Tokenization transforms real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and transparent transaction records. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to provide open, permissionless financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how tokenization and DeFi are reshaping the financial landscape.
Why it is important
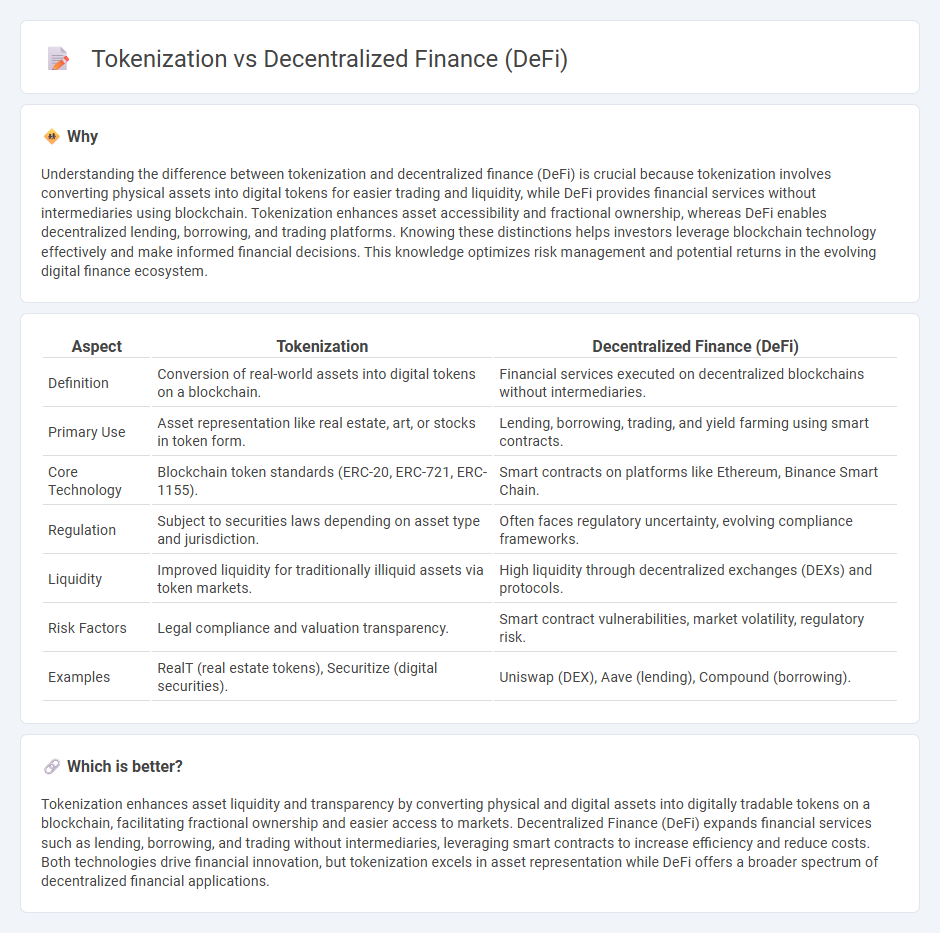
Understanding the difference between tokenization and decentralized finance (DeFi) is crucial because tokenization involves converting physical assets into digital tokens for easier trading and liquidity, while DeFi provides financial services without intermediaries using blockchain. Tokenization enhances asset accessibility and fractional ownership, whereas DeFi enables decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading platforms. Knowing these distinctions helps investors leverage blockchain technology effectively and make informed financial decisions. This knowledge optimizes risk management and potential returns in the evolving digital finance ecosystem.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenization | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion of real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. | Financial services executed on decentralized blockchains without intermediaries. |
| Primary Use | Asset representation like real estate, art, or stocks in token form. | Lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming using smart contracts. |
| Core Technology | Blockchain token standards (ERC-20, ERC-721, ERC-1155). | Smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain. |
| Regulation | Subject to securities laws depending on asset type and jurisdiction. | Often faces regulatory uncertainty, evolving compliance frameworks. |
| Liquidity | Improved liquidity for traditionally illiquid assets via token markets. | High liquidity through decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and protocols. |
| Risk Factors | Legal compliance and valuation transparency. | Smart contract vulnerabilities, market volatility, regulatory risk. |
| Examples | RealT (real estate tokens), Securitize (digital securities). | Uniswap (DEX), Aave (lending), Compound (borrowing). |
Which is better?
Tokenization enhances asset liquidity and transparency by converting physical and digital assets into digitally tradable tokens on a blockchain, facilitating fractional ownership and easier access to markets. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) expands financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries, leveraging smart contracts to increase efficiency and reduce costs. Both technologies drive financial innovation, but tokenization excels in asset representation while DeFi offers a broader spectrum of decentralized financial applications.
Connection
Tokenization transforms real-world assets into digital tokens on blockchain platforms, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages these tokens to create open financial applications such as decentralized exchanges, lending protocols, and yield farming. The synergy between tokenization and DeFi enhances transparency, reduces intermediaries, and expands access to financial services globally.
Key Terms
Smart Contracts
Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages smart contracts to automate financial transactions, ensuring transparency and reducing the need for intermediaries, whereas tokenization employs smart contracts to digitize assets, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity. DeFi protocols such as Uniswap and Aave use smart contracts to facilitate lending, borrowing, and trading without centralized control, while tokenization platforms like Polymath create security tokens representing real-world assets through programmable agreements. Explore how smart contracts bridge DeFi and tokenization to revolutionize financial ecosystems.
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are fundamental to decentralized finance (DeFi), enabling automated trading and lending without intermediaries through smart contracts. Tokenization transforms real-world assets into digital tokens, enhancing liquidity by allowing fractional ownership and seamless transfer within these pools. Explore how liquidity pools and tokenization synergize to revolutionize asset management and trading efficiency.
Asset-backed Tokens
Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial services without traditional intermediaries, while tokenization converts real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. Asset-backed tokens specifically represent ownership of physical assets like real estate, commodities, or fine art, providing liquidity and fractional ownership opportunities previously unavailable in traditional markets. Explore how asset-backed tokens are transforming investment strategies and enhancing market accessibility.
Source and External Links
Decentralized finance - DeFi provides financial instruments and services through smart contracts on a programmable, permissionless blockchain, enabling peer-to-peer financial activities without intermediaries like banks, but carries risks like coding errors and hacks.
What is DeFi? - DeFi is an umbrella term for peer-to-peer financial services on public blockchains, mainly Ethereum, allowing users to borrow, lend, trade, and earn interest without accounts or intermediaries, making finance open, fast, flexible, and transparent.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Transformative Potential & Associated Risks - DeFi operates without trusted intermediaries by using blockchains and smart contracts for payments, lending, trading, and insurance, offering innovative financial products but also posing financial stability and regulatory challenges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com