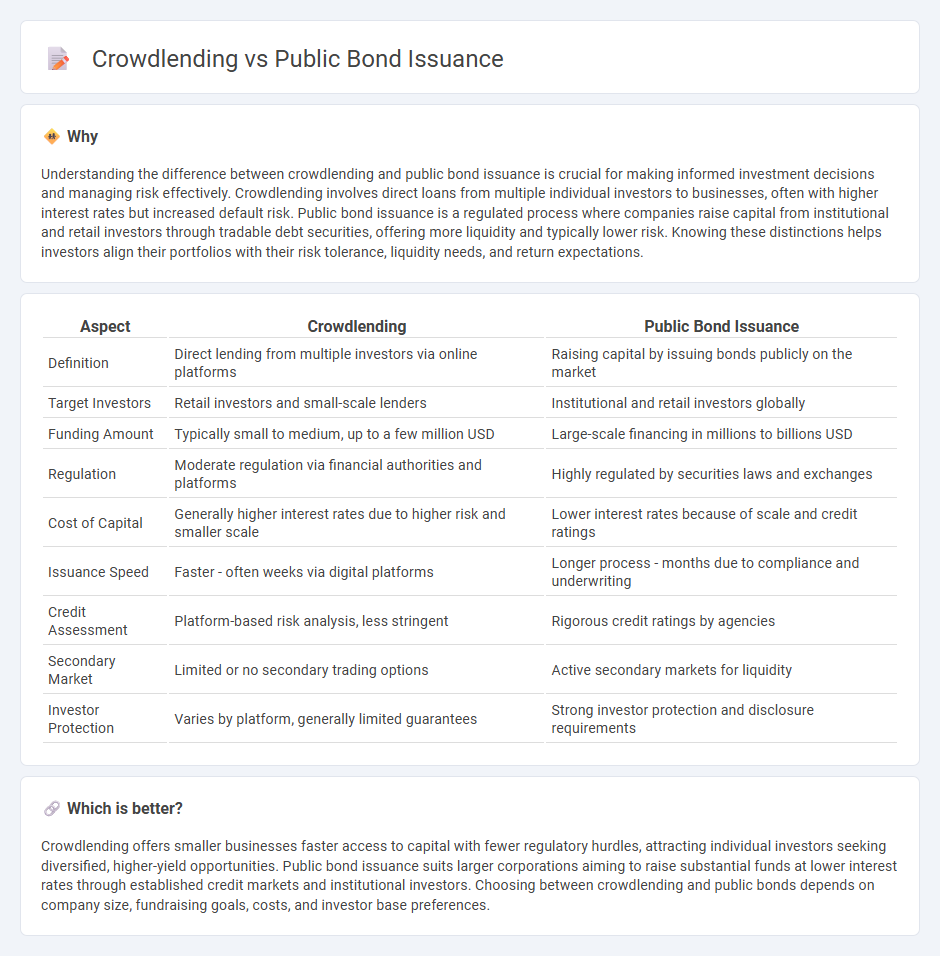
Understanding the difference between crowdlending and public bond issuance is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing risk effectively. Crowdlending involves direct loans from multiple individual investors to businesses, often with higher interest rates but increased default risk. Public bond issuance is a regulated process where companies raise capital from institutional and retail investors through tradable debt securities, offering more liquidity and typically lower risk. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their portfolios with their risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and return expectations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Crowdlending | Public Bond Issuance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct lending from multiple investors via online platforms | Raising capital by issuing bonds publicly on the market |
| Target Investors | Retail investors and small-scale lenders | Institutional and retail investors globally |
| Funding Amount | Typically small to medium, up to a few million USD | Large-scale financing in millions to billions USD |
| Regulation | Moderate regulation via financial authorities and platforms | Highly regulated by securities laws and exchanges |
| Cost of Capital | Generally higher interest rates due to higher risk and smaller scale | Lower interest rates because of scale and credit ratings |
| Issuance Speed | Faster - often weeks via digital platforms | Longer process - months due to compliance and underwriting |
| Credit Assessment | Platform-based risk analysis, less stringent | Rigorous credit ratings by agencies |
| Secondary Market | Limited or no secondary trading options | Active secondary markets for liquidity |
| Investor Protection | Varies by platform, generally limited guarantees | Strong investor protection and disclosure requirements |
Which is better?
Crowdlending offers smaller businesses faster access to capital with fewer regulatory hurdles, attracting individual investors seeking diversified, higher-yield opportunities. Public bond issuance suits larger corporations aiming to raise substantial funds at lower interest rates through established credit markets and institutional investors. Choosing between crowdlending and public bonds depends on company size, fundraising goals, costs, and investor base preferences.
Connection
Crowdlending and public bond issuance both serve as alternative financing methods allowing entities to raise capital directly from multiple investors, bypassing traditional bank loans. Crowdlending platforms enable small and medium-sized enterprises to access funds through numerous individual lenders, while public bond issuance attracts institutional and retail investors by offering tradable debt securities. Both approaches emphasize transparency, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance to facilitate trust and liquidity in debt financing markets.
Key Terms
Underwriting
Public bond issuance involves underwriting by financial institutions that assess credit risk, set interest rates, and guarantee bond sales to investors, ensuring capital is secured efficiently. Crowdlending platforms rely on decentralized lenders who individually evaluate borrower risk without a formal underwriting process, offering more flexible but potentially riskier financing. Discover the nuances of underwriting in both models to optimize your financing strategy.
Interest Rate
Public bond issuance typically offers fixed interest rates set by market demand, often appealing to institutional investors seeking predictable returns. Crowdlending platforms present varying interest rates influenced by borrower risk profiles and platform fees, attracting retail investors aiming for higher yields. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which financing method aligns best with your investment goals.
Default Risk
Public bond issuance typically involves a lower default risk due to stringent regulatory oversight and credit rating assessments by agencies such as Moody's or S&P, which provide investors with risk transparency. Crowdlending platforms often present a higher default risk as they cater to smaller businesses with limited credit histories and less regulatory scrutiny, increasing the probability of borrower default. Explore the nuances of default risk in different financing methods to make informed investment decisions.
Source and External Links
Bond Issue Fundamentals: A Guide to the Participants and the Process - Public bond issuance begins with the issuer selecting bond counsel and financial advisors, structuring the transaction to define the purpose and legal parameters, deciding the sale method, and preparing disclosure and legal documents before the bonds are offered.
What are municipal bonds and how are they used? - Tax Policy Center - Municipal bonds are issued by state and local governments to fund large public projects, typically as general obligation bonds backed by taxing power or revenue bonds secured by project-generated income.
Municipal Bonds - Fidelity Investments - Municipal bonds are public debt obligations used to finance infrastructure like schools and hospitals and come in various forms including zero-coupon bonds, original-issue discount bonds, and pre-refunded bonds with different tax and market characteristics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com