Decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) treasuries manage digital assets through blockchain-based governance, enabling transparent and community-driven financial decisions. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer investors diversified portfolios of stocks, bonds, or commodities traded on traditional exchanges with regulatory oversight. Explore the unique benefits and risks of DAO treasuries versus ETFs to optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
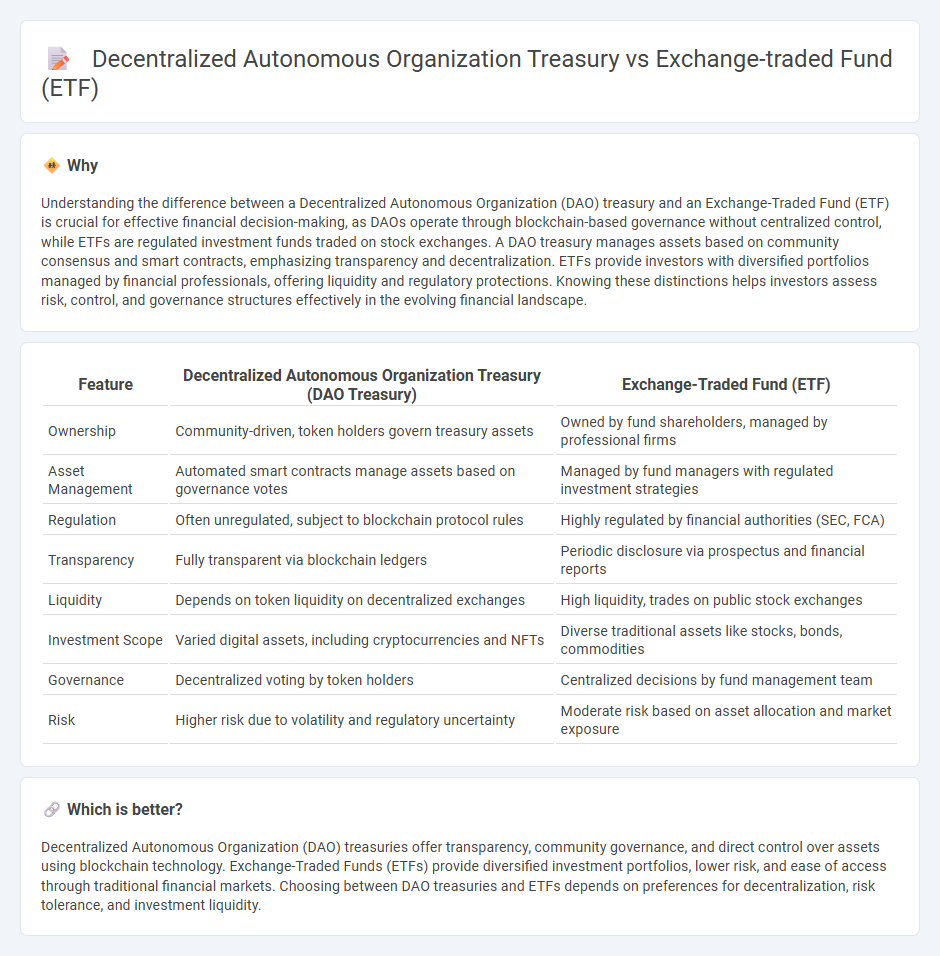
Understanding the difference between a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) treasury and an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is crucial for effective financial decision-making, as DAOs operate through blockchain-based governance without centralized control, while ETFs are regulated investment funds traded on stock exchanges. A DAO treasury manages assets based on community consensus and smart contracts, emphasizing transparency and decentralization. ETFs provide investors with diversified portfolios managed by financial professionals, offering liquidity and regulatory protections. Knowing these distinctions helps investors assess risk, control, and governance structures effectively in the evolving financial landscape.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Autonomous Organization Treasury (DAO Treasury) | Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Community-driven, token holders govern treasury assets | Owned by fund shareholders, managed by professional firms |
| Asset Management | Automated smart contracts manage assets based on governance votes | Managed by fund managers with regulated investment strategies |
| Regulation | Often unregulated, subject to blockchain protocol rules | Highly regulated by financial authorities (SEC, FCA) |
| Transparency | Fully transparent via blockchain ledgers | Periodic disclosure via prospectus and financial reports |
| Liquidity | Depends on token liquidity on decentralized exchanges | High liquidity, trades on public stock exchanges |
| Investment Scope | Varied digital assets, including cryptocurrencies and NFTs | Diverse traditional assets like stocks, bonds, commodities |
| Governance | Decentralized voting by token holders | Centralized decisions by fund management team |
| Risk | Higher risk due to volatility and regulatory uncertainty | Moderate risk based on asset allocation and market exposure |
Which is better?
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) treasuries offer transparency, community governance, and direct control over assets using blockchain technology. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) provide diversified investment portfolios, lower risk, and ease of access through traditional financial markets. Choosing between DAO treasuries and ETFs depends on preferences for decentralization, risk tolerance, and investment liquidity.
Connection
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) treasuries and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are connected through their shared focus on decentralized asset management and liquidity optimization. DAO treasuries typically hold a diversified portfolio of digital assets, similar to ETFs that bundle various securities into a single tradable fund, enabling risk diversification and streamlined access to markets. Both structures leverage blockchain technology and transparent governance to enhance investor trust and operational efficiency in financial ecosystems.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer high liquidity due to their trading on regulated exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell shares throughout market hours at transparent prices. In contrast, decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) treasuries often hold a diverse portfolio of cryptographic assets, which may face varying liquidity levels depending on market depth and protocol-specific restrictions. Explore how liquidity dynamics influence investment strategies in ETFs and DAO treasuries to gain deeper insights.
Governance
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are governed by regulatory bodies and structured with formal management teams ensuring compliance and investor protection, whereas decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) treasuries operate on blockchain-based smart contracts, enabling collective stakeholder governance through token-weighted voting. ETF governance emphasizes transparency, regulatory adherence, and centralized decision-making, while DAO treasuries prioritize decentralization, community-driven proposals, and real-time protocol adjustments. Explore the nuances of governance models in financial innovation to understand their impact on investor control and operational efficiency.
Transparency
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer high transparency through daily disclosure of holdings, regulatory oversight by bodies like the SEC, and standardized reporting practices. Decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) treasuries provide transparency by utilizing blockchain technology, allowing public, real-time access to transaction records and fund allocations without intermediaries. Explore how these transparency mechanisms impact investor confidence and decision-making in both financial structures.
Source and External Links
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) - An ETF is an investment product traded on stock exchanges that pools money from many investors to buy a diversified portfolio of assets, similar to mutual funds but traded like stocks throughout the day, often with tax advantages.
What is an ETF? - ETFs are tradeable funds containing groups of investments like stocks or bonds, organized around a theme or index, allowing investors to easily diversify their portfolios with intraday liquidity and trading flexibility.
What is an ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund)? - ETFs combine stock-like trading with mutual-fund-like diversification, providing affordable access to a variety of asset classes with benefits like portfolio diversification, lower costs, tax efficiency, and trading flexibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com