Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to identify investment opportunities through data-driven techniques and financial statement evaluation. Fundamental investing relies solely on analyzing company financials, management quality, and market positioning to determine intrinsic value and long-term potential. Explore the advantages and strategies of both approaches to enhance your investment decisions.
Why it is important
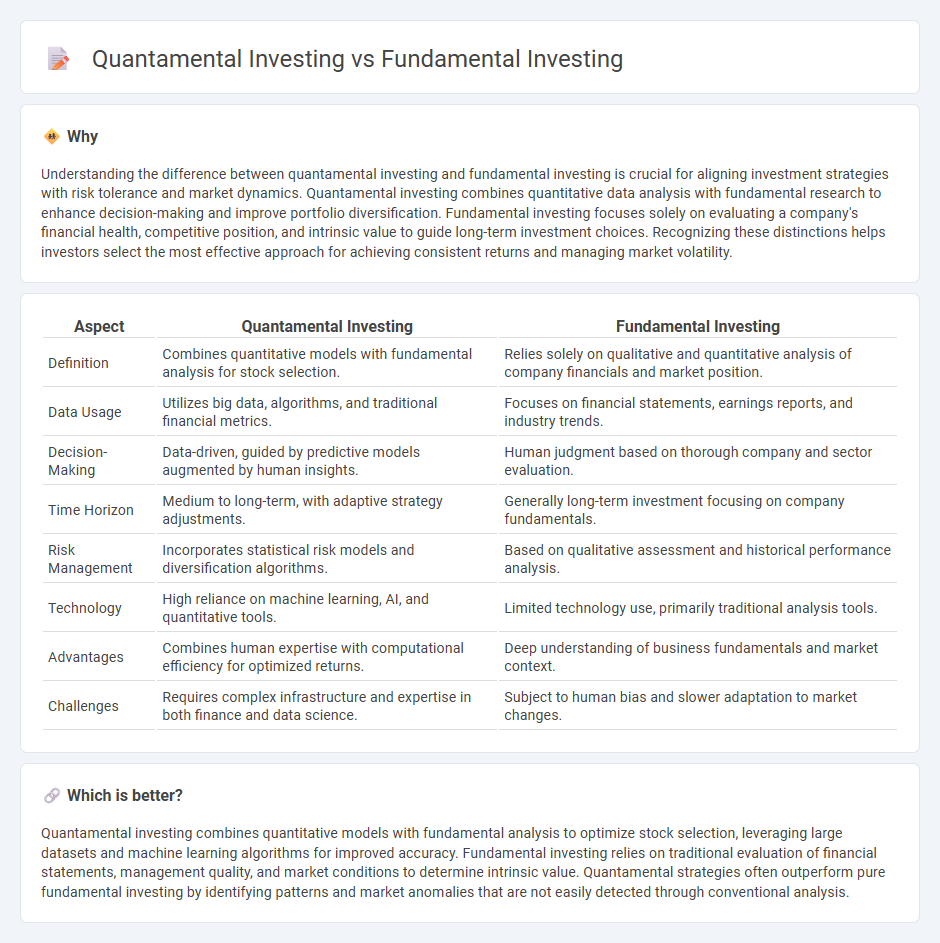
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing and fundamental investing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with risk tolerance and market dynamics. Quantamental investing combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research to enhance decision-making and improve portfolio diversification. Fundamental investing focuses solely on evaluating a company's financial health, competitive position, and intrinsic value to guide long-term investment choices. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors select the most effective approach for achieving consistent returns and managing market volatility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Fundamental Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis for stock selection. | Relies solely on qualitative and quantitative analysis of company financials and market position. |
| Data Usage | Utilizes big data, algorithms, and traditional financial metrics. | Focuses on financial statements, earnings reports, and industry trends. |
| Decision-Making | Data-driven, guided by predictive models augmented by human insights. | Human judgment based on thorough company and sector evaluation. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long-term, with adaptive strategy adjustments. | Generally long-term investment focusing on company fundamentals. |
| Risk Management | Incorporates statistical risk models and diversification algorithms. | Based on qualitative assessment and historical performance analysis. |
| Technology | High reliance on machine learning, AI, and quantitative tools. | Limited technology use, primarily traditional analysis tools. |
| Advantages | Combines human expertise with computational efficiency for optimized returns. | Deep understanding of business fundamentals and market context. |
| Challenges | Requires complex infrastructure and expertise in both finance and data science. | Subject to human bias and slower adaptation to market changes. |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to optimize stock selection, leveraging large datasets and machine learning algorithms for improved accuracy. Fundamental investing relies on traditional evaluation of financial statements, management quality, and market conditions to determine intrinsic value. Quantamental strategies often outperform pure fundamental investing by identifying patterns and market anomalies that are not easily detected through conventional analysis.
Connection
Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to identify undervalued stocks by integrating data-driven algorithms and traditional financial metrics. Fundamental investing focuses on assessing a company's intrinsic value through earnings, cash flow, and balance sheet strength. This synergy enhances investment decisions by leveraging both statistical patterns and deep financial insights.
Key Terms
**Fundamental Investing:**
Fundamental investing emphasizes analyzing a company's financial statements, management quality, industry position, and economic factors to determine its intrinsic value. This approach relies on metrics such as earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and return on equity (ROE) to identify undervalued stocks with strong growth potential. Explore more about how fundamental investing strategies can enhance your portfolio performance.
Earnings
Fundamental investing centers on evaluating a company's earnings growth, stability, and profitability metrics to determine intrinsic value, while quantamental investing integrates these traditional financial indicators with quantitative data analysis and algorithmic models to enhance investment decisions. This hybrid approach leverages earnings reports alongside statistical patterns to identify undervalued stocks with higher precision. Explore more insights on optimizing investment strategies through the blend of fundamental and quantitative methods.
Valuation
Fundamental investing centers on analyzing a company's intrinsic value through financial statements, earnings reports, and market conditions to identify undervalued stocks. Quantamental investing integrates quantitative models with traditional fundamental analysis, using algorithms to process large data sets, including valuation metrics, to enhance investment decisions. Explore more to understand how combining quantitative methods with fundamental valuation can optimize your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Basics of Fundamental Investing - TrendSpider - Fundamental investing is a strategy for selecting stocks based on analyzing a company's financials and other data to determine its intrinsic value for long-term investment decisions.
Fundamental Analysis vs. Technical Analysis - SmartAsset - Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health, industry status, and economic conditions to estimate the intrinsic value of its stock, using key metrics like earnings per share, P/E ratio, and dividend yield.
Fundamental analysis - Wikipedia - Fundamental analysis involves studying financial statements and economic indicators, using top-down or bottom-up approaches, to identify undervalued or strong companies for various investment styles like buy and hold or value investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com