Carbon credits represent tradable certificates allowing companies to offset their greenhouse gas emissions by investing in emission reduction projects. Climate bonds are debt instruments issued to finance projects that contribute to environmental sustainability and climate change mitigation. Explore their distinct mechanisms and benefits to understand how each supports global climate goals.
Why it is important
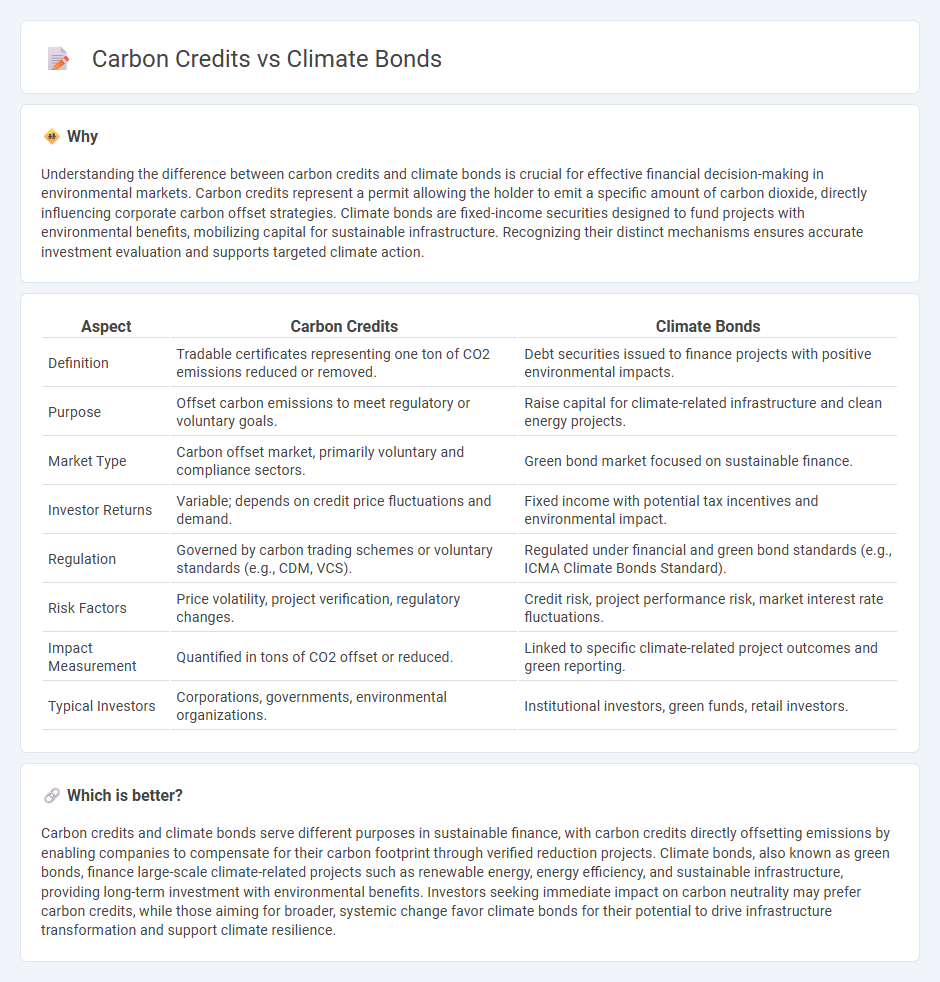
Understanding the difference between carbon credits and climate bonds is crucial for effective financial decision-making in environmental markets. Carbon credits represent a permit allowing the holder to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide, directly influencing corporate carbon offset strategies. Climate bonds are fixed-income securities designed to fund projects with environmental benefits, mobilizing capital for sustainable infrastructure. Recognizing their distinct mechanisms ensures accurate investment evaluation and supports targeted climate action.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credits | Climate Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tradable certificates representing one ton of CO2 emissions reduced or removed. | Debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts. |
| Purpose | Offset carbon emissions to meet regulatory or voluntary goals. | Raise capital for climate-related infrastructure and clean energy projects. |
| Market Type | Carbon offset market, primarily voluntary and compliance sectors. | Green bond market focused on sustainable finance. |
| Investor Returns | Variable; depends on credit price fluctuations and demand. | Fixed income with potential tax incentives and environmental impact. |
| Regulation | Governed by carbon trading schemes or voluntary standards (e.g., CDM, VCS). | Regulated under financial and green bond standards (e.g., ICMA Climate Bonds Standard). |
| Risk Factors | Price volatility, project verification, regulatory changes. | Credit risk, project performance risk, market interest rate fluctuations. |
| Impact Measurement | Quantified in tons of CO2 offset or reduced. | Linked to specific climate-related project outcomes and green reporting. |
| Typical Investors | Corporations, governments, environmental organizations. | Institutional investors, green funds, retail investors. |
Which is better?
Carbon credits and climate bonds serve different purposes in sustainable finance, with carbon credits directly offsetting emissions by enabling companies to compensate for their carbon footprint through verified reduction projects. Climate bonds, also known as green bonds, finance large-scale climate-related projects such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure, providing long-term investment with environmental benefits. Investors seeking immediate impact on carbon neutrality may prefer carbon credits, while those aiming for broader, systemic change favor climate bonds for their potential to drive infrastructure transformation and support climate resilience.
Connection
Carbon credits and climate bonds are financial instruments designed to support environmental sustainability by incentivizing reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon credits represent a tradable permit allowing organizations to emit a specified amount of carbon dioxide, creating a market-driven approach to emission reduction. Climate bonds, on the other hand, are debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, often using proceeds to fund initiatives that generate or benefit from carbon credits, thus linking financial markets to climate action.
Key Terms
Green Bonds
Green Bonds finance projects that generate positive environmental impacts, primarily in renewable energy, clean transportation, and energy efficiency, offering investors a direct way to support sustainable development. Climate Bonds are a subset certified under the Climate Bonds Standard, ensuring transparency and strict environmental criteria, while carbon credits represent tradable permits that offset emissions rather than directly fund projects. Explore how Green Bonds serve as powerful financial tools driving climate action and sustainable investment.
Emissions Trading
Climate bonds finance projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, offering fixed returns linked to environmental impact, while carbon credits are tradable permits allowing companies to emit a specific amount of CO2, facilitating compliance with Emissions Trading Systems (ETS). Emissions Trading, or cap-and-trade, sets a limit on total emissions and uses carbon credits to incentivize reductions within that cap. Explore how these mechanisms drive sustainable finance and emission reductions in global markets.
Sustainable Finance
Climate bonds fund projects specifically designed to reduce carbon emissions and promote renewable energy, aligning with the goals of sustainable finance by providing transparent, impact-driven investment opportunities. Carbon credits represent quantifiable emission reductions or removals, allowing companies to offset their carbon footprint and comply with regulatory or voluntary sustainability targets. Discover how these financial instruments drive environmental goals and catalyze green investments in sustainable finance.
Source and External Links
Green Bonds - World Bank Treasury - The World Bank Green Bond is a fixed income product that raises funds to support projects aimed at mitigating climate change and helping affected populations adapt, highlighting a global cooperative effort to address environmental and social challenges.
What are Green Bonds and How Can They Fight the Climate Crisis? - Green bonds finance projects with positive environmental impacts and began in 2008 with the World Bank issuing the first official green bond, establishing standards for impact reporting and project eligibility.
Climate Bonds | Homepage - Climate Bonds Initiative is an international organization that mobilizes global capital to combat climate change by certifying green bonds through a science-based standard, with aligned market volume reaching USD 670.9 billion in 2024 and over USD 6 trillion outstanding globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com