Liquid staking enables users to earn rewards on their staked assets while maintaining liquidity by receiving tokenized representations of their staked holdings. Direct on-chain staking involves locking up crypto assets in a blockchain protocol to support network security and consensus, typically restricting access to the staked tokens until the unstaking period completes. Explore the advantages and trade-offs of liquid staking versus direct on-chain staking to optimize your decentralized finance strategy.
Why it is important
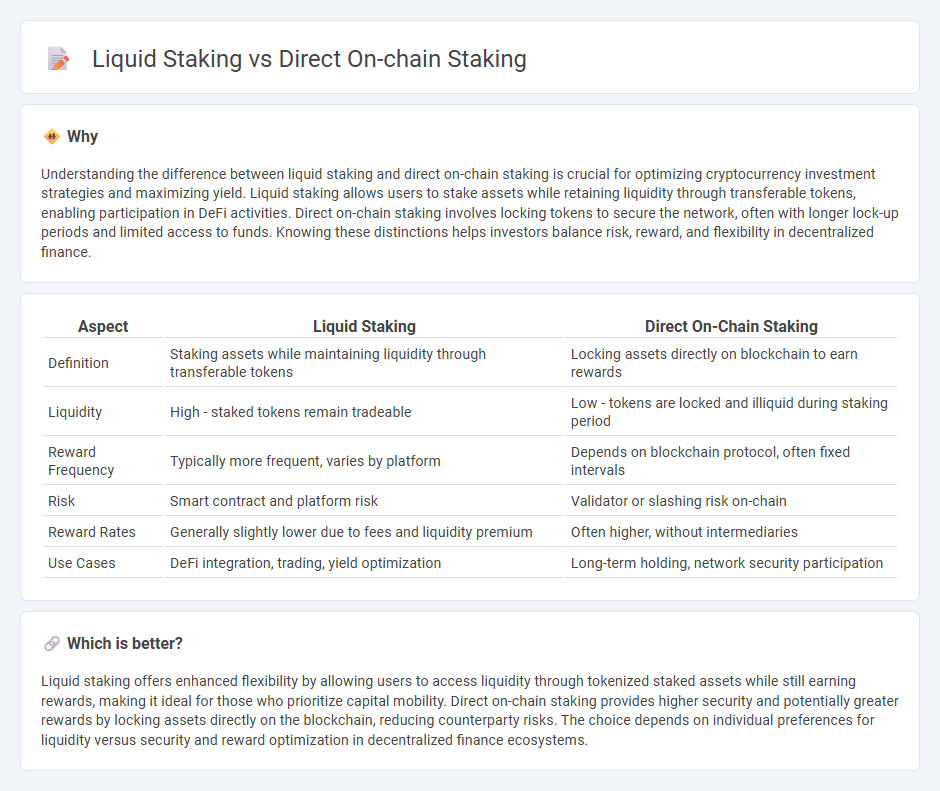
Understanding the difference between liquid staking and direct on-chain staking is crucial for optimizing cryptocurrency investment strategies and maximizing yield. Liquid staking allows users to stake assets while retaining liquidity through transferable tokens, enabling participation in DeFi activities. Direct on-chain staking involves locking tokens to secure the network, often with longer lock-up periods and limited access to funds. Knowing these distinctions helps investors balance risk, reward, and flexibility in decentralized finance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquid Staking | Direct On-Chain Staking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staking assets while maintaining liquidity through transferable tokens | Locking assets directly on blockchain to earn rewards |
| Liquidity | High - staked tokens remain tradeable | Low - tokens are locked and illiquid during staking period |
| Reward Frequency | Typically more frequent, varies by platform | Depends on blockchain protocol, often fixed intervals |
| Risk | Smart contract and platform risk | Validator or slashing risk on-chain |
| Reward Rates | Generally slightly lower due to fees and liquidity premium | Often higher, without intermediaries |
| Use Cases | DeFi integration, trading, yield optimization | Long-term holding, network security participation |
Which is better?
Liquid staking offers enhanced flexibility by allowing users to access liquidity through tokenized staked assets while still earning rewards, making it ideal for those who prioritize capital mobility. Direct on-chain staking provides higher security and potentially greater rewards by locking assets directly on the blockchain, reducing counterparty risks. The choice depends on individual preferences for liquidity versus security and reward optimization in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Connection
Liquid staking and direct on-chain staking both enable crypto holders to earn rewards by participating in network security and consensus. Liquid staking allows users to stake assets while maintaining liquidity through derivative tokens, whereas direct on-chain staking requires locking assets without immediate access. Both methods contribute to securing Proof-of-Stake blockchains but offer different trade-offs between liquidity and staking control.
Key Terms
Validator
Direct on-chain staking requires delegators to select and stake tokens directly with validators, ensuring maximum control and security while earning staking rewards. Liquid staking allows token holders to stake through protocols that issue derivative tokens, providing liquidity but depending on the protocol's chosen validators and potentially higher counterparty risk. Explore detailed comparisons of validator performance, security models, and reward structures to optimize your staking strategy.
Liquidity
Direct on-chain staking involves locking up tokens in a blockchain protocol to earn rewards, but these assets become illiquid and cannot be moved or traded during the staking period. Liquid staking, in contrast, issues tokenized derivatives representing staked assets, allowing users to maintain liquidity and participate in DeFi activities without sacrificing staking rewards. Explore the benefits and trade-offs of both staking methods to optimize your crypto portfolio effectively.
Derivative Token
Direct on-chain staking involves locking native blockchain tokens to secure the network and earn rewards, with stakers often facing liquidity constraints as assets remain locked. Liquid staking issues derivative tokens representing staked assets, enabling users to maintain asset liquidity and participate in DeFi ecosystems while still earning staking yields. Explore how derivative tokens transform staking flexibility and asset utility in decentralized finance.
Source and External Links
On-Chain Staking Guide - Direct on-chain staking means you stake your tokens by locking them on the blockchain itself, where after approval, the assets are staked on-chain to start generating rewards, with statuses like Pending, Activating, and finally Staked indicating the process progress.
Best crypto staking platforms in 2024 - On-chain staking is more secure and decentralized because tokens are staked directly on the blockchain, requiring users often to run their own nodes, contrasting with off-chain staking done via intermediaries like exchanges.
REX-Osprey Launches First US Solana + Staking ETF, ... - In a regulated investment context, direct on-chain staking involves staking SOL tokens directly on-chain with rewards distributed periodically, as exemplified by the first US Solana staking ETF offering real on-chain protocol participation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com