Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading offers direct peer-to-peer asset exchanges without centralized intermediaries, enhancing transparency and reducing counterparty risk. Dark pools provide institutional investors with private, anonymous environments to execute large block trades away from public exchanges, minimizing market impact. Explore the nuances and benefits of decentralized OTC trading compared to dark pool mechanisms to optimize your trading strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading and Dark pools is crucial for investors because OTC trading involves direct peer-to-peer transactions with greater flexibility and less regulation, while Dark pools are private exchanges where large blocks of securities are traded anonymously to minimize market impact. Decentralized OTC trading offers transparency in settlement and custody through blockchain technology, whereas Dark pools provide liquidity without revealing trade intentions to the public market. Knowing these distinctions helps in assessing risks, execution speed, market impact, and regulatory exposure. This knowledge optimizes trading strategies and ensures compliance in complex financial markets.
Comparison Table
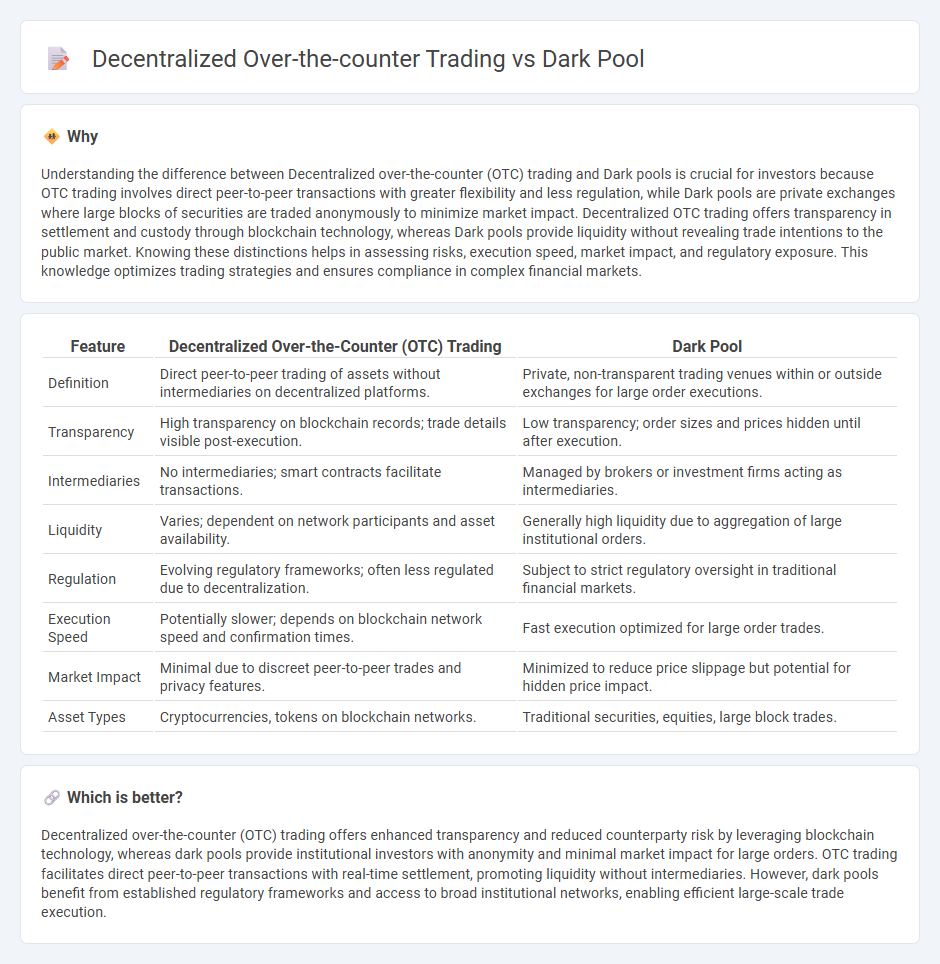
| Feature | Decentralized Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading | Dark Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer trading of assets without intermediaries on decentralized platforms. | Private, non-transparent trading venues within or outside exchanges for large order executions. |
| Transparency | High transparency on blockchain records; trade details visible post-execution. | Low transparency; order sizes and prices hidden until after execution. |
| Intermediaries | No intermediaries; smart contracts facilitate transactions. | Managed by brokers or investment firms acting as intermediaries. |
| Liquidity | Varies; dependent on network participants and asset availability. | Generally high liquidity due to aggregation of large institutional orders. |
| Regulation | Evolving regulatory frameworks; often less regulated due to decentralization. | Subject to strict regulatory oversight in traditional financial markets. |
| Execution Speed | Potentially slower; depends on blockchain network speed and confirmation times. | Fast execution optimized for large order trades. |
| Market Impact | Minimal due to discreet peer-to-peer trades and privacy features. | Minimized to reduce price slippage but potential for hidden price impact. |
| Asset Types | Cryptocurrencies, tokens on blockchain networks. | Traditional securities, equities, large block trades. |
Which is better?
Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading offers enhanced transparency and reduced counterparty risk by leveraging blockchain technology, whereas dark pools provide institutional investors with anonymity and minimal market impact for large orders. OTC trading facilitates direct peer-to-peer transactions with real-time settlement, promoting liquidity without intermediaries. However, dark pools benefit from established regulatory frameworks and access to broad institutional networks, enabling efficient large-scale trade execution.
Connection
Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading and dark pools both facilitate private asset transactions outside traditional public exchanges, enhancing market liquidity while minimizing price impact and information leakage. These trading venues use blockchain and encrypted protocols to ensure transaction confidentiality and counterparty anonymity, attracting institutional investors seeking discretion. By operating off-exchange, decentralized OTC platforms and dark pools reduce systemic risk and enable large-volume trades with improved execution efficiency and lower trading costs.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Dark pools provide institutional investors with high liquidity by enabling large block trades to occur without public order book exposure, minimizing market impact and price slippage. Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading offers liquidity through peer-to-peer networks and smart contracts, facilitating direct and transparent asset swaps without intermediaries but may face challenges in matching large orders efficiently. Explore how liquidity dynamics differ between dark pools and decentralized OTC platforms to optimize trading strategies.
Anonymity
Dark pools provide institutional investors with high anonymity by allowing large block trades to occur away from public exchanges, minimizing market impact and maintaining privacy. Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading enhances anonymity by using blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, preserving user identity and offering transparency through distributed ledgers. Explore the nuances of anonymity in dark pools versus decentralized OTC trading to better understand which option suits your trading strategy.
Transparency
Dark pools offer private trading venues where large orders execute without public visibility, reducing market impact but limiting transparency. Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading utilizes blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions, enhancing transparency through immutable ledger records accessible to participants. Explore the benefits and challenges of transparency in these trading methods to understand their impact on financial markets.
Source and External Links
Dark Pool - Overview, How It Works, Pros and Cons - Dark pools are privately organized financial exchanges where securities are traded without public exposure, primarily catering to institutional investors who want to conceal their large trades and avoid market price impact.
Can You Swim in a Dark Pool? | FINRA.org - Dark pools are alternative trading systems designed for anonymous, off-exchange block trades by large investors, shielding order details from public view until after execution.
A Beginner's Guide to Dark Pool Trading - Nasdaq - Dark pools are private venues that allow institutional investors to execute substantial trades discreetly, avoiding significant market disruption and price movement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com