Flash loan attacks exploit decentralized finance protocols by borrowing vast amounts of cryptocurrency without collateral, aiming to manipulate market prices or execute arbitrage strategies. Dark pool manipulation involves trading large blocks of securities anonymously to influence market prices and mislead other investors, often impacting liquidity and transparency. Explore these complex financial tactics to understand their impact on market integrity and regulatory challenges.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loan attacks and dark pool manipulation is crucial for financial security and regulatory compliance. Flash loan attacks exploit smart contract vulnerabilities for instant, uncollateralized loans leading to market exploits and potential losses. Dark pool manipulation involves undisclosed trading strategies that can distort market prices and undermine investor trust. Identifying these distinct threats helps in devising targeted defenses and promoting transparent, fair markets.
Comparison Table
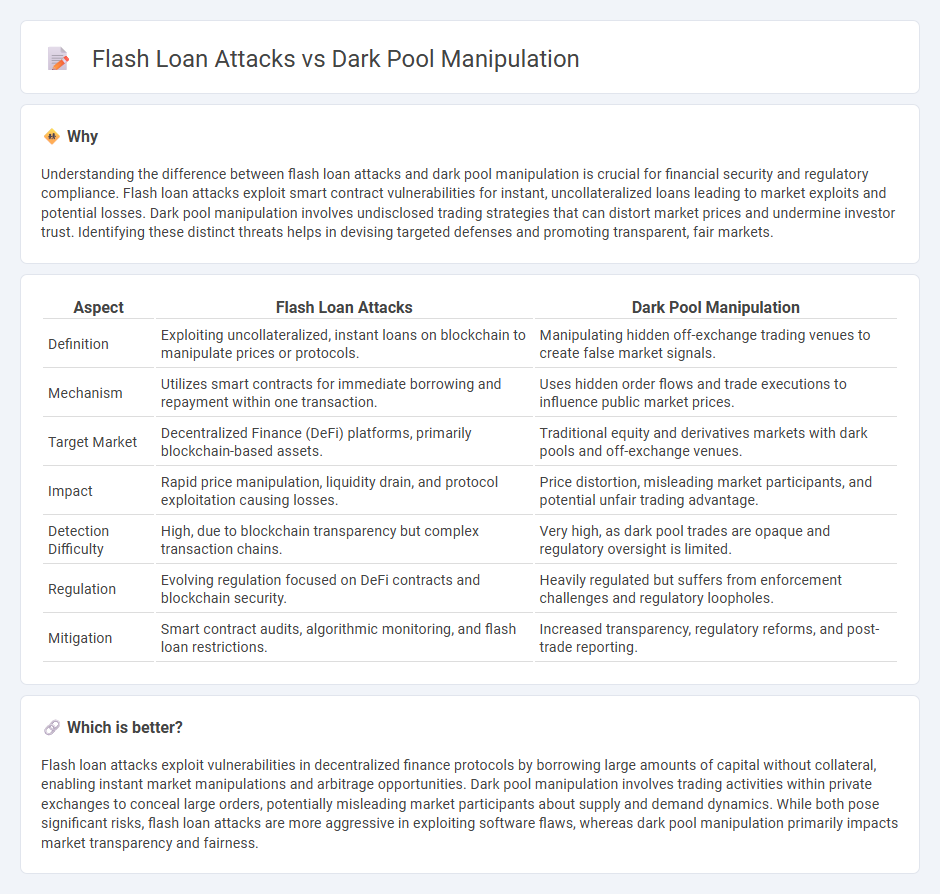
| Aspect | Flash Loan Attacks | Dark Pool Manipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting uncollateralized, instant loans on blockchain to manipulate prices or protocols. | Manipulating hidden off-exchange trading venues to create false market signals. |
| Mechanism | Utilizes smart contracts for immediate borrowing and repayment within one transaction. | Uses hidden order flows and trade executions to influence public market prices. |
| Target Market | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms, primarily blockchain-based assets. | Traditional equity and derivatives markets with dark pools and off-exchange venues. |
| Impact | Rapid price manipulation, liquidity drain, and protocol exploitation causing losses. | Price distortion, misleading market participants, and potential unfair trading advantage. |
| Detection Difficulty | High, due to blockchain transparency but complex transaction chains. | Very high, as dark pool trades are opaque and regulatory oversight is limited. |
| Regulation | Evolving regulation focused on DeFi contracts and blockchain security. | Heavily regulated but suffers from enforcement challenges and regulatory loopholes. |
| Mitigation | Smart contract audits, algorithmic monitoring, and flash loan restrictions. | Increased transparency, regulatory reforms, and post-trade reporting. |
Which is better?
Flash loan attacks exploit vulnerabilities in decentralized finance protocols by borrowing large amounts of capital without collateral, enabling instant market manipulations and arbitrage opportunities. Dark pool manipulation involves trading activities within private exchanges to conceal large orders, potentially misleading market participants about supply and demand dynamics. While both pose significant risks, flash loan attacks are more aggressive in exploiting software flaws, whereas dark pool manipulation primarily impacts market transparency and fairness.
Connection
Flash loan attacks exploit vulnerabilities in decentralized finance protocols by executing rapid, uncollateralized loans to manipulate asset prices or governance mechanisms. Dark pool manipulation involves covert trading within private exchanges to create misleading market signals, which can be targeted and amplified through flash loan attacks. Both exploit opacity and speed in financial markets, resulting in distorted asset valuations and increased systemic risk.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Dark pool manipulation exploits opaque trading venues to artificially influence asset prices by creating false liquidity signals, undermining market transparency and stability. Flash loan attacks leverage uncollateralized loans within decentralized finance protocols to rapidly execute trades and manipulate liquidity pools, causing sudden price distortions and arbitrage opportunities. Explore how these liquidity-centric tactics impact financial ecosystems and safeguard mechanisms.
Arbitrage
Dark pool manipulation exploits opaque private exchanges to create artificial price discrepancies, enabling arbitrage opportunities by misleading market participants. Flash loan attacks leverage uncollateralized loans in decentralized finance to execute rapid arbitrage trades, often manipulating token prices across multiple protocols within a single transaction. Explore deeper insights into arbitrage mechanics and preventative measures in these advanced financial exploits.
Market integrity
Dark pool manipulation involves concealed trading in private exchanges to distort market prices, undermining market integrity by creating false liquidity signals and disadvantaging regular investors. Flash loan attacks exploit decentralized finance protocols through rapid, uncollateralized borrowing to manipulate asset prices, leading to significant financial losses and eroding trust in blockchain ecosystems. Explore deeper insights into how these threats impact financial markets and strategies to enhance market integrity.
Source and External Links
Sharks in the dark: quantifying HFT dark pool latency arbitrage - Dark pool manipulation often involves high-frequency traders (HFTs) exploiting stale prices and latency advantages to trade aggressively, mostly consuming liquidity rather than providing it, and regulatory actions have addressed systematic mispricings in dark pools.
Dark pool - Wikipedia - Dark pools are private trading venues used by institutional investors to hide order size and avoid market impact, but they can facilitate manipulation by high-frequency traders who can use information asymmetry across venues to their advantage, raising transparency and fairness concerns.
Dark Pools and High Frequency Trading: A Brief Note - IEF - Dark pools are vulnerable to manipulation through HFT strategies like pinging to detect hidden orders and front-running large trades, as seen in legal cases such as Barclays' fine for misrepresenting HFT activity, with some countermeasures like minimum order sizes proposed to reduce such predatory practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com