Degen Box is a decentralized finance protocol focusing on capital efficiency and leverage management, enabling users to interact with multiple lending and borrowing positions simultaneously. Automated Market Makers (AMMs) are smart contracts that facilitate decentralized trading by automatically determining asset prices using liquidity pools without traditional order books. Explore the distinctions between Degen Box and AMMs to optimize your DeFi strategies.
Why it is important
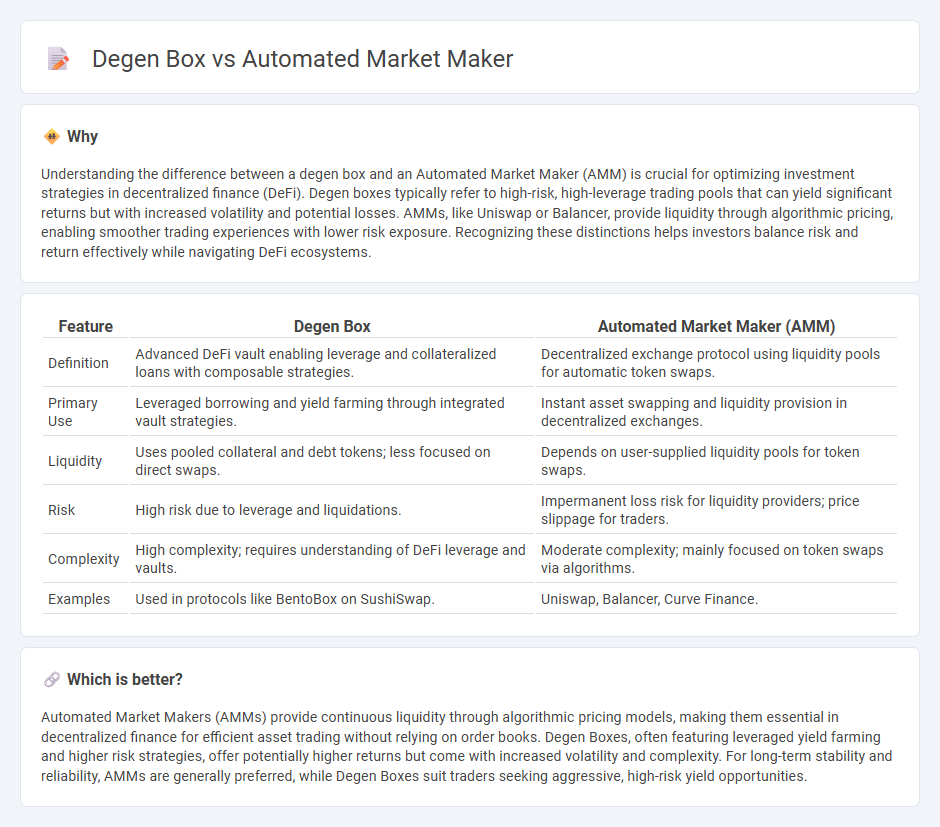
Understanding the difference between a degen box and an Automated Market Maker (AMM) is crucial for optimizing investment strategies in decentralized finance (DeFi). Degen boxes typically refer to high-risk, high-leverage trading pools that can yield significant returns but with increased volatility and potential losses. AMMs, like Uniswap or Balancer, provide liquidity through algorithmic pricing, enabling smoother trading experiences with lower risk exposure. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors balance risk and return effectively while navigating DeFi ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Degen Box | Automated Market Maker (AMM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advanced DeFi vault enabling leverage and collateralized loans with composable strategies. | Decentralized exchange protocol using liquidity pools for automatic token swaps. |
| Primary Use | Leveraged borrowing and yield farming through integrated vault strategies. | Instant asset swapping and liquidity provision in decentralized exchanges. |
| Liquidity | Uses pooled collateral and debt tokens; less focused on direct swaps. | Depends on user-supplied liquidity pools for token swaps. |
| Risk | High risk due to leverage and liquidations. | Impermanent loss risk for liquidity providers; price slippage for traders. |
| Complexity | High complexity; requires understanding of DeFi leverage and vaults. | Moderate complexity; mainly focused on token swaps via algorithms. |
| Examples | Used in protocols like BentoBox on SushiSwap. | Uniswap, Balancer, Curve Finance. |
Which is better?
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) provide continuous liquidity through algorithmic pricing models, making them essential in decentralized finance for efficient asset trading without relying on order books. Degen Boxes, often featuring leveraged yield farming and higher risk strategies, offer potentially higher returns but come with increased volatility and complexity. For long-term stability and reliability, AMMs are generally preferred, while Degen Boxes suit traders seeking aggressive, high-risk yield opportunities.
Connection
In decentralized finance (DeFi), the degen box acts as a collateral management system that aggregates assets, while Automated Market Makers (AMMs) provide continuous liquidity for trading these assets without order books. The degen box optimizes capital efficiency by leveraging AMMs to enable seamless swaps and lending, integrating liquidity pools that support price discovery and asset utilization. This synergy enhances market depth, reduces slippage, and allows users to maximize yield through automated liquidity provisioning and collateralization.
Key Terms
Liquidity Pools
Automated market makers (AMMs) like Uniswap use liquidity pools where users provide paired tokens to enable decentralized trading and earn fees, optimizing liquidity and price stability. Degen Box, an advanced yield optimization platform, leverages complex liquidity pool strategies and multi-layered token management to maximize returns and minimize impermanent loss risks. Explore how these innovative liquidity pool mechanisms transform decentralized finance by driving efficiency and capital utilization.
Yield Farming
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) streamline yield farming by enabling decentralized token swaps and liquidity provisioning with minimal slippage, incentivizing liquidity providers through trading fees and rewards. Degen Box strategies amplify yield farming potential by leveraging complex debt collateralization and token vaults to maximize returns, albeit with higher risk and complexity. Explore the detailed mechanics and risk profiles of AMMs and Degen Box yield farming to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Smart Contracts
Automated market makers (AMMs) rely on smart contracts to facilitate decentralized token swaps by using liquidity pools and algorithmic pricing models, enabling users to trade without order books. The degen box, a specialized smart contract vault, optimizes yield strategies by leveraging collateralized debt positions and compound interest mechanisms within decentralized finance protocols. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how smart contract architecture shapes their operational efficiencies and security features.
Source and External Links
What is an Automated Market Maker? - An automated market maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange model that uses smart contracts to price and execute trades automatically without an order book, enabling 24/7 onchain trading with transparency and liquidity provision rewards.
What Is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? - Gemini - AMMs are DeFi protocols that enable crypto trading automatically through liquidity pools and an algorithmic pricing formula, allowing permissionless and constant liquidity without traditional buyers and sellers.
The Ecology of Automated Market Makers - This paper explores the ecosystem of AMMs including user adoption, trading volumes, and governance models of notable platforms like Uniswap, Curve, Sushiswap, and Balancer, highlighting their unique non-discretionary algorithmic pricing and community roles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com