Tokenized treasury bills represent government debt issued on blockchain platforms, offering enhanced liquidity and transparency compared to traditional instruments. Corporate bonds are debt securities issued by companies to raise capital, often carrying higher risk and yield relative to government-backed treasury bills. Explore the differences and benefits of tokenized treasury bills versus corporate bonds to optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
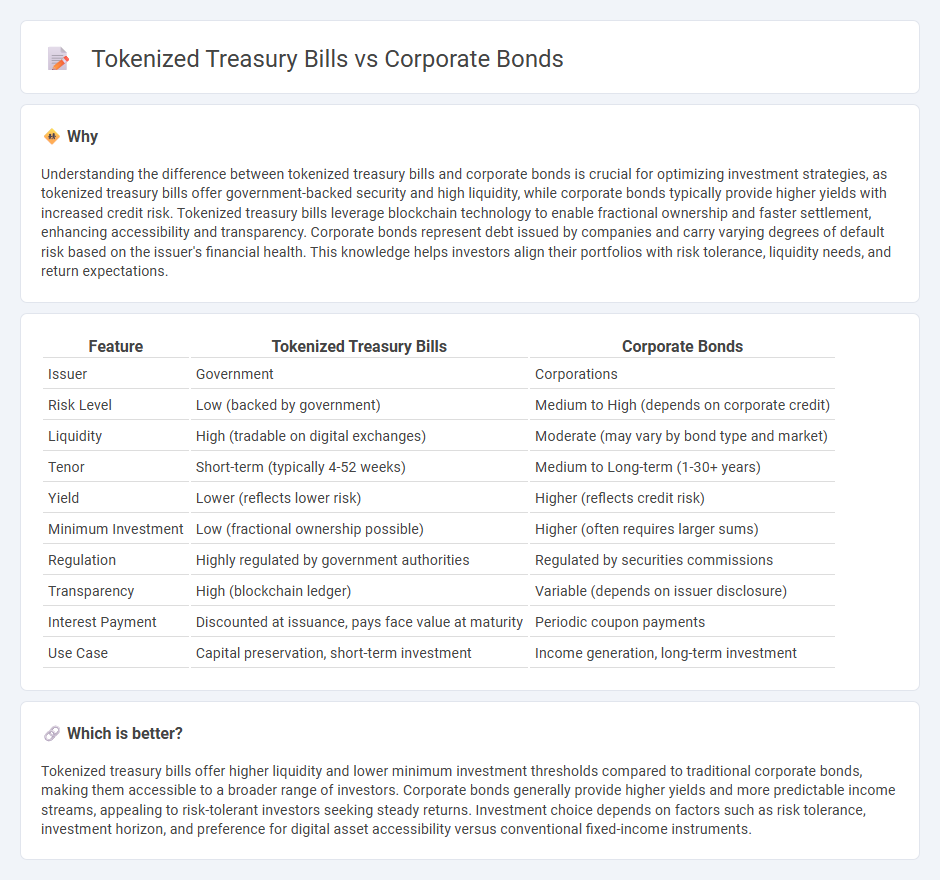
Understanding the difference between tokenized treasury bills and corporate bonds is crucial for optimizing investment strategies, as tokenized treasury bills offer government-backed security and high liquidity, while corporate bonds typically provide higher yields with increased credit risk. Tokenized treasury bills leverage blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership and faster settlement, enhancing accessibility and transparency. Corporate bonds represent debt issued by companies and carry varying degrees of default risk based on the issuer's financial health. This knowledge helps investors align their portfolios with risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and return expectations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tokenized Treasury Bills | Corporate Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Government | Corporations |
| Risk Level | Low (backed by government) | Medium to High (depends on corporate credit) |
| Liquidity | High (tradable on digital exchanges) | Moderate (may vary by bond type and market) |
| Tenor | Short-term (typically 4-52 weeks) | Medium to Long-term (1-30+ years) |
| Yield | Lower (reflects lower risk) | Higher (reflects credit risk) |
| Minimum Investment | Low (fractional ownership possible) | Higher (often requires larger sums) |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by government authorities | Regulated by securities commissions |
| Transparency | High (blockchain ledger) | Variable (depends on issuer disclosure) |
| Interest Payment | Discounted at issuance, pays face value at maturity | Periodic coupon payments |
| Use Case | Capital preservation, short-term investment | Income generation, long-term investment |
Which is better?
Tokenized treasury bills offer higher liquidity and lower minimum investment thresholds compared to traditional corporate bonds, making them accessible to a broader range of investors. Corporate bonds generally provide higher yields and more predictable income streams, appealing to risk-tolerant investors seeking steady returns. Investment choice depends on factors such as risk tolerance, investment horizon, and preference for digital asset accessibility versus conventional fixed-income instruments.
Connection
Tokenized treasury bills and corporate bonds are connected through blockchain technology, which enables the digital representation and fractional ownership of traditional financial instruments. This connection improves liquidity, transparency, and accessibility for investors by allowing seamless trading of tokenized assets on decentralized platforms. Both tokenized treasury bills and corporate bonds benefit from reduced settlement times and lower transaction costs compared to conventional securities.
Key Terms
Yield
Corporate bonds typically offer higher yields than tokenized treasury bills due to the increased credit risk associated with corporate debt compared to government securities. Tokenized treasury bills tend to provide lower yields but come with greater liquidity and lower risk, benefiting from government backing and blockchain transparency. Explore detailed yield comparisons and risk assessments to make informed investment decisions.
Liquidity
Corporate bonds traditionally offer moderate liquidity through established secondary markets, but trading can be limited by regulatory constraints and longer settlement times. Tokenized treasury bills leverage blockchain technology to provide enhanced liquidity with near-instant settlement and 24/7 trading capabilities, reducing counterparty risks and increasing market accessibility. Explore the evolving landscape of liquidity in tokenized financial instruments to understand their potential impact on investment strategies.
Settlement
Corporate bonds typically settle within T+2 business days, involving intermediaries such as clearinghouses and custodians, which can delay the final transfer of ownership. Tokenized treasury bills leverage blockchain technology to enable near-instantaneous settlement, drastically reducing counterparty risk and enhancing liquidity through automated smart contracts. Explore how these differences impact investment efficiency and security for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Understanding Corporate Bonds - Corporate bonds are debt issued by companies to raise funds for expansion, paying investors interest and principal at maturity, categorized by maturity (short, medium, long-term) and credit quality (investment-grade vs speculative-grade).
Corporate Bonds - Corporate bonds are debt obligations from corporations with fixed-rate coupons and are rated by agencies as investment grade or high yield, reflecting different risk and return profiles.
Corporate Bonds - Buying corporate bonds means lending money to a company in exchange for interest payments and principal repayment, with bondholders having priority over shareholders in case of bankruptcy but facing default risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com