Crowdlending allows multiple investors to fund a business through online platforms, offering diversified risk and fixed returns, whereas angel investing involves affluent individuals providing capital and mentorship in exchange for equity stakes. Crowdlending is accessible to a broader audience with lower minimum investments, while angel investing typically requires substantial capital and offers more active involvement. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which financing method suits your investment goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between crowdlending and angel investing is crucial for making informed financial decisions concerning risk, control, and return. Crowdlending involves multiple investors lending money to businesses or individuals with fixed interest returns, while angel investing entails affluent individuals providing capital for equity stakes in startups with high growth potential. Investors must evaluate factors such as liquidity, involvement level, and regulatory implications to align investments with their financial goals. This knowledge optimizes portfolio diversification and mitigates investment risks in alternative financing markets.
Comparison Table
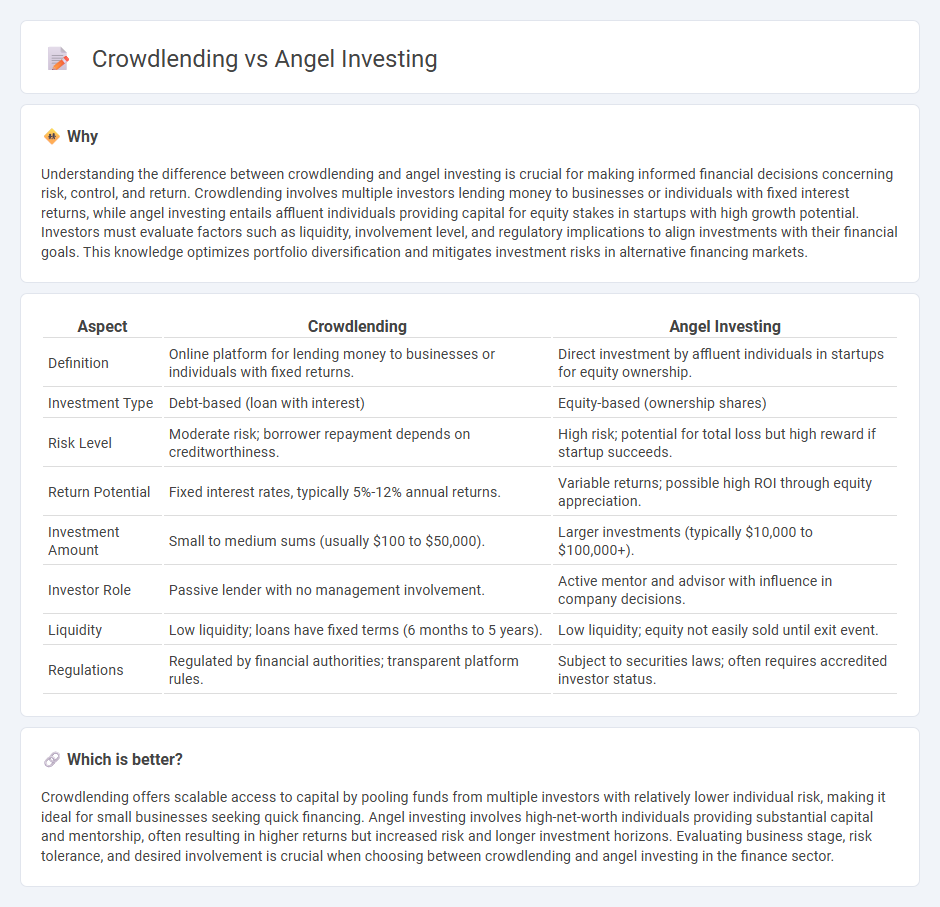
| Aspect | Crowdlending | Angel Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online platform for lending money to businesses or individuals with fixed returns. | Direct investment by affluent individuals in startups for equity ownership. |
| Investment Type | Debt-based (loan with interest) | Equity-based (ownership shares) |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk; borrower repayment depends on creditworthiness. | High risk; potential for total loss but high reward if startup succeeds. |
| Return Potential | Fixed interest rates, typically 5%-12% annual returns. | Variable returns; possible high ROI through equity appreciation. |
| Investment Amount | Small to medium sums (usually $100 to $50,000). | Larger investments (typically $10,000 to $100,000+). |
| Investor Role | Passive lender with no management involvement. | Active mentor and advisor with influence in company decisions. |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity; loans have fixed terms (6 months to 5 years). | Low liquidity; equity not easily sold until exit event. |
| Regulations | Regulated by financial authorities; transparent platform rules. | Subject to securities laws; often requires accredited investor status. |
Which is better?
Crowdlending offers scalable access to capital by pooling funds from multiple investors with relatively lower individual risk, making it ideal for small businesses seeking quick financing. Angel investing involves high-net-worth individuals providing substantial capital and mentorship, often resulting in higher returns but increased risk and longer investment horizons. Evaluating business stage, risk tolerance, and desired involvement is crucial when choosing between crowdlending and angel investing in the finance sector.
Connection
Crowdlending and angel investing both serve as alternative financing methods that directly connect entrepreneurs with non-traditional investors, enabling startups to access capital without relying on conventional banks. Crowdlending allows a large number of individual lenders to provide small loans to businesses, while angel investors offer equity funding or convertible debt, often bringing industry expertise and mentorship. Together, these models expand funding opportunities and diversify investment risks within the finance ecosystem.
Key Terms
Equity
Angel investing involves individuals providing capital to startups in exchange for equity ownership, offering potential high returns linked to the company's success. Crowdlending, by contrast, entails lending money to businesses or projects with fixed interest repayments, without acquiring ownership stakes. Explore the detailed differences and benefits of equity-focused funding approaches to make informed investment decisions.
Interest Rate
Angel investing typically offers lower immediate interest rates but the potential for significant equity gains, whereas crowdlending provides fixed interest rates that deliver consistent returns over a set period. Crowdlending interest rates often range between 5% and 12%, appealing to investors seeking predictable income streams without ownership stakes. Discover more about how these financing methods impact your investment strategy and risk profile.
Risk
Angel investing involves high risk as investors provide capital to early-stage startups with uncertain prospects, potentially leading to total loss of investment. Crowdlending risks include borrower default and platform insolvency, though typically with more predictable returns due to fixed interest payments. Discover detailed comparisons and risk mitigation strategies to make informed investment decisions.
Source and External Links
Understanding angel financing and investing - J.P. Morgan - Angel investors are individuals who invest their own money into startups in exchange for equity or convertible debt, helping founders move beyond initial funding from family and friends to reach their first professional financing round, often providing mentorship, advice, and networks to de-risk the business and accelerate progress.
Demystifying Angel Investing - Angel Capital Association - Angel investing involves providing capital to startups in exchange for potential high returns and the opportunity to make a positive economic impact, with tax incentives and a supportive community available to help new investors learn and connect.
Angel Investors - The Hartford Insurance - Angel investors are wealthy individuals who use their own funds to invest smaller amounts in early-stage businesses, generally seeking equity and an eventual exit, and often provide mentoring and management support to help startups grow without the need to repay loans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com