Laddered bond ETFs structure maturities across multiple dates, reducing interest rate risk and providing steady income streams. Core bond funds typically offer diversified exposure to investment-grade bonds, focusing on stability and long-term growth. Explore the benefits and differences to determine the best fit for your investment strategy.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between Laddered Bond ETFs and Core Bond Funds is crucial for managing interest rate risk and liquidity in a fixed-income portfolio. Laddered Bond ETFs provide staggered maturities to reduce reinvestment risk and offer higher flexibility with daily tradability on exchanges, while Core Bond Funds typically invest in a broad range of maturities and bond types for diversified exposure but may have less predictable cash flows. Investors seeking steady income streams and precise duration control benefit from laddered strategies, whereas those aiming for diversified exposure with professional management may prefer core funds. Understanding these differences enables tailored investment strategies aligned with individual risk tolerance and financial goals.
Comparison Table
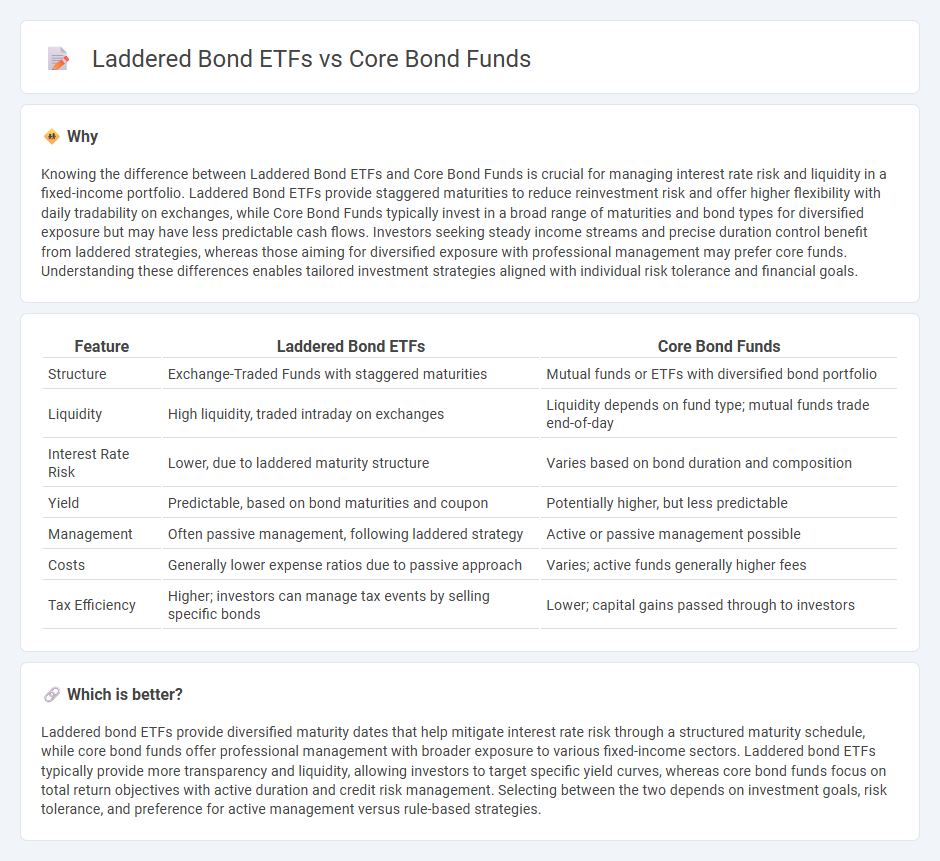
| Feature | Laddered Bond ETFs | Core Bond Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Exchange-Traded Funds with staggered maturities | Mutual funds or ETFs with diversified bond portfolio |
| Liquidity | High liquidity, traded intraday on exchanges | Liquidity depends on fund type; mutual funds trade end-of-day |
| Interest Rate Risk | Lower, due to laddered maturity structure | Varies based on bond duration and composition |
| Yield | Predictable, based on bond maturities and coupon | Potentially higher, but less predictable |
| Management | Often passive management, following laddered strategy | Active or passive management possible |
| Costs | Generally lower expense ratios due to passive approach | Varies; active funds generally higher fees |
| Tax Efficiency | Higher; investors can manage tax events by selling specific bonds | Lower; capital gains passed through to investors |
Which is better?
Laddered bond ETFs provide diversified maturity dates that help mitigate interest rate risk through a structured maturity schedule, while core bond funds offer professional management with broader exposure to various fixed-income sectors. Laddered bond ETFs typically provide more transparency and liquidity, allowing investors to target specific yield curves, whereas core bond funds focus on total return objectives with active duration and credit risk management. Selecting between the two depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and preference for active management versus rule-based strategies.
Connection
Laddered bond ETFs and core bond funds both manage fixed-income portfolios by spreading maturities to reduce interest rate risk and enhance cash flow predictability. Laddered bond ETFs systematically hold bonds with staggered maturities, while core bond funds invest broadly in diversified, high-quality bonds serving as the foundational fixed-income allocation in portfolios. Both investment vehicles aim to provide stable income streams and mitigate duration risk for conservative investors seeking steady returns.
Key Terms
Interest Rate Risk
Core bond funds typically offer diversified exposure with active management to mitigate interest rate risk, adjusting duration based on market outlook. Laddered bond ETFs employ a strategy of staggered maturities, reducing sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations by holding bonds that mature at different intervals. Explore the nuances of each approach to manage interest rate risk effectively in your portfolio.
Maturity Structure
Core bond funds typically feature a diversified maturity structure spanning short to long durations, providing balanced interest rate risk and income stability. Laddered bond ETFs invest in a series of bonds with staggered maturities to systematically manage reinvestment risk and offer predictable cash flows over time. Explore the nuances of maturity strategies to determine which option aligns best with your investment goals.
Yield
Core bond funds typically offer stable income with moderate yields, leveraging diversified portfolios managed by professionals to mitigate risks across various bond sectors. Laddered bond ETFs provide enhanced yield potential by staggering maturities, allowing investors to capture rising interest rates while maintaining liquidity and reducing reinvestment risk. Explore the differences in yield strategies between core bond funds and laddered bond ETFs to optimize your fixed-income portfolio.
Source and External Links
VCOBX Core Bond Fund Admiral Shares - Vanguard Advisors - Core Bond Fund aims to provide total return with a moderate level of current income primarily through investment-grade bonds.
LAPLX | Core Plus Bond Fund Class A | Lord Abbett - This fund invests broadly in fixed income securities, including non-U.S. debt, seeking enhanced returns through diversified bond exposure with a 0.63% expense ratio.
Nuveen Core Bond Fund | TIBHX TIBDX TIORX TIDPX TIDRX TBBWX - Nuveen's Core Bond Fund invests across a broad range of bonds such as government, corporate, and asset-backed securities, focusing on identifying undervalued bonds for outperformance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com