Tokenized treasuries represent a digital innovation in finance, offering fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity through blockchain technology, while commercial paper remains a traditional form of unsecured short-term debt issued by corporations to meet immediate funding needs. Tokenized treasuries provide increased transparency and accessibility to investors, contrasting with commercial paper's reliance on credit ratings and issuer reputation. Explore how these financing instruments reshape capital markets and investment strategies.
Why it is important
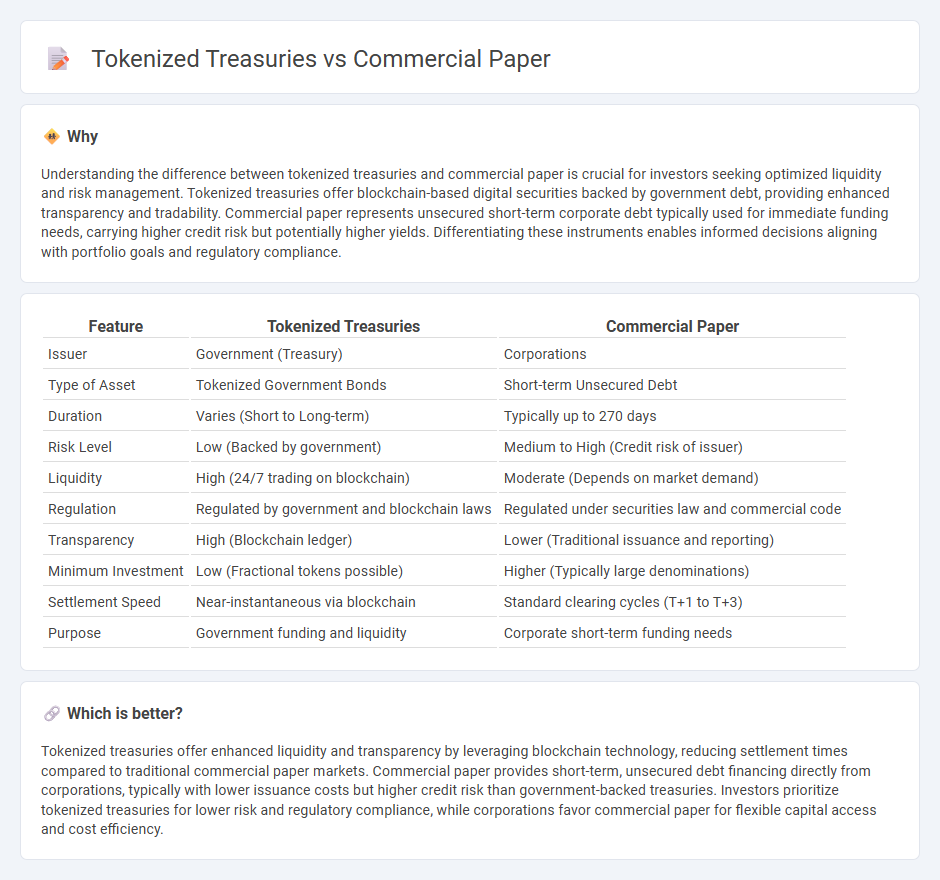
Understanding the difference between tokenized treasuries and commercial paper is crucial for investors seeking optimized liquidity and risk management. Tokenized treasuries offer blockchain-based digital securities backed by government debt, providing enhanced transparency and tradability. Commercial paper represents unsecured short-term corporate debt typically used for immediate funding needs, carrying higher credit risk but potentially higher yields. Differentiating these instruments enables informed decisions aligning with portfolio goals and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tokenized Treasuries | Commercial Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Government (Treasury) | Corporations |
| Type of Asset | Tokenized Government Bonds | Short-term Unsecured Debt |
| Duration | Varies (Short to Long-term) | Typically up to 270 days |
| Risk Level | Low (Backed by government) | Medium to High (Credit risk of issuer) |
| Liquidity | High (24/7 trading on blockchain) | Moderate (Depends on market demand) |
| Regulation | Regulated by government and blockchain laws | Regulated under securities law and commercial code |
| Transparency | High (Blockchain ledger) | Lower (Traditional issuance and reporting) |
| Minimum Investment | Low (Fractional tokens possible) | Higher (Typically large denominations) |
| Settlement Speed | Near-instantaneous via blockchain | Standard clearing cycles (T+1 to T+3) |
| Purpose | Government funding and liquidity | Corporate short-term funding needs |
Which is better?
Tokenized treasuries offer enhanced liquidity and transparency by leveraging blockchain technology, reducing settlement times compared to traditional commercial paper markets. Commercial paper provides short-term, unsecured debt financing directly from corporations, typically with lower issuance costs but higher credit risk than government-backed treasuries. Investors prioritize tokenized treasuries for lower risk and regulatory compliance, while corporations favor commercial paper for flexible capital access and cost efficiency.
Connection
Tokenized treasuries and commercial paper are linked through blockchain technology that transforms traditional debt instruments into digital assets for more efficient trading and settlement. Tokenization enhances liquidity and transparency in the finance sector by enabling fractional ownership and real-time auditing of treasury securities and short-term corporate debts. This connection reduces transaction costs and counterparty risks, creating a more accessible and streamlined market for institutional and retail investors.
Key Terms
Maturity
Commercial paper typically offers short-term maturity ranging from a few days up to 270 days, providing issuers with quick liquidity solutions. Tokenized treasuries, on the other hand, can offer flexible maturity dates depending on the underlying government bond, often extending from short to long-term durations. Explore the nuances of maturity profiles between commercial paper and tokenized treasuries to optimize your investment strategy.
Liquidity
Commercial paper offers high liquidity with short-term maturity and easy tradability among institutional investors, making it an efficient tool for managing immediate cash flow needs. Tokenized treasuries provide enhanced liquidity through blockchain technology, enabling fractional ownership and 24/7 trading on digital platforms with real-time settlement. Explore how tokenization revolutionizes liquidity management compared to traditional commercial paper.
Settlement
Commercial paper settlements typically occur within one to three business days through traditional clearinghouses, relying heavily on intermediaries and paper-based documentation. Tokenized treasuries leverage blockchain technology to enable near-instantaneous, transparent settlements with reduced counterparty risk and minimal reliance on intermediaries. Explore how these innovations are transforming settlement efficiency and security in modern financial markets.
Source and External Links
Commercial paper - Wikipedia - Commercial paper is a short-term money-market security issued by large corporations to finance short-term debt obligations, usually maturing within 270 days, and it is not regulated by the SEC if it meets certain qualifications.
Commercial Paper - Overview, How It Works, Risks - Commercial paper is an unsecured, short-term debt instrument (1-270 days) issued by highly rated corporations and financial institutions at a discount, used as a cheaper borrowing alternative without collateral backing.
Commercial Paper - Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued at a discount by finance companies, banks, and corporations with strong credit, typically sold in large denominations of $100,000, and mainly purchased by institutional investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com